

Northern India has reported many lightning strikes at different part- Amer Fort, Dwarkadheesh Temple, Chambal region etc claiming many lives and inflicting damages to the structures.
Context
Northern India has reported many lightning strikes at different part- Amer Fort, Dwarkadheesh Temple, Chambal region etc claiming many lives and inflicting damages to the structures.
Background
- At least 70 people have died in lightning strikes in India over the past few days, a weather event that claims more lives than other natural calamities in India every year
- As many as 1,697 deaths have been attributed to lightning during 2020-21, according to a report by Lightning Resilient India Campaign (LRIC).
- An app named Damini, which means lightning in Hindi, has also been launched to issue waringsabout lightning strikes three hours in advance.
Analysis
What is lightning?
- Lightning is a giant spark of electricity in the atmosphere between clouds, the air, or the ground.
- In the early stages of development, air acts as an insulator between the positive and negative charges in the cloud and between the cloud and the ground.
- When the opposite charges build up enough, this insulating capacity of the air breaks down and there is a rapid discharge of electricity that we know as lightning.
What causes thunder?
- The bright light of the lightning flash caused by the return stroke mentioned above represents a great deal of energy.
- This energy heats the air in the channel to above 50,000° F in only a few millionths of a second.
- The air that is now heated to such a high temperature had no time to expand, so it is now at a very high pressure.
- The high pressure air then expands outward into the surrounding air compressing it and causing a disturbance that propagates in all directions away from the stroke.
- The disturbance is a shock wave for the first 10 yards, after which it becomes an ordinary sound wave, or thunder.
Types of Lightning
- Cloud-to-Ground (CG) Flashes
- A channel of negative charge, called a stepped leader, will zigzag downward.
- A “bolt from the blue”is a CG which starts inside a cloud, goes out the side of the storm, then travels horizontally away from the cloud before going to ground.
- Intra-cloud Lightning
- The most common type of discharge - lightning inside a single storm cloud where both ends of the bidirectional leader stay entirely in the storm cloud.
- Cloud Flashes
- There are many flashes which do not reach ground. Most of these remain within the cloud and are called intra-cloud (IC)lightning flashes.
- Cloud flashes sometimes have visible channels that extend out into the air around the storm (cloud-to-air or CA), but do not strike the ground.
- Heat Lightning
- any lightning (IC or CG) or lightning-induced illumination that is too far away for the thunder to be heard.
- It may have reddish (“heat”) color, like sunsets, because of scattering of blue light.
- Spider Lighting
- It refers to long, horizontally traveling flashes often seen on the underside of stratiform clouds. Spider lightning is often linked to +CG flashes.
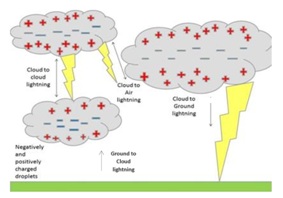
- It refers to long, horizontally traveling flashes often seen on the underside of stratiform clouds. Spider lightning is often linked to +CG flashes.
What happens at the ground when lightning strikes?
- Formation of Fulgurite:
- When lightning strikes ground it fuses dirt and clays in to silicas.
- The result is often a glassy rock (called a fulgurite) in the shape of a convoluted tube. Fulgurite has been found all over the world, but is relatively rare.
- Damage to trees:
- Lightning traveling down a tree trunk turns water to steam.
- If it gets under the bark into the surface moisture of the wood, the rapidly expanding steam can blast pieces of bark and branches from the tree, and the wood along the path is often killed.
- Damage to structures
- The lightning current can travel even farther through water, metal fences, power lines or plumbing.
- Lightning current may enter a building and transfer through wires or plumbing and damage everything in its path.
- Damage in urban areas
- In urban areas, it may strike a pole or tree and the current then travels to several nearby houses and other structures and enter them through wiring or plumbing
|
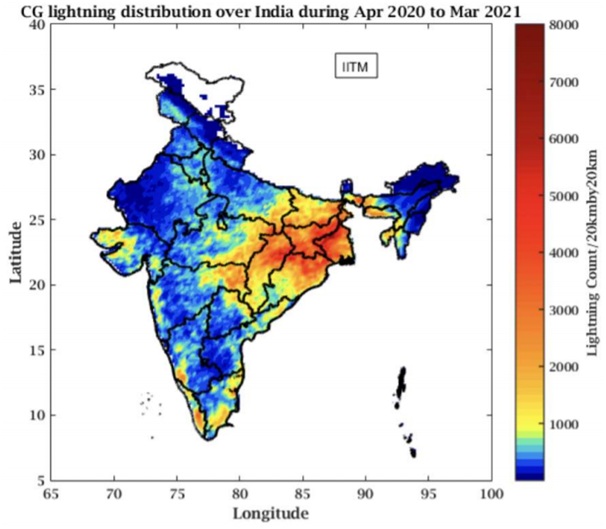
Annual Lightning Report 2020-21 (in comparison with 2019-20)
|
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Though lightning incidents are less, whenever they strike, they cause severe damages to life and properties. Casualties due to Lightning can be easily, efficiently and inexpensively avoided, and lightning safety can be achieved mainly by creating public awareness, technical education on Lightning Protections, educating people on lightning and surge protection.
Stringent steps to ensure adherence of building standards and codes wherever necessary and promoting research and development on lightning protection are essential. There is a need to give lightning its due attention as a natural disaster and give it a priority in National Disaster Management Programmes.


