

Context
A recent study suggests that climate change is causing a significant impact on the ‘structure of the Earth’s atmosphere.
Background
- The study considered decades of weather balloon observations and specialized satellite measurements.
- Based on these observations and measurements, scientists determined how much the top of the lowest level of the atmosphere is rising.
Analysis
Understanding Earth’s atmosphere
- Earth’s atmosphere is very thin, with a mass of only about one-millionth that of the planet itself.
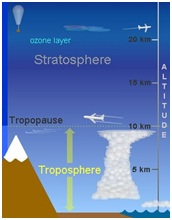
- Earth’s atmosphere has five major and several secondary layers. From lowest to highest, the major layers are the
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere
- Exosphere
|
Layers |
Location |
Function |
|
Troposphere |
Extends from Earth’s surface to, on average, about 12 kilometers (7.5 miles) in height, with its height lower at Earth’s poles and higher at the equator. |
|
|
Stratosphere |
Located between approximately 12 and 50 kilometers (7.5 and 31 miles) above Earth’s surface |
Known as home to Earth’s ozone layer, it protects from the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation |
|
Mesosphere |
Located between about 50 and 80 kilometers (31 and 50 miles) above Earth’s surface, the mesosphere gets progressively colder with altitude. |
|
|
Thermosphere |
Located between about 80 and 700 kilometers (50 and 440 miles) above Earth’s surface |
|
|
Exosphere |
Located between about 700 and 10,000 kilometers (440 and 6,200 miles) above Earth’s surface |
|
What has been found?
- They found that the tropopause region is pushing up the boundary with the Stratosphere by about 50-60 meters (about 165-195 feet) per decade.
|
Tropopause The tropopause is the upper limit of the troposphere and therefore constitutes the boundary between it and the Stratosphere. Depending on the season, it ranges from about 5 miles above Earth’s surface at the poles to 10 miles at the equator. About 80 percent of the atmosphere is contained within its lowest layer, the troposphere. The location of the tropopause is of interest to flight crew because it indicates the altitude at which temperature becomes constant with increasing altitude, which is an essential factor in performance and fuel calculations. It also indicates the location of jet streams and the high winds and turbulence associated with them. |
What is responsible for this change?
- This rising is caused by warming temperatures near Earth’s surface, causing the lower atmosphere to expand.
Conclusion & Way forward
Unfortunately, greenhouse gas emissions from human activities are going to affect Earth’s climate for decades and even centuries. In addition to this, humans will keep on adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere at a rate far greater than it is removed by a natural process, thus creating a long-lived reservoir of the gas in the atmosphere and oceans.
In the coming decade, climate change will particularly depend on the number of greenhouse gases emitted into the atmosphere and how much they get absorbed by the ocean, the biosphere, and other sinks. It will also depend on how sensitive Earth’s climate is to those emissions.


