

Context
The climate change has shifted the world’s focus towards ‘nuclear energy’ to help wean all economies off polluting fossils fuels. But it creates a heated issue that whether nuclear energy is good for the climate or not.
This brief attempts to analyse the correct nature of nuclear energy and its significance for the climate.
Background
- Climate change is happening at a faster rate and it is visible in almost all areas.
- The latest figures on global carbon dioxide emissions call into question the world's efforts to tackle the climate crisis.
- CO2 emissions are set to soar 4.9% in 2021, compared with the previous year, according to a study published earlier this month by the Global Carbon Project (GCP).
- In 2020, emissions dropped 5.4% due to the COVID-19 pandemic and associated lockdowns.
- The energy sector continues to be the largest emitter of greenhouse gases, with a share of 40% — and rising.
- This raises the demand of an alternative source of energy which is good for the climate.
What is nuclear energy?
- Nuclear energy comes from splitting atoms in a reactor to heat water into steam, turn a turbine and generate electricity.
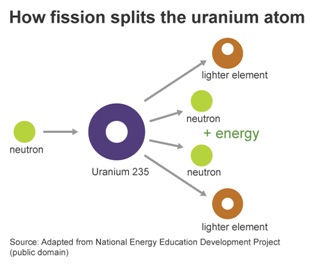
|
Atoms
|
What are the benefits of Nuclear Energy?
Nuclear energy offers many advantages and its unique value cannot be found in any other energy source.
- Protection of national security: Leadership in nuclear energy maintains safety and nonproliferation standards globally, supports a resilient electrical grid at home, and fuels a strong navy.
- Solution for climate change.It provides large amounts of 24/7 carbon-free electricity now (approximately), which is irreplaceable in protecting the environment.
- Reduction in air pollution: Nitrogen oxide, sulfur dioxide, particulate matter and mercury: all things are present in polluted air. Nuclear energy provides power 24/7 without a trace of those pollutants (approximately).
- Production of electricity reliably.Around-the-clock electricity is a must for our nation to prosper in the 21st century and nuclear energy helps in maintaining that.
- Employment generation:Nuclear energy provides more than 100,000 well-paid, long-term jobs and supports local economies with millions of dollars in state and local tax revenues.
- Nuclear boosts international development:Nuclear energy helps developing nations meet sustainable development goals.
- Nuclear powers electric vehicles.Electrified transportation promises to reduce carbon emissions. When powered by carbon-free nuclear energy, electric vehicles can reach their full potential.
The benefits of nuclear energy extend far beyond carbon-free electricity too. Nuclear powers space exploration, sterilizes medical equipment, provides potable water through desalination, supplies radioisotopes for cancer treatment and much more.
Is nuclear power really a zero-emissions energy source?
The answer is no. Nuclear energy is also responsible for greenhouse gas emissions. In fact, no energy source is completely free of emissions, but more on that later.
- Transportation and processing: When it comes to nuclear, uranium extraction, transport and processing produces emissions.
- Construction & demolition of plants: The long and complex construction process of nuclear power plants also releases CO2, as does the demolition of decommissioned sites.
- Nuclear waste: And, last but not least, nuclear waste also has to be transported and stored under strict conditions — here, too, emissions must be taken into account.
|
At COP26, environmental initiative Scientists for Future (S4F) presented a paper on nuclear energy and the climate. The group came to a very different conclusion. Taking into account the current overall energy system, nuclear energy is by no means CO2 neutral. |
How much CO2 does
The results vary significantly, depending on whether only the process of electricity generation is considered, or take into account the entire life cycle of a nuclear power plant.
- A reportreleased in 2014 by the UN's Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), for example, estimated a range of 7 to 110 grams of CO2 equivalent per kilowatt-hour (kWh).
- It's long been assumed that nuclear plants generate an average of 66 grams of CO2/kWh.
- New power plants, for example, generate more CO2 during construction than those built in previous decades, due to stricter safety regulations.
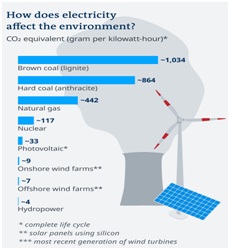
How climate-friendly is nuclear compared to other energies?
- If the entire life cycle of a nuclear plant is included in the calculation, nuclear energy certainly comes out ahead of fossil fuels like coal or natural gas.
- But the picture is drastically different when compared with renewable energy. According to a study
- nuclear powerreleases 3.5 times more CO2 per kilowatt-hour than photovoltaic solar panel
- Compared with onshore wind power, that figure jumps to 13 times more CO2.
- When up against electricity from hydropower installations, nuclear generates 29 times more carbon.
Other important arguments against nuclear power
- Availability issue: Construction of power plants takes too long to complete and the costs too high to have a noticeable effect on climate change. It takes too long for nuclear energy to become available.
- An expensive affair: Nuclear power plants are about four times as expensive as windor solar, and take five times as long to build.
- Blocked financial resources: Due to the high costs associated with nuclear energy, it also blocks important financial resources that could instead be used to develop renewable energy.
- Affected by climate change: In addition, nuclear energy itself has been affected by climate change. During the world's increasingly hot summers, several nuclear power plants have already had to be temporarily shut down or taken off the grid.
A combination of excessive costs, environmental consequences and lack of public support were all arguments against nuclear power.


