

Context
Recently, the results of the 2020 census of the US population were released. Following this, the use of Gerrymandering was made in all legal constituencies of the U.S. Congress and the District every decade.
Analysis
What is Gerrymandering?
- Gerrymandering or redistricting is the process of redrawing electoral boundaries. However, this work has been criticized for undermining democracy in the US.
- The objective behind redefining is to ensure that the election of government officials includes the purpose of real democracy, by transforming the spread of the human world.
- Gerrymandering, this name is derived from the name of Gov. Elbridge Gerry of Massachusetts, his superiors passed a law in 1812 defining new states of the senate.
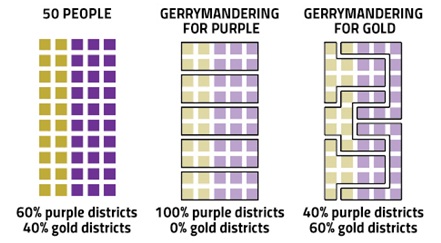
Why is it a threat in US democracy?
- Gerrymandering empowers extremism in both parties by creating noncompetitive districts in which politicians have to worry about winning only primary elections.
- It diminishes minority representation because districts with high minority populations are often broken apart to reduce their voting power.
- It rejects one of the core values and promises of our country: that politicians answer to the people, not the other way around.
How this concept can be compared to India?
India is a parliamentary democracy with elections being held to national and state legislature every five years. Elections are held on a first-past-the-post basis in explicitly demarcated electoral constituencies.
- Delimitation Commission: Political restrictions are administered by the Boundary Commission of India or Delimitation Commission. Delimitation is an act of redrawing the boundaries of LokSabha and the seats of the Assembly to represent the changes in the people. In this process, the number of seats allocated to the state can also change.
- Indian Constitution:
- Under Article 82 of the Indian Constitution, the Demarcation Commission was established by the Central Government after Parliament passed the Demarcation Act after the census.
- Under Article 170, states are further geographically subdivided under the Boundaries Act after each census.
- Delimitation Commissions till date: Boundary Commissions have been suspended four times - 1952, 1963, 1973 and 2002 under Acts 1952, 1962, 1972 and 2002.
- The first demarcation work was done by the President (with the help of the Electoral Commission) in 1950-51. There were no cuts after the 1981 and 1991 censuses.
- The 42nd Amendment Act of 1976 banned the allocation of seats in Lok Sabha provinces and the division of each State into districts until 2000 at the 1971 level.
- In addition, the Amendment Act 84 of 2001 extended this ban to amendment for another 25 years (that is, until 2026), without compromising the total number of seats based on those persons in 1971.
- The 84th Amendment Act of 2001 also empowered the government to effect the restructuring and rehabilitation of polling stations in the provinces on the basis of the 1991 census.
- Later, the 87th Amendment Act of 2003 provided for the determination of polling stations based on the 2001 census and not the 1991 census.
- Therefore, the current state of border crossing in India is frozen until 2026 as the census in 2001.
|
Delimitation Commission
|


