

- Prime Minister rolled out the centre’s flagshipAyushman Bharat which includes National Health Protection Scheme renamed as Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojna (PMJAY)and Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs).
- The scheme will subsume two ongoing centrally sponsored health insurance schemes namely RashtriyaSwasthyaBimaYojna(RSBY) and the Senior Citizen Insurance Scheme(SCHIS)
Issue
Context
- Prime Minister rolled out the centre’s flagshipAyushman Bharat which includes National Health Protection Scheme renamed as Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojna (PMJAY)and Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs).
- The scheme will subsume two ongoing centrally sponsored health insurance schemes namely RashtriyaSwasthyaBimaYojna(RSBY) and the Senior Citizen Insurance Scheme(SCHIS)
About
- Ayushman Bharat is an integrated approach covering primary, secondary and tertiary healthcare through
a. Access to Health and Wellness centres(HWCs) at the primary healthcare level. - These centres will provide Comprehensive Primary Health Care (CPHC).
- HWCs will cover both maternal and child health services, and non-communicable diseases, including free essential drugs and diagnostic services.
b. Financial protection for accessing curative care at the secondary and tertiary levels through PMJAY.
Background
- As per 71st Round of National Sample Survey Organization (NSSO), 85.9% of rural households and 82% of urban households have no access to healthcare insurance/assurance.
- More than 17% of Indian population spend at least 10% of household budgets on health services.
- Catastrophic healthcare related expenditure pushes families into debt. More than 24% households in rural India and 18% population in urban areameet their healthcare expenses through some sort of borrowings.
- To target the situation, in tandem with National Health Policy 2017 goals, central government in Union Budget 2018-19 announced two major initiatives as a part of Ayushman Bharat Programme, namely PMJAY and HWCs.
|
Mainfeatures of PMJAY:
|
Analysis
- Ayushman Bharat is assumed to be giant leap towards providing accessible and affordable health care to the common man.
- With PMJAY, the government is taking healthcare protection to a new aspirational level. This would be the world’s largest government funded healthcare program targeting more than 50 crore beneficiaries.
Challenges:
Financial:
Implementation of such scale and benefit is bound to face obstacles, the most substantial of which is for it to be economically sustainable.
- The proposed package rates under NHPS for various treatments according to hospitals are loss-making.
- Not all the states and Union Territories are in position to raise their own share, and few have not even joined the scheme.
Human Resource:
- There is limited and uneven distribution of human resources at various levels of health services.
- Most primary health care centres suffer from perennial shortage of doctors and even district hospitals are without specialists.
- Further, 40 per cent of health worker posts are lying vacant in some states.
Negligence of primary healthcare:
- With greater emphasis on secondary and tertiary healthcare, the scheme pays little attention to primary healthcare which is fundamental for sustainable quality healthcare.
Technical:
- There is absence of a large-scale Information Technology network for cashless treatment.
Administrative
- The secondary and tertiary public hospital infrastructure suffers from severe efficiency and accountability problems. Since, majority of the beneficiaries will be families from rural areas, this is a worrisome scenario.
Significance:
PMJAY is a visionary step towards advancing the agenda of Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
- Itwill help reduce catastrophic expenditure for hospitalizations, which is mostly out of the pocket expenditure. Entitled families will be able to use the quality health services they need without facing financial hardships.
- The cover includes many items typically excluded in standard medi-claims such as pre-existing diseases, mental health conditions, and internal congenital diseases, among others.
- The scheme encourages hospitals to maintain certain minimum standards.
- It will also enhance organisational capacity at the district and state levels, to oversee the programme.
- HWCs can help unleash a people’s movement for a healthy India. It would be a right step in realising the goals of National Health Policy 2017
- For insurers and third-party administrators, this is a large new market that will open up.
Thus, as a driver of development and growth, Ayushman Bharat will spur increased investment in health and generate lakhs of jobs, especially for women.
Learning Aid
Key Issues : 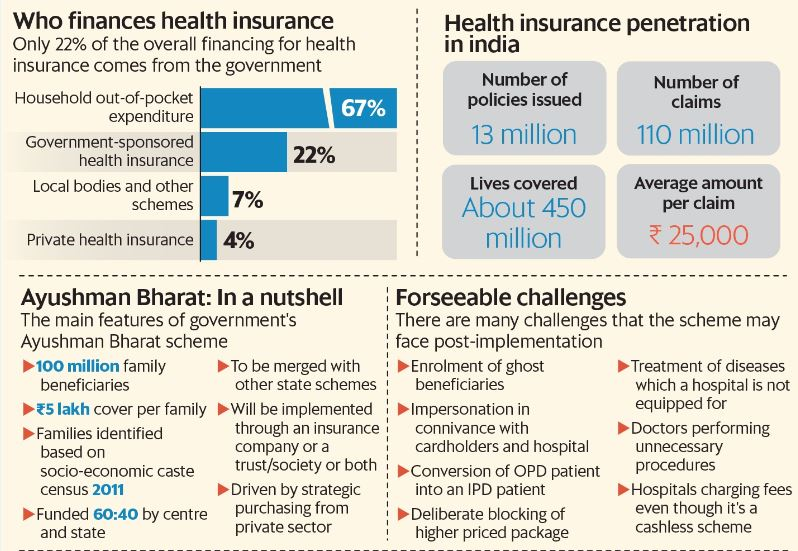
Practice Question:
Ayushman Bharat is assumed to be giant leap towards providing accessible and affordable health care to the common man.Examine.


