

Context
The Prime Minister has recently praised the Bharuch district administration and the Gujarat Government for covering 100 percent of beneficiaries in the district under four national schemes.
Background
- Welfare schemes are programmes that are meant to improve lives and provide support to vulnerable people in society.
- Indian Government, at all levels, announces welfare schemes from time to time like Antyodaya Anna Yojana, Bharat Nirman, etc.
- Although these programs have helped to alleviate poverty and benefit many, most of the programs are mired with leakages and corruption.
- Implementation is the major stage that impacts the grass root level of society and hence this stage should never be neglected by the agencies.
- The result of good governance is seen in the event in Bharuch. So let us examine the situation.
About
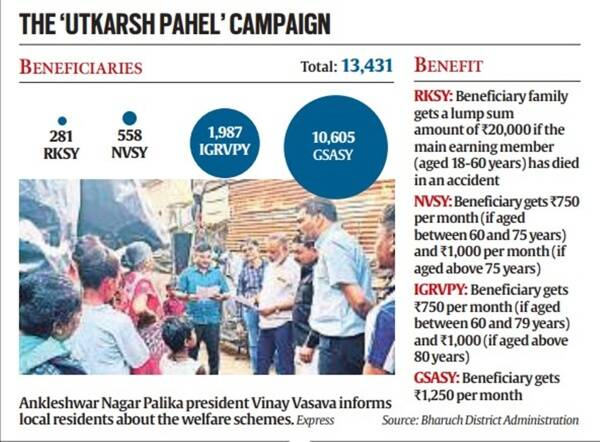
- Between January and May, Surat enrolled 13,431 beneficiaries under four schemes — Indira Gandhi Rashtriya Vrudhhavasta Pension Yojana (IGRVPY), Niradhar Vrudh Sahay Yojana (NVSY), Ganga Swaroop Arthik Sahay Yojana (GSASY) and Rashtriya Kutumb Sahay Yojana (RKSY).
- The schemes are for widows and senior citizens and the district’s drive to enroll all beneficiaries were named “Utkarsh Pahel”.
How did Bharuch achieve this milestone?
Bharuch is a good example of public, administration, and private sector cooperation.
Step 1: Dissemination of Information
- A campaign drive was started by the name of “UTKARSH PAHEL” with WhatsApp helpline numbers to identify beneficiaries.
- District administration also shared information about the schemes at the Samaj Suraksha office at the taluka and district levels.
- Hoardings were put up at different locations and advertisements were issued in the newspapers and local news channels.
Step 2: Registration of Beneficiaries
- The response started coming after the information campaign and the administration sent teams to different villages in the talukas, to get the forms of beneficiaries filled out.
Utkarsh Sahayaks: they are the youths who are 10 class pass hired by private industry to help the administration in filling up the forms of beneficiaries.
Remuneration: 305 Utkarsh Sahayaks were identified and paid an incentive of Rs 250 to Rs 500 per enrolment.
|
Good Governance
|
What are the impacts of Good governance?
- Participation of locals: People should be able to voice their own opinions through legitimate immediate organizations or representatives.
- Consensus Oriented: Consensus-oriented decision-making ensures that even if everyone does not achieve what they want to the fullest, a common minimum can be achieved by everyone which will not be detrimental to anyone.
- Accountability: Good governance aims toward the betterment of people, and this cannot take place without the government being accountable to the people.
- Responsiveness: Institutions and processes should serve all stakeholders in a reasonable period of time.
Conclusion
Corruption in welfare programmes leads to fiscal waste and hinders the development of society. Schemes like MGNREGA, PDS, mid-day meals, etc. had been mired with controversies of corruption. Proper scrutiny with stringent punishments is needed.


