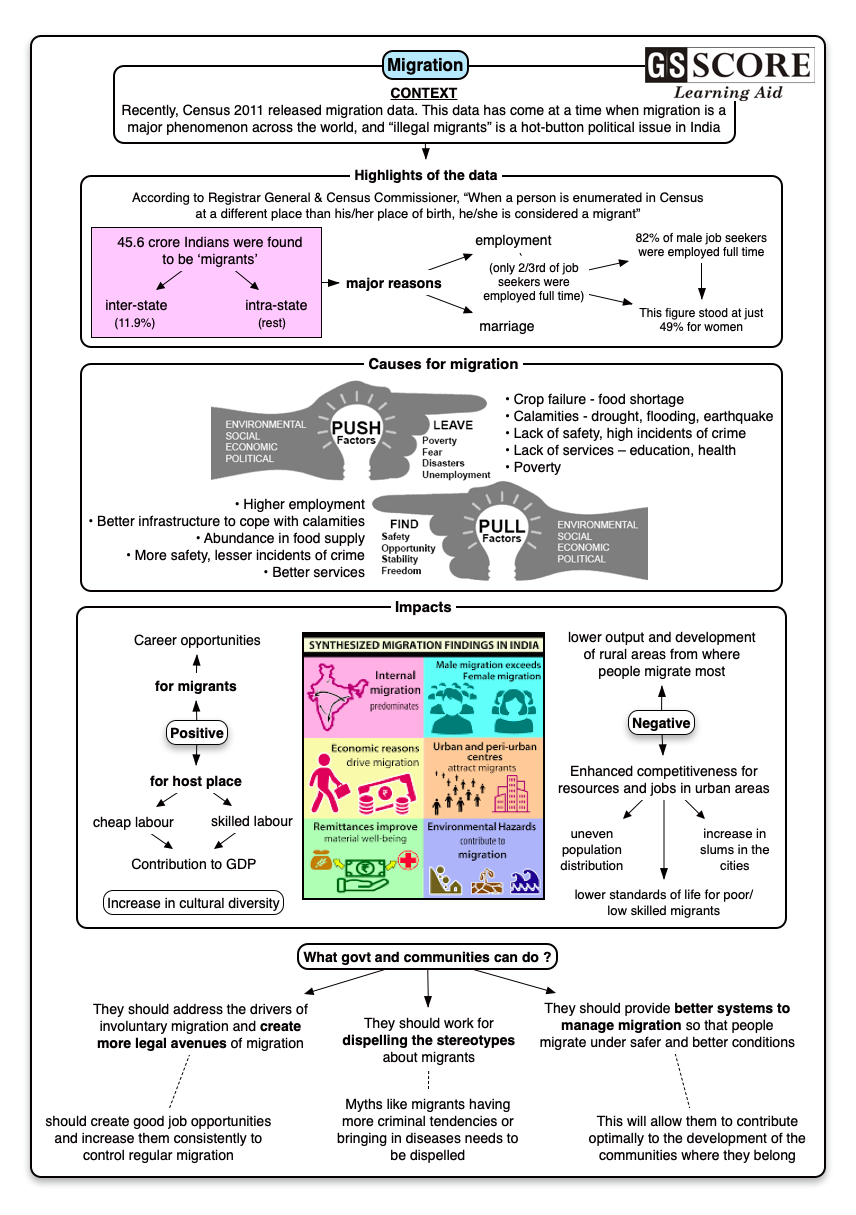
- Recently Census 2011 released migration data.
- The data has come at a time when migration is a major phenomenon across the world, and “illegal Bangladeshis” is a hot-button political issue in India.
Issue
Context:
- Recently Census 2011 released migration data.
- The data has come at a time when migration is a major phenomenon across the world, and “illegal Bangladeshis” is a hot-button political issue in India.
Background:
Migration:
- According to Registrar General & Census Commissioner, “When a person is enumerated in Census at a different place than his/her place of birth, he/she is considered a ‘migrant’.”
- Migration data began to be collected with the Census of 1872, but was not very detailed until 1961.
- Changes introduced in 1961 continued until 2001; in the Census of 2011, a more detailed format for collecting information on migrants was adopted.
Analysis
Key inferences regarding migration from the Census numbers:
- Maharashtra had more migrants from Madhya Pradesh than from Bihar, and Gujarat had almost double the number of migrants from Rajasthan than from Bihar.
- Data from Delhi show only 2,321 persons declared Bangladesh as their last place of residence. Over 1.17 lakh said Pakistan — not surprising given the history of Partition.
- Over 58 crore Indians were found to be “migrants” for various reasons during the enumeration exercises of Census 2011. The previous Census (2001) had recorded the number of migrants at 31.45 crore — more than 30% lower than the 2011 figure.
- Marriage and employment are the major reasons for migration.
- The bulk of the migration takes place within individual states — out of the total number of persons registered as “migrants” in the 2011 Census, only 11.91% (5.43 crore) had moved to one state from another, while nearly 39.57 crore had moved within their states.
- Only 63% of internal migrants who wanted to work were employed as full-time workers. Another 25% were working on a part-time basis, while 12% were not employed—despite wanting to be employed—at the time of the Census.
- The finding that only two out of three individuals who left their place of birth in search of work had full-time employment underscores the uncertain journey migrant workers make and the vulnerabilities they face, that too in a place away from home.
- Spread of full-time workers:
|
In just six of the 640 districts did the figure of full-time workers cross 90%. These are the two districts of Mumbai—Mumbai City and Mumbai Suburban—Delhi West, Surat (Gujarat), Daman and Mamit (Mizoram), though the last two draw a lesser number of migrants. |
In nearly one-third of the districts (204), full-time work was available to only 50% of migrants who wanted to work. This was true of a majority of districts in Jharkhand, Jammu and Kashmir, Bihar, West Bengal, Odisha and Uttar Pradesh.
|
Among the states, the share of workers who found full-time work ranged from 70% to 80% were Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, undivided Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat. |
- Comparison of employment between women and men:
|
Among men who sought work, 82% got full-time employment, compared to just 49% among women. |
In only 20 districts over 85% of women seeking work secured full-time employment. As many as 12 of these districts are in Maharashtra, four in Tamil Nadu, two in Karnataka and one each in Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram. |
- Generally in urban areas, 78% of migrants were involved in full-time work, against 58% in rural areas.
Causes for migration: Causes for migration can be categorized into 2 factors:
|
Push Factors |
Pull Factors |
|
These are reasons for leaving a place, which is called emigration, because of certain difficulties. |
These are reasons for moving into a place, which is called immigration, because of an aspiration, dream, or something desirable. |
|
|
Impacts of Migration
Positive impact
- Avail career opportunities and cheap labour: Most of the migrants often seek to migrate in their quest for better career opportunities than the ones they have back home. This, in turn, provides the host country with a ready source of cheap labour.
Example: Some of the top electronics industries in the West, owe their success today to migrant labour and the fact that they were able to utilize cheap labour which resulted in them in becoming more competitive.
- Provide highly skilled labour: It is a fact that there is an acute shortage of highly skilled labour in certain parts of the world. Immigration enables these countries to get highly skilled labour in the form of doctors, engineers, scientists and much more.
- Contribution to GDP: According to a study conducted the estimated contribution of immigrants to gross domestic product (GDP) ranges from about one percent Ghana to 19 percent in Cote d'Ivoire, with an average of 7 percent across the ten countries. The contribution of immigrants to the GDP value added exceeds their population share in employment.
- Increase cultural diversity: Migration helps to increase cultural diversity; as people are introduced to newer cultures and customs, they often react along predictable lines. But cultural diversity is good in the sense it enables the community to come together and even helps it to act as a cohesive unit.
Negative Impact
- The loss of a person from rural areas, impact on the level of output and development of rural areas.
- The influx of workers in urban areas increases competition for the job, houses, school facilities etc.
- Having large population puts too much pressure on natural resources, amenities and services.
- Migration changes the population of a place, therefore, the distribution of the population is uneven in India.
- Many migrants are completely illiterate and uneducated, therefore, they are not only unfit for most jobs, but also lack basic knowledge and life skills. Poverty and urban inflation makes them unable to live a normal and healthy life.
- Children growing up in poverty have no access to proper nutrition, education or health.
- Migration increased the slum areas in cities which increase many problems such as unhygienic conditions, crime, pollution etc.
- Migration is one of the main causes of increasing nuclear family where children grow up without a wider family circle.
Way forward:
- The government should address the drivers of involuntary migration and create more legal avenues of migration. It should create good job opportunities and increase them consistently to control regular migration.
- Migrants bring new ideas and high motivation. They contribute to the economy of their host countries and even more to the economy of their countries of origin by sending remittances to their families. They send back home $450 billion every year to put food on the table, for the education of their children, for the people who are sick, and for the elderly. Government should provide better systems to manage migration so that people migrate under safer and better conditions, thereby allowing them to contribute optimally to the development of the communities where they belong.
- The government should work for dispelling the stereotypes - there is nothing on the record that shows that migrants have more criminal tendencies or records than nationals. It is even usually the opposite. There is nothing on the record that migrants bring in diseases. These perceptions need to be changed.
- The government of countries that are not traditional destinations for migrants should learn to manage an extremely growing economic, social, religious and ethnic diversity. People are going to arrive who don’t look or speak exactly as we do, but who might be brought to share the same values if they are properly welcomed and integrated.
Learning Aid
Practice Question:
Migration has been a historical process, but nowadays, it is increasing at an exponential rate. Discuss the various reasons for this, how it is impacting the society and how can this process be made beneficial for both migrant and immigrating country.