The International Day against Drug Abuse and Illicit Trafficking is observed on June 26 every year to raise awareness about the major problem that illicit drugs poses to the society.
Issue
Context
- The International Day against Drug Abuse and Illicit Trafficking is observed on June 26 every year to raise awareness about the major problem that illicit drugs poses to the society.
About:
Against Drug Abuse:
- The trade in drugs was already recognized as a global problem requiring a global solution at the beginning of the 20th century.
- The Commission on Narcotic Drugs (CND) was established by Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) resolution to assist ECOSOC in supervising the application of the international drug control treaties.
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) supports Member States in implementing a balanced, health- and evidence-based approach to the world drug problem that addresses both supply and demand.
- It is guided by human rights and the agreed international drug control framework.
This approach involves:
- Treatment, support, and rehabilitation.
- Ensuring access to controlled substances for medical purposes.
- Working with farmers who previously cultivated illicit drug crops to develop alternative sustainable livelihoods for them.
- Establishing adequate legal and institutional frameworks for drug control through using international conventions.
Illicit Trafficking:
United Nations Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, 1988
- This Convention provides comprehensive measures against drug trafficking, including provisions against money laundering and the diversion of precursor chemicals.
- It provides for international cooperation through, for example, extradition of drug traffickers, controlled deliveries and transfer of proceedings.
Background:
What are drugs?
- They are chemical substances that affect the normal functioning of the body and/or brain.
- Not all drugs are illegal. For example, caffeine (found in coffee or Coca-Cola), nicotine (in cigarettes) and alcohol are all technically legal drugs.
- Medicines, whether prescribed by a doctor or available over the counter at pharmacies, are legal drugs to help us recover from illnesses, although they can also be abused.
Analysis
Drug trafficking
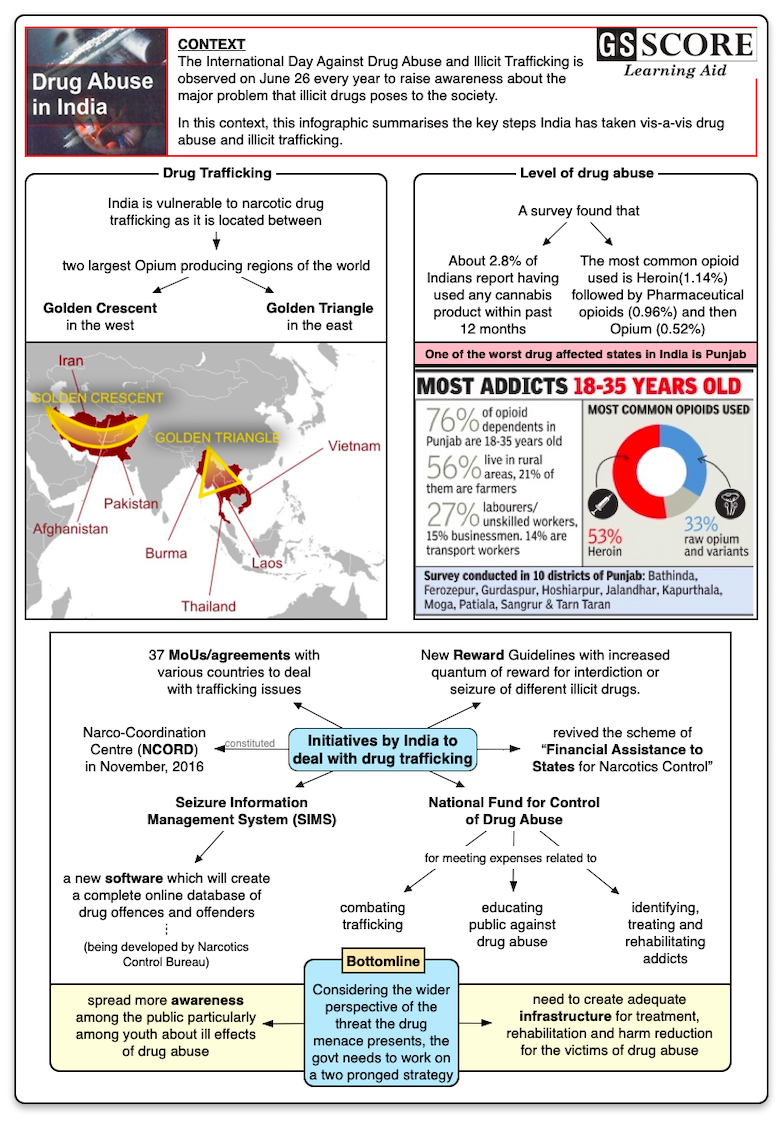
- India is vulnerable to narcotic drug trafficking as it is located between two largest Opium producing regions of the world i.e. Golden Crescent in the west and Golden Triangle in the east.
Golden Crescent
- The Golden Crescent is the name given to one of Asia's two principal areas of illicit opium production, located at the crossroads of Central, South, and Western Asia. This space overlaps three nations, Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan, whose mountainous peripheries define the crescent.
Golden Triangle
- This is a region that joins Burma, Thailand, and Laos and is one of the global centers of opiate and methamphetamine production.
Magnitude of Substance abuse in India
Substance categories studied were: Alcohol, Cannabis (Bhang and Ganja/Charas), Opioids (Opium, Heroin and Pharmaceutical Opioids), Cocaine, Amphetamine Type Stimulants (ATS), Sedatives, Inhalants and Hallucinogens.
Alcohol
- At the national level, about 14.6% of people (among 10-75 year old) are current users of alcohol, i.e. about 16 Crore people. Prevalence is 17 times higher among men than women.
- States with the high prevalence of alcohol use are Chhattisgarh, Tripura, Punjab, Arunachal Pradesh and Goa.
Cannabis
- About 2.8% of Indians (3.1 Crore individuals) report having used any cannabis product within past 12 months (Bhang – 2% or 2.2 crore people; Ganja/Charas – 1.2% or 1.3 Crore people).
- States with the higher than national prevalence of cannabis use are Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Sikkim, Chhattisgarh and Delhi.
Opioids
- At the national level, the most common opioid used is Heroin, (current use 1.14%) followed by Pharmaceutical opioids (current use 0.96%) and then Opium (current use 0.52%).
- In terms of percentage of population affected, the top states in the country are those in the north east (Mizoram, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Manipur) along with Punjab, Haryana and Delhi.
Sedatives and Inhalants
- States with the highest prevalence of current Sedative use are Sikkim, Nagaland, Manipur and Mizoram. However, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Punjab, Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat are the top five states which house the largest populations of people using sedatives.
Drugs cloud the judgment of users. There is the risk of becoming addicted. In the longer run, the human capital is severely depleted.
Instead of contributing to the economy and social growth, the addicts end up becoming a burden.
There are lots of reasons why people take illegal drugs
- Some take them to escape problems
- While others are bored, curious or just want to feel good
- People may be pressured into taking drugs to “fit in” with a particular crowd
- To rebel or get attention.
Why controlling drug menace is difficult:
- Over the counter and easy availability
- Porous international borders
- Detached lifestyles: loss of morals and family support
- Replacement of cross-border terrorism by Narco-terrorism by Pakistan
- Variation in Drug control Policy: Cultivation and sale of opium poppy husk is legal in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh, accounting for the presence of these two substances in abundance in the districts near Rajasthan, such as Bathinda, Fazilka and Mansa.
- There is hardly any coordination among the police, the BSF, and the state and central intelligence agencies for curbing the problem
Policy and other initiatives by the Government to deal with drug trafficking problem:
- Constituted Narco-Coordination Centre (NCORD) in November, 2016 and revived the scheme of “Financial Assistance to States for Narcotics Control”.
- Approved new Reward Guidelines with increased quantum of reward for interdiction or seizure of different illicit drugs.
- For effective coordination with foreign countries including neighboring countries, India has signed 37 Bilateral Agreements/Memoranda of Understanding.
- The government has scheduled 07 new substances into the list of Narcotic drugs in the year 2017 so that action can be taken against trafficking in these substances.
- Narcotics Control Bureau has been provided funds for developing a new software i.e. Seizure Information Management System (SIMS) which will create a complete online database of drug offences and offenders.
- The government has constituted a fund called “National Fund for Control of Drug Abuse” to meet the expenditure incurred in connection with combating illicit traffic in Narcotic Drug, Psychotropic Substances; identifying, treating and rehabilitating addicts, and educating public against drug abuse.
Way Forward:
- Considering the wider perspective of the threat the drug menace presents, India has to spread more awareness among the public particularly among youth about ill effects of drug abuse and need to create adequate infrastructure for treatment, rehabilitation and harm reduction for the victim of the drug abuse.
- Make treatment available on Request Like Any Other Health Service: Making treatment services widely available undermines the drug market and reduces the harms from drug abuse.
- Treatment should be defined broadly and must include abstinence-based treatment and easier access to methadone and other alternative maintenance drug.
- The most effective way to prevent adolescent drug abuse is to invest in youth and keep them interested and involved in life.
- Government should increase funding for after school programs, mentor programs, skills building/job training programs and summer job programs.
- Psychiatrist counseling of drug patients: Early recognition Program
- Include drug abuse related topics in school curriculum at appropriate age.
- Build more rehabilitation centers and create support groups like Alcoholic anonymous.
Learning Aid
Practice Question:
India’s vulnerability to drug trafficking due to its location in Golden Crescent and Golden Triangle. Drug trafficking and abuse endanger peace, health and stability across regions and it places a heavy burden on public health system. Analyze factors behind spread of drug menace and evaluate the measures taken at national and international level in tackling the problem.