Context
India’s Union Minister for Science and Technology and Earth Sciences Dr. Jitendra Singh held a bilateral meeting with the Minister for Climate and Environment of Norway MrEspen Barth Eide on the side-lines of the UN Ocean Conference in Lisbon, Portugal and discussed several issues of mutual interest.
Background
- India and Tajikistan diplomatic relations were established on 28 August 1992, since then regular high level visits between the two countries cemented the bilateral ties.
- India was one of the first countries to recognize independence of Tajikistan and set up diplomatic relations. Indian embassy was opened in Dushanbe in
- Both the countries are celebrating 30 years of diplomatic ties
|
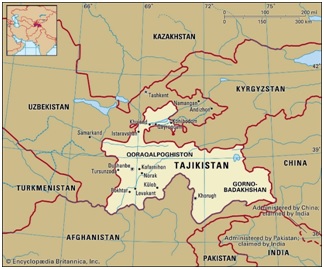
The country profile
|
Analysis
Key highlights of the recent meeting:
- Water resource & energy:The discussion revolved around water resources research, with special focus on Glaciers and their monitoring and understanding, Non-conventional Energy, etc.
- Tajikistan Minister requested India to support global water action and climate resistance on Water for sustainable Development.
- Agendas of the 11th meeting of the Intergovernmental Commission of Tajikistan and India on trade-economic, scientific and technical cooperation in 2020 were discussed that included industry, agriculture, education etc.
- The Eight MoUs/agreements that were signed in 2018 between the two nations were revisited.
- Those were in the areas of Peaceful Use of Space Technology, Disaster Management, Renewable Energy, and Agricultural Research and Education to name important ones.
|
India recently hosted the first meeting of the India-Central Asia Summit with the participation of the Presidents of Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan. |
Mapping the historical ties:
- India’s relations with Tajikistan have been recorded in the Buddhist annals which means around 2500 years BC.
- The excavations in Panjikent in modern Tajikistan are dependable record in this connection.
- In medieval times, two streams of relations were there-
- Flow of Buddhist missionaries from India to Central Asia via Tajikistan
- Trade and commerce carried along these links
- In the Mughal period, Central Asian Sufi ideas, tomb architecture, Farsi literature became popular in India.
- Their mother tongue – Tajik – is a branch of Irano-Aryan group of languages and hence drawing extensively from Sanskrit.
Relation in today’s era
- Cooperation in International Forums/initiatives
- In 2020, Tajikistan extended support for India’s candidature for a non-permanent seat in UNSC for the term 2021-22.
- Tajikistan has publicly supported India’s bid for UNSC permanent membership during the state visit of President Shri Ram NathKovind (in 2018).
- Tajikistan strongly supported SCO Member status for India.
- India supported Tajikistan's accession to WTO in March 2013.
- India also supported Tajikistan’s candidature to ECOSOC.
- Development & Aid Partnership
Since Tajikistan’s independence in 1991, India has played the role of a development and aid partner for Tajikistan.
a) Developmental Project Assistance:
- With a grant of about USD 0.75 million India set up a Modern Engineering Workshop and commissioned it on 02 June 2011. The project is running successfully.
- A project for setting up of computer labs in 37 schools in Tajikistan (announced during Prime Minister Shri NarendraModi’s visit in July 2015 ) was completed and delivered in August 2016 at a cost of USD 6,02,701/-.
- India has commenced the construction of phase-I of a 8-lane highway project from Chortut village to Ayni roundabout in Dushanbe at a cost of approximately USD 17.54 million.
- India provided USD 2 million financial assistance to Tajikistan to help conduct SCO Head of State Summit in Dushanbe in September 2021.
b). Humanitarian Assistance:
- After the outbreak of Polio in southwest Tajikistan, India provided doses of oral polio vaccine through UNICEF in November 2010.
- In September 2015, India granted USD 100,000 as humanitarian assistance to Tajikistan for providing relief to the flood and mudslide-affected people of GBAO (Pamir) and Rasht valley.
- India also help the country during the outbreak of Covid19.
- Connectivity, Trade & Economic Relation:
- Trade and Economy is the weakest link in India-Tajikistan’s relationship.
- Reason:lack of reliable land connectivity between the two countries.
|
Indian exports to Tajikistan |
Tajikistan exports to India |
|
In 2020-2021, 53.45 million USD
|
In 2020-2021, 1.06 million USD
|
- Cultural & People-to-People Relation:
India and Tajikistan share strong historical, cultural and linguistic ties. There is great liking for Indian culture and films and films and TV serials dubbed in Russian language are routinely shown on local TV channels.
- Swami Vivekananda Cultural Centre in Dushanbe offers courses in Kathak&Tabla through teachers deployed by ICCR from India.
- From Tajikistan a 20-member art and cultural troupe participated in Surajkund International Crafts Mela in 2017, 2018, 2019 and in 2020.
- In 2019, under an MEA sponsored program, a Tajik national visited India to witness and participate in the cultural traditions of
- A Hindi-Urdu Chair was established in the Tajik State University and since January 2019 a Professor has been deployed by ICCR at the university.
- Yoga is very popular among local people in Tajikistan.
- Defense Cooperation:
- India has gifted military liveries for two brigades, aviation suits, computers, language training material, military jeeps and trucks and two Mi-8 helicopters along with spare parts and consumables.
- As a component of officers training, batches of young military cadets from Tajikistan are undergoing training at the National Defense Academy [NDA] at Khadakwasla.
- The Tajik Ministry of Defense will receive a grant of US$ 0.5 million to renovate and upgrade the Tajik Military Institute.
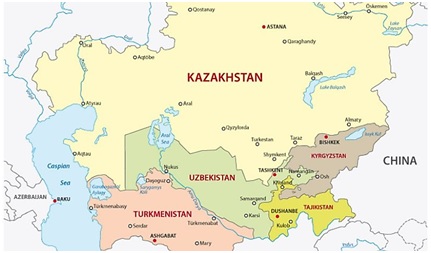
How India’s interaction is increasing with Central Asia?
|
Central Asia is home to the world’s biggest untapped resources of oil, gas and minerals. It is also a key gateway for connectivity with Russia, the Middle East and Europe. India’s relations with CA countries have acquired a strategic dimension.
- Attractive hydrocarbon deposits: Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan have emerged as important suppliers of uranium to fuel India’s nuclear power plants.
- Strategic location: Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan have considerable strategic importance.
|
Tajikistan’s strategic location
|
|
Tajikistan provided critical help in the evacuation of Indians from Afghanistan. |
It will be in India’s interest to augment its linkages with these countries to reduce their dependence on China.
Conclusion:
Tajikistan holds huge significance for fulfilling India’s broader interests in the Central Asian region especially its ‘Connect Central Asia’ policy. More importantly, stronger India-Tajikistan partnership is of key importance for India to amplify its goodwill in the region as well as to add stability to Afghanistan and meet India’s future energy demands.