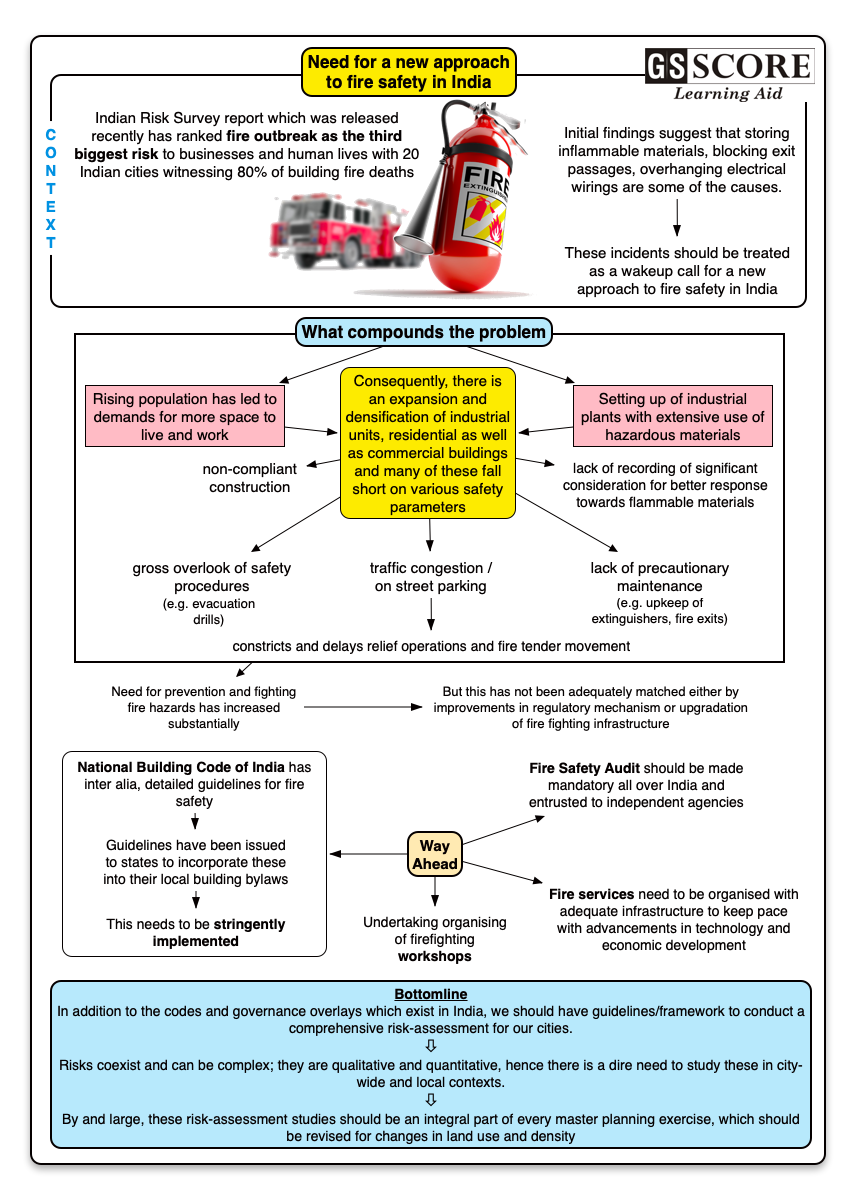
- Recently, released Indian Risk Survey report ranks fire outbreak as the third biggest risk to businesses and human lives.
- 20 Indian cities witnessed 80% of building fire deaths.
Issue
Context
- Recently, released Indian Risk Survey report ranks fire outbreak as the third biggest risk to businesses and human lives.
- 20 Indian cities witnessed 80% of building fire deaths.
About
- A slew of fire accidents occurred in less than a month damaging human lives, properties and goods.
- Initial findings suggest that storing inflammable materials, blocking exit passages, overhanging electrical wirings are some of the causes.
- These incidents should be treated as a wakeup call.
- According to National Crime Record Bureau, 18,450 cases of fire accidents were reported in 2015 which injured 1,193 and killed 17,700.
- The India risk survey, 2017 (though the report is old, but the eventualities makes it pretty much relevant), ranks natural hazards the fourth highest risk to business up from last year’s seventh position.
- India is considered at a high risk of natural hazards with a significant risk to businesses and communities compared to developed economies.
- As per the India risk survey- 2017, fire has been ranked fifth, up by three positions from the last year’s ranking, cites the report.
- Now, fire outbreak is the third biggest risk to business continuity and operations, according to India Risk Survey (IRS) 2018.
Background
- The fire services are not well organized in India. In recent years, the requirements for fire safety cover have increased manifold whereas the development of Fire Service has not made much headway.
- The setting up of industrial plants at a fast pace with extensive use of hazardous materials and the construction of larger and taller buildings have multiplied the problems of firefighting.
- The fire hazards are no longer confined to big cities and manufacturing centres only.
- Vast quantities of hazardous commodities are daily moved by different modes of transport all across the country posing complicated fire rescue problems.
- If the objective of ensuring safety of life and property in urban and rural areas is to be achieved, then a complete over-hauling of fire service organization is called for.
- The fire services need to be organized properly with adequate infrastructure and equipment for keeping pace with advancement of technology and economic growth.
Analysis
Urbanization: unplanned and didn’t factor in hazard safety:
- There has been a steep rise in the constructions of buildings in India, especially high rise buildings.
- Some of the safety standards which are being adhered to were made in the 1960s onwards, which are no longer relevant
- In metro cities, high rise buildings lack adequate in-built fire protection systems
- Poorly stored goods, even though they are not flammable, may help to spread fire and hinder fire fighters gain access to the seat of the fire or reduce the effectiveness of sprinkler systems
Fire incidents take place due to:
- non-compliant construction
- lack of precautionary maintenance (non-upkeep of extinguishers, ire doors, fire exits and their markings and assembly areas)
- gross overlook of safety procedures such as evacuation drills
- Lack of recording of significant consideration for better response towards flammable materials, and their use in cladding and partitions walls.
Other factors which act as catalyst:
- dense habitation with virtual no room for quick evacuation
- non-compliant use of properties
- local traffic congestions, on-street parking that constricts fire tender movement or delays their access to the affected area
Comptroller and Auditor General of India, the country's federal audit body, had warned last year that fire disasters were possible in high-rise buildings, petrol stations, sawmills and firecracker shops.
If one analyses the findings, it appears that sufficient warnings were issued to the oversight bodies to conduct pre-emptive investigations and seal errant buildings, workshops etc to prevent cases of fire accidents.
However, the action consequences were marred by long pendency, sever understaffing, fund crunch, corruption and inability of these bodies to bring the culprits to the books of law.
National Building Code of India covers the detailed guidelines for construction, maintenance and fire safety of the structures.
- National Building Code of India is published by Bureau of Indian Standards and it is recommendatory document.
- Guidelines have been issued to the States to incorporate the recommendations of National Building Code into their local building bylaws making the recommendations of National Building Code of India as mandatory requirement.
- Fire and life safety norms:Specified for high rise buildings and a proper horizontal evacuation system in high-rise hospitals and public buildings.
Fire Safety Audit (FSA) is found to be an effective tool to assess fire safety standards of an organization or occupancy.
It is aimed to assess the building for compliance with the National Building Code of India, relevant Indian standards and the legislations enacted by state governments and local bodies, on fire prevention, fire protection and life safety measures.
FSA should be made mandatory all over India and the work should be entrusted to independent agencies. It is reasonable to have a fire safety audit every year.
In India, although there are many rules and regulations, codes and standards related to fire safety, these are seldom followed.
Subject classification:
- Fire service is a state subject and has been included as municipal function in the XII schedule of the Constitution.
- Due to lack of resources, fire services are ill equipped in providing adequate fire safety cover to the population
- Based on a 2011 study, 65 per cent deficiency was reported in fire stations. According to Ministry of Home Affairs, in 144 towns with population over 1 lakh, there is a huge deficiency of firefighting infrastructure.
How to prevent fire accidents?
- Organizing fire fighting workshop once in six months in localities/mohallas/schools with the involvement of local councillor/elected representatives is one way to achieve awareness.
- There are many offices/high rise buildings/mandi and religious places having firefighting equipment’s installed but hardly any person has the knowledge of using them.
- Lack of maintenance makes the equipment’s dysfunctional.
- The schools where mid-day meals are cooked are potential fire hazards. Fire service departments should visit above mentioned installations periodically (once in six months) and take appropriate actions against erring establishments.
Has the lesson been learnt?
Days after a fire tragedy killed 17 people at a hotel in Karol Bagh, the Delhi government approved certain amendments to the Delhi Building By-Laws 2016 to enhance fire safety.
- All existing and future guest houses must install carbon monoxide smoke alarms, fire doors on each floor and remove all kinds of combustible materials from passages exit routes and rooftops.
- no kitchen will be allowed on rooftops or basements
- "Inflammable materials of construction will not be used in used in passages, corridors or staircases like wooden foam panelling, carpet etc.
While legislative actions give way to directions what is crucial is to ensure their executive compliance. The accidents may happen, what is important to prevent their “can happen” phenomena.
This is possible only when the agencies and oversight bodies perform their job honestly.
Sense of urgency within the relevant state agencies, coupled with a general understanding of fire safety awareness among people in India are the two prime movers which can reduce instances of deadly fire accidents in India.
Learning Aid
Practice question:
Fire service is a state subject and has been included as municipal function. However, Municipalities are suffering from funds, functionaries and strong teethed law. Is the fire safety itself in need of rescue and rehabilitation? Discuss in reference to recent events of fire accidents that happened in Delhi and Mumbai.