Context
There are certain discrepancies in the recent report by the State Bank of India (SBI) which highlights that India has witnessed a significant fall in inequality over the last decade.
Key Concerns with the Report –
- Challenges in Data Analysis:
- The analysis is based on taxpayer data, presenting challenges as a significant portion of income-earners falls below the tax threshold.
- Preliminary nature of the study necessitates further research to account for potential errors, self-reporting issues, and seasonal adjustments.
- Gini Coefficient Trends (2017-18 to 2022-23)
|
What is Gini Coefficient?
|
- The Gini coefficient, representing income inequality, decreased from 0.4297 to 0.4197 during the period.
- Disaggregated by employment type, the Gini coefficient fell for regular wage and casual wage workers but rose slightly for the self-employed.
- Polarisation in Income Growth
- An analysis of decile-wise income growth reveals a polarisation trend, especially among self-employed workers.
- While the majority experienced healthy income growth (8%-9%), the top 10% saw a rate of around 7.23%, outpacing the bottom 20% with only 1.67% growth.
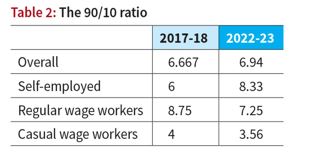
- 90/10 Ratio and Self-Employed Divergence
- The 90/10 ratio, measuring income gap between the top and bottom 10%, increased from 6.7 to 6.9.
- Notably, the 90/10 ratio significantly rose for self-employed individuals, with the income of the top 10% being 8.3 times that of the bottom 10%.
- Impact of Women's Labor Force Participation
- The rise in women's labor force participation, primarily in low-paid, part-time self-employed work, contributes to increased income gaps among the self-employed.
- While overall Gini coefficient reduction suggests lower inequality, the divergence in self-employed incomes contradicts this trend.
Consequences of Discrepancies in Income Inequality Studies
- Policy Misdirection:
- Inaccuracies in studies can lead to misguided policy decisions, hindering effective strategies to address income inequality.
- Public Trust Erosion:
- Conflicting findings may erode public trust, creating skepticism about the severity of income inequality and impeding support for necessary interventions.
- Inequality Denial:
- Discrepancies provide room for denial, hindering efforts to tackle root causes and promote social and economic justice.
- Resource Allocation Challenges:
- Challenges in resource allocation arise, with policymakers struggling to distribute resources effectively based on inconsistent data.
- Benchmarking Difficulty:
- Establishing benchmarks for measuring progress becomes challenging, impeding the assessment of policy impact over time.
- Impact on Research:
- Persistent discrepancies may slow progress in understanding income inequality dynamics within the academic community.
- Ineffective Advocacy:
- Advocacy efforts are weakened as inconsistent data hampers the ability to strengthen arguments and mobilize support for change.
- Global Cooperation Hurdles:
- Global comparisons and cooperation face obstacles due to inconsistent data, hindering coordinated strategies to address income disparities globally.