Context
Sweden is set to join NATO after Hungary's parliament ratified its bid. Hungary's decision comes two years after both Sweden and Finland applied to join NATO in May 2022 following Russia's full-scale invasion of Ukraine.
Dimension 1: Significance for the alliance
- Break from neutrality: Sweden has not been involved in a war since 1814and has “pursued a policy of non-alignment in peacetime and neutrality in wartime, basing its security on a strong national defense. Sweden’s entry into NATO move signals a break from a history of neutrality for both countries.
- Reducing the vulnerability: Sweden's NATO membership strengthens alliance in Baltic Sea region.
|
NATO Lake After Finland joined last year, Sweden's membership means all the countries surrounding the Baltic Sea, except Russia, will be part of the US-led military alliance. |
- Sense of security: At the time that Russia’s invasion threatened Europe’s security order and made Sweden’s need for guaranteed securitygranted through NATO membership apparent.
- Reinforcing the Baltic states: Three countries breathing a particular sigh of relief over the entry of Sweden - and Finland - are NATO's Baltic states, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, long seen as an Achilles heel for the alliance.
- Strategic position:Sweden’s geographical position makes it an essential part of any NATO defence plans. Its location means it can serve as a land transit route to reinforce both Norway and Finland, while also allowing NATO to largely take control of the Baltic Sea in any potential conflict with Russia.
- This provides an alternative sea reinforcement option to the Baltic states other than the vulnerable land border between Poland and Lithuania which is within artillery range of the Russian-held Kaliningrad area and Belarus.
- Kaliningrad threat: Beyond its long Baltic coastline, Sweden brings with it the island of Gotland which would play a central role in helping NATO impose its will. But just across the water, Russia has its vital outpost -- the exclave of Kaliningrad.
- Wedged between Poland and Lithuania, Moscow has in recent years turned the region into one of the most militarised in Europe, with nuclear-capable missiles stationed there.
|
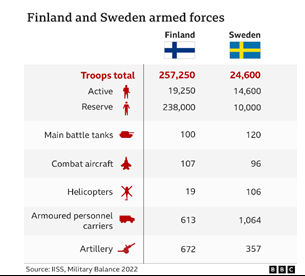
Fact Box: Sweden’s military power Unlike many countries who have joined NATO since the end of the Cold War, Sweden has maintained highly capable military forces with a good deal of cutting-edge technology, including fourth generation Gripen fighter aircraft equipped with Meteor air-to-air missiles, Leopard 2 main battle tanks and Gotland-class attack submarines powered by an air-independent propulsion system. |
Dimension 2: Concerns
- Russia:For now, Russia is the biggest loser of Sweden joining NATO.Moscow has threatened Sweden and Finland since both countries turned toward NATO. Since the two Nordic countries began the process to join the alliance, the West has tightened its grip on the Baltic Sea, complicating a vital transit route for the Russian navy.
- Fissure within the NATO alliance:Not all NATO members view Russia as the principal security threat. In both cases, Sweden’s membership has become embroiled in wider domestic issues.
|
Fact Box: NATO
|