

16th November 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
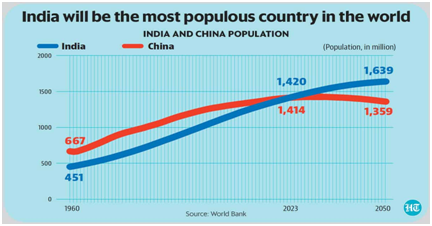
As per the United Nations, India's population growth appears to be stabilising which is a positive sign for the country's efforts and national policies in health systems, including access to family planning services.
About
About the UN Statistics: (India-specific data)
- As the World’s population reached 8 billion, where India was a significant contributor to the number with an addition of 177 million
- Although, the UN regarded India's population growth appears to be stabilising.
- As per the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), the Total Fertility Rate (average number of children born per woman) has declined from 2 to 2.0 at the national level in India.
- The main reasons for the decline in fertility include the following;
- Increase in adoption of ‘modern family planning methods (from 47.8 percent in 2015-16 to 56.5 percent in 2019-21) and
- A reduction in ‘unmet need for family planning by four percentage points over the same period.
|
Facts:
|
Factors influencing population growth can be grouped into the following 3 categories-
- Unmet need for Family Planning: This includes the currently married women, who wish to stop childbearing or wait for the next two or more years for the next child birth, but not using any contraceptive method.
- The real unmet need for Family Planning is 4 (NFHS-V) in our country.
- Age at Marriage and first childbirth: In India, 23.3% (NFHS-V)of the girls get married below the age of 18 years and out of the total deliveries 6.8% are among teenagers i.e. 15-19 years. The situation regarding the age of girls at marriage is more alarming in a few states like,
- Bihar (40.8%), Rajasthan (25.4%), Jharkhand (32.2%), UP (15.8%), and MP (23.1%).
- Delaying the age at marriage and first childbirth could reduce the impact of Population Momentum on population growth.
- Spacing between Births: The chances of survival of infants depend upon the spacing between the children and also helps in reducing the impact of population momentum on population growth.
Other causes of Increasing Population:
- The decline in death rate: If the number of children born each year equals the number of adults that die, then the population will stabilize.
- Agricultural advancements: Agricultural advancements have allowed humans to increase food production using fertilizers, herbicides, and pesticides and yields further.
- Better medical capabilities: Illnesses that had claimed thousands of lives until now were cured because of the invention of vaccines. Combining the increase in food supply with fewer means of mortality tipped the balance and became the starting point of overpopulation.
- More hands to work: Families that have been through poverty, or natural disasters, or are simply in need of more hands to work are major factors in overpopulation.
- Advanced fertility treatment: Today there are effective medicines that can increase the chance of conception and increase the birth rate. Moreover, due to modern techniques, pregnancies today are far safer.
- Immigration: Many people prefer to move to urban areas, where the best facilities are available. The result is that those people settle over there, eventually making those places overcrowded.
- Lack of family planning/unawareness: There are a large number of illiterate people, who live below the poverty line, and have little or no knowledge about family planning.
- Poor contraceptives use: A study by the World Health Organization (WHO) shows that women aged between 16 and 49 used at least one form of contraceptive 43% in underdeveloped countries, which leads to higher birth rates.
Areas to be focused on for Sustainable development:
- Social security and universal health
- Demographic liability
- Resource allocation and Achieving SDGs
- Poverty and quality of life
Government Interventions to promote family planning:
- Mission Parivar Vikas was initially for 146 high-priority districts in the 7 high focus states.
- It includes Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan & Jharkhand, to ensure the availability of contraceptive products to clients at all levels of Health Systems.
- National Population policy: The National Population Policy 2000 affirmed a commitment to achieve replacement levels of fertility (total fertility rate of 2.1) by 2010.
- Most of the southern states controlled their population.
- However, low socio-economic development in northern and central India has led to a population explosion in these regions.
Way Forward
- Strengthening community-based distribution of contraceptives by involving ASHAs and Focussed IEC/ BCC efforts for enhancing demand and creating awareness on family planning
- Ensuring quality care in Family Planning services by establishing Quality Assurance Committees at the state and district levels Plan for accreditation of more private/ NGO facilities to increase the provider base for family planning services under PPP.
- Demand generation activities in the form of display of posters, billboards, and other audio and video materials in the various facilities are planned and budgeted.
- Increasing male participation
More Articles


