Context
The consequences of the irreparable damage by soil degradation on human and healthy ecosystems can affect the government’s food security efforts for sustainable future.
Importance of Healthy soil:
- Essential for our survival: It contributes to a number of cycles that make all life on Earth possible. These include carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycles.
- Essential for Plant growth: They support healthy plant growth to enhance both our nutrition and water percolation to maintain groundwater levels.
- Regulate Earth’s Climate: Soils help to regulate the planet’s climate by storing carbon and are the second largest carbon sink after the oceans.
- Maintain Landscapes: They help maintain a landscape that is more resilient to the impacts of droughts and floods.
- Water Filtration: It filters the rainwater and regulates the discharge of excess rainwater, preventing flooding.
- Holds organic matter: It is capable of storing large amounts of organic carbon; it buffers against pollutants.
Food security:
- Food is as essential for living as air is for breathing. But food security means something more than getting two square meals. It has following dimensions:
- Availability: It means food production within the country, food imports and the stock stored in government granaries.
- Accessibility: It means food is within reach of every person without any discrimination.
- Affordability: It implies that having enough money to buy sufficient, safe and nutritious food to meet one's dietary needs.
- Thus, Food security is ensured in a country only when sufficient food is available for everyone, if everyone has the means to purchase food of acceptable quality, and if there are no barriers to access.
Soil management for food security:
- Soil plays a significant role in enhancing food security of the world population. However, only 10%–12% of the natural soils are suitable for agriculture.
|
Main drivers contributing to soil degradation:
Reasons behind soil nutrient loss:
|
- Therefore, maintaining optimum food production proper land-use policies should be framed considering the degradation of the soil ecosystem day by day.
What is soil degradation?
- Soil degradation describes what happens when the quality of soil declines and diminishes its capacity to support animals and plants.
- Soil can lose certain physical, chemical or biological qualities that underpin the web of life within it.
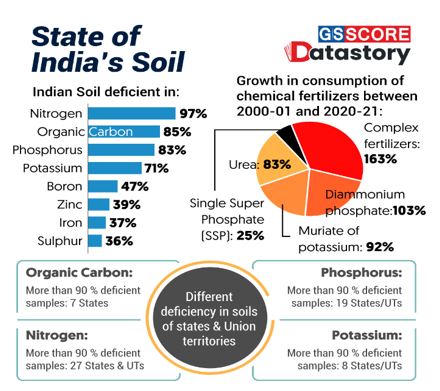
How nutrient-deficient are Indian soils?
- Delhi based environmental think-tank the Centre for Science and Environment in its report State of Biofertilizers and Organic Fertilizers in India has flagged poor status of soil health and increasing consumption of chemical fertilizers in India.
Key observations:
|
Macronutrient Deficiency |
Micronutrients Deficiency |
|
|
State-wise analysis:
- Organic carbon deficiency is widespread across the country.
- Haryana’s soils are the most deficient in organic carbon, followed by those of Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, and Mizoram.
- Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium deficiencies were recorded in at least half the samples in 32 states and UTs.
What is India’s conservation strategy?
- The Government of India is implementing a five-pronged strategy for soil conservation.
- This includes making soil chemical-free, saving soil biodiversity, enhancing soil organic matter, maintaining soil moisture, mitigating soil degradation, and preventing soil erosion.
|
Some Important initiatives:
|