

Context
As per an analysis from CMIE’s Economic Outlook data, shows that while India may be the country with the most youthful population, its workforce is rapidly ageing.
What does the ageing population means to India?
- An ageing workforce basically means that if one looks at all the employed people in India, the share of young people is going down while the share of those closer to 60 years of age is going up.
- In CMIE’s data, youth is defined as those belonging to ages above 15 years and below 25 years.
- However, since the PM has talked about those under 30 years as the youth.
- The report has divided the workforce into three groups:
- Those aged 15 years or more but less than 30 years,
- Those aged 30 years or more but less than 45 years, and
- Those aged 45 years and older.
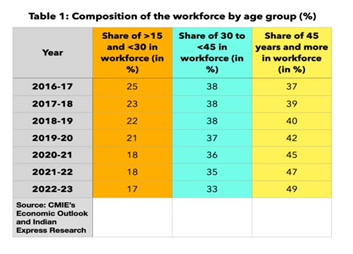
- The data shows that the oldest age category however has grown its share from 37% to 49%.
- In other words, just in the past seven years, the workforce has aged so much that the share of people 45 years and older has gone from one-third to almost one-half.
Why is India’s workforce ageing?
- Simply put, even though its numbers are swelling up, the youth is getting driven out of the job market.
- A good way to track this is from “Employment Rate”.
|
The Employment Rate (ER) for any population or age group tells us what proportion of that age group or population is employed. |
- So, if there are 100 people in the ages 15 to 29 and only 10 are employed then the ER would be 10%.
How demographic dividend can change into ‘demographic curse’?
- Challenge to harness the demographic dividend: As India definitely has large youth population as compared to other developing nations, however, if India remains unable to give them employments can make the situation more worse.
- Burdening economy: If situation prevails for unemployment, poverty and other social impacts then, economy of India is burden even more.
Impacts of ageing population:
Economic Challenges:
- Labor Force Decline: As the older population increases, the working-age population shrinks, leading to potential labor shortages and reduced productivity.
- Increased Healthcare Costs: Aging populations require more healthcare services, leading to higher healthcare expenditures, which can strain public budgets.
- Pension and Social Security Pressures: A larger elderly population puts pressure on pension and social security systems, potentially leading to financial sustainability issues.
Healthcare and Social Services:
- Higher Healthcare Demand: Older individuals tend to have more chronic health conditions and require more medical care, leading to increased demand for healthcare services.
- Long-Term Care Needs: Aging populations require more long-term care services, including nursing homes and assisted living facilities.
- Caregiver Stress: The burden on family members and informal caregivers can increase, impacting their mental and physical well-being.
Policy and Planning:
- Healthcare Infrastructure: Aging populations necessitate investments in healthcare infrastructure and geriatric care facilities.
- Pension and Social Programs: Governments may need to reform pension and social programs to ensure their sustainability.
- Labor Market Policies: Governments may need to implement policies to encourage older individuals to stay in the workforce or facilitate their transition to retirement.



