

The 1959 Antarctic Treaty celebrates its 60th anniversary.
Context
The 1959 Antarctic Treaty celebrates its 60th anniversary.
Background
- Various international conflicts motivated the creation of an agreement for the Antarctic.
- After the Second World War, the U.S. considered establishing a claim in Antarctica. From August 26, 1946, and until the beginning of 1947, Operation Highjump was carried out, the largest military expeditionary force that the United States has sent to Antarctica to the present.
- In 1949, Argentina, Chile, and the United Kingdom signed a Tripartite Naval Declaration committing not to send warships south of the 60th South parallel, which was renewed annually until 1961 when it was deemed unnecessary when the treaty entered into force.
- This tripartite declaration was signed after the tension generated when Argentina sent a fleet of 8 warships to Antarctica.
- Scientific bases increased in international tension concerning Antarctica, and the danger of the Cold War spreading to that continent, caused the President of the United States, Dwight D. Eisenhower, to convene an Antarctic Conference to the twelve countries active in Antarctica during the International Geophysical Year, to sign a treaty.
Analysis
What is Antarctic Treaty?
- The Antarctic Treaty was signed in Washington on 1 December 1959 by the twelve countries whose scientists had been active in and around Antarctica during the International Geophysical Year (IGY) of 1957-58.
- It entered into force in 1961 and has since been acceded to by many other nations.
- The total number of Parties to the Treaty is now 54.
- The treaty is remarkably short and contains only 14 articles.
- It remains the only example of a single treaty that governs a whole continent.
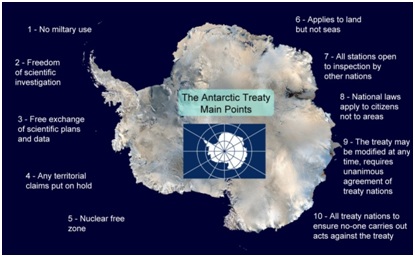
- Principal provisions include promoting the freedom of scientific research, the use of the continent only for peaceful purposes, and the prohibition of military activities, nuclear tests and the disposal of radioactive waste.
|
Some important provisions of the Treaty:
|
Expansion of the treaty
- A key reason why the treaty has been able to survive has been its ability to evolve through a number of additional conventions and other legal protocols. These have dealt with the conservation of marine living resources, prohibitions on mining, and the adoption of comprehensive environmental protection mechanisms.
- As disputes have arisen over the years, many have been addressed through the expansion of the treaty framework with these agreements. This framework is now referred to as the “Antarctic Treaty System”.
- Scientific engagement in Antarctica is considered critical to exercising influence under the treaty.
- New treaty parties have to meet certain criteria relating to active scientific programs before they are able to participate in meetings as “consultative parties”. A total of 29 treaty parties, including Australia, meet these scientific engagement thresholds.
Significance of Treaty
- Peace purpose: The most important provision of the treaty is Article IV, which effectively seeks to neutralise territorial sovereignty in Antarctica.
- No formal recognition was given to any of the seven territorial claims on the continent, by Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway and the United Kingdom.
- Russia, the United States and China — signatories with significant Antarctic interests who have not formally made territorial claims — are also bound by the limitations of Article IV.
- And one sector of Antarctica is not subject to the claim of any country, which effectively makes it the last unclaimed land on earth.
- The treaty also put a freeze on any disputes between claimants over their territories on the continent. Claimants agreed to abide by the rules and obligations of the treaty, which meant countries that don’t recognise claims (such as China and Russia) are free to go about scientific research and peaceful activities.
- Environment protection: Protection of the Antarctic environment has been a central theme in the cooperation among Antarctic Treaty Parties. In 1964, the ATCM adopted Agreed Measures for the Conservation of Antarctic Fauna and Flora.
- Scientific research: It has been the main activity on the Antarctic continent, and both the Antarctic Treaty and the Environment Protocol emphasize the importance of science and scientific cooperation in the Antarctic Treaty System.
- Tourism guidelines: The main ATCM regulations and guidelines for tourists and expedition organizers are contained in the Environment Protocol and Tourism Guidelines. The ATCM also issues specific guidelines for the sites most visited by tourists.
Conclusion
Antarctic watchers say though that the strength – and the weakness – is that it operates on consensus. One solution to the lack of inspections is to set up an independent group of inspectors – this is something that was provisioned for in the Antarctic Treaty but never established.


