

Context
Environmental degradation due to the waste production by the India’s Textile Industries.
Background
- Indian textile industry is the second largest producer of textiles in the worldwith a massive raw material and textiles manufacturing base. China is the largest textile producing and exporting country in the world.
- India is one of the largest producers of cotton and jute in the world. India is also the 2nd largest producer of silk in the worldand 95% of the world’s hand-woven fabric comes from India.
- Textiles is the third largest source of waste in most of the Indian states after Plastic, Paper & compost.
|
Indian Textile Journal
|
ISSUES WITH TEXTILE INDUSTRY:
- Global production of clothing and its consumption has increased in the last fifty years. It has become a way of making an impression and non-verbal communication.
- The average life span of a garment is roughly three years, and so, textiles generate a huge amount of waste.
|
What are the waste products of textile industry?
|
IMPACT ON ENVIRONMENT:
- Five per cent of all global landfills is being taken up by dumped textile waste.
- Clothes do not biodegrade while in a landfill, and could remain there for more than 200 years before decomposing. This also increases the carbon footprint of the garments in the landfill.
- Greenhouse gas emissions by the global textile industry are greater than those from shipping and international air travel combined.
|
ENVIRONMENTAL PERFORMANCE INDEX
|
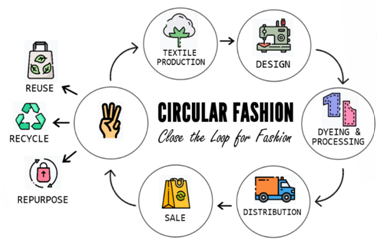
CIRCULAR TEXTILES PRODUCTION:
In this green process, discarded textiles are shredded, cleaned, organised, revamped and reassembled. The products are then tested for quality and marketed after adding new parts.
BENEFITS:
- Circular textiles production (CTP) is designed to be recuperative and renews and increases a product’s life cycle.
|
EXAMPLE:
|
- It overcomes the limits of the linear economy model by addressing concerns such as resource scarcity, natural resource use and recycling of discarded items within the economy.
- It safeguards the environment by reducing up to 80 per cent of emissions.
- It decreases energy usage by up to 60 per cent, raw material consumption up to 70 per cent and product costs up to 60 per cent.
- Sustainable production of textiles.
- Recycling industry provides Employment to handloom weavers who have lost their job because of power looms.
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES:
- Mega Investment Textiles Parks (MITRA) scheme launched by Ministry of Textiles- This scheme will build a world-class infrastructure with plug-and-play facilities to let global champions in exportation.
- FDI- India has approved 100% FDI in the Indian textiles sector under the automatic route.
- Project SU.RE. – Sustainable Resolutionlaunched by Ministry of Textiles- It is a commitment by India's apparel industry to establish a sustainable pathway for the fashion industry.
INITIATIVES BY TEXTILE INDUSTRY
- Eco-friendly textile: Creation of eco-friendly textiles to process waste material into a fibre.
|
Example: Disposed PET bottles are turned into flakes that are finely turned into a thread in several deniers and cut for spinning into yarn, utilizing waste PET bottles that could otherwise have been incinerated or discharged into landfills or oceans. |
- Cotton: Cotton is a vital ally of textile industry so for this industries are relying on Regenerative Organic Farming practice to magnify their sustainable cotton portfolio.
- Green energy: industries are focusing on increasing their green power mix like applying solar rooftops and also allying the biomass supply.
- Plastic recycling: Industries are committing to plastic recycling for packaging as they are substituting virgin polyester with recycled LDPE. They are also reducing plastic consumption by utilizing textile scrap by recycling factory trash.
|
CONCERNS:
|
REQUIRED MEASURES
|
|
|


