Context
Given the porosity along the Northeast (NE) border, drug trafficking is likely to be a huge matter of concern in the coming years.
Background
- There has been an increasing trend of drug smuggling and illicit activities carried out at the border, attracting the centre of attention to highlight two important issues.
- First is related to the involvement of locals in illicit trade; and youth and their addiction to drugs.
- The second issue is related to the implications of illicit trade at borders to India’s Act East Policy (AEP).
- Many experts have apprehension about the success of AEP not because of lack of connectivity, but because of close proximity with Myanmar with a porous border.
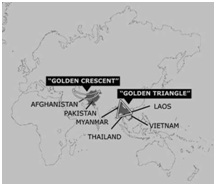
|
Golden Triangle
|
In this vein, this brief aims to examine the illegal trade and drug trafficking at the border and how is it an internal security challenge for India.
Analysis
What substances are consumed by masses?
- In India, alcohol is the most commonly consumed psychoactive substance by the masses.
- Next to alcohol is-
- Cannabis: legal form: bhang and illegal form: ganja and charas. It is used widely in states like Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Sikkim, Chhattisgarh and Delhi
- Opioids: opium, Heroinand other pharmaceutical Opioids: It is used in Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur and Mizoram.
- Heroin is the most used Opioids nationwide and people in the NE region mostly use the Opioid at a large scale.
What is the region a troubled hotspot for drug-trafficking?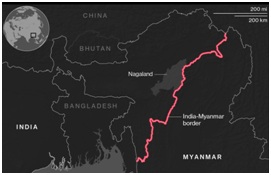
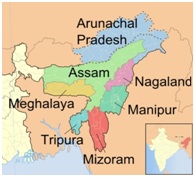
- Unregulated border: Among the seven Northeastern states plus Sikkim, states like Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Mizoram and Nagaland share an international border with Myanmar.
- Since, there is no strict fencing across the Indo-Myanmar Border (IMB), cross border crimes are frequent in these states.
- Narcotic drugs from Myanmar enters India through Mizoram, Nagaland and Manipur and is then en-routed to Assam and distributed to different drug lords in other parts of the country.
- Free flow of items: The unregulated border has resulted in the free flow of many items through illegal trade including drugs, illegal immigration, tax evasion and supply of contraband.
- Free movement: Additionally, the Free Movement Regime (FMR) between India and Myanmar has again facilitated such activities across the border.
- According to FMR, people who are living on both sides of the border are allowed to move freely within 16 km from the border without any restrictions including visa.
- Furthermore, insurgents, criminal gangs and drug lords to carry out illegal trade including Chinese products and smuggling of drugs often misuse FMR.
- Illegal cultivation: In addition, drug mafias from parts of India use remote places such as NE region for opium cultivation.
|
Major drugs
|
Why more and more people are getting engaged in the drug nucleus?
Population residing at the border area is vulnerable and neglected and thus gets involved in illicit trade and illegal activities. The following are a few reasons:
- Poverty: They are economically poor and they do not have other sources.
- Lack of opportunities: They do not have job opportunities in the region due to lack of education and other unavailable options.
- Easy manipulation: Criminals and drug lords acknowledge the poor socio-economic condition of the people and hence, they manipulate the minds of people to join such illegal activities to extract easy money out of this.
How drug trafficking pose a threat to security?
- There is no doubt the region is becoming a nucleus of drug trafficking and thus pose a serious threat to India’s internal security.
- Drug trafficking intersects with a vast array of security issues ranging from war and terrorism to human trafficking, drug trafficking and national stability.
- Terrorism: The threat of radicalization and recruitment of youth by terrorist groups is serious corollary of drug-trafficking.
- Threatened national security: Cyber security is increasingly becoming a global challenge with terrorists and drug traffickers utilizing new methods of communication and operations, thereby threatening national security.
- Multifarious security issues: Drug-trafficking brings along with it multifarious security issues and challenges, notably an intricate network of actors across various levels of handling narcotics management, which in most instances extend to foreign jurisdictions.
- Laundering of drug money: Emergence of new criminal avenues to launder drug-money such as crypto currency and money transfer systems.
- Political chaos: Politicization of the fight against drug-trafficking by leaders from across the political divide creates insurmountable legal and political problems.
- Increased crime and violence: The lucrative trade in methamphetamine, cocaine, and ecstasy will result in crime and violence perpetrated by users and armed gangs, including petty crime, violence against women and children, and “drug money-fuelled” violence.
- The security threats caused by drug trafficking can impact all levels of society, and at all levels of government right down to the family.
Government measures against drug trafficking
- NDPS Act: The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (NDPS Act) came into force in 1985. Under the Act, it is illegal for any person to produce/ manufacture/cultivate, possess, sell, purchase, transport, store, and/or consume any narcotic drug or psychotropic substance.
- The Act has been amended three times – in 1988, 2001, and 2014.
- The Act extends to the whole of India and it also applies to all Indian citizens outside India and to all persons on ships and aircraft registered in India.
- Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB): The Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) was created in 1986 to enable the full implementation of the NDPS Act.
- The NCB is the chief law enforcement and intelligence agency of India responsible for fighting drug trafficking and the abuse of illegal substances.
- E-portal, SIMS: For digitization of pan-India drug seizure data, the MHA has launched an e-portal called ‘SIMS’ (Seizure Information Management System) in 2019 for all the drug law enforcement agencies under the mandate of NDPS Act.
- Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan: The Centre launched the ‘Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan’ under the aegis of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- Coordination with international organization: The Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) coordinated with various international organizations for sharing information and intelligence to combat transnational drug trafficking. They included the
- SAARC Drug Offences Monitoring Desk
- Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa (BRICS)
- Colombo Plan
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
- ASEAN Senior Officials on Drug Matters (ASOD)
- Bay of Bengal Initiative For Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Co-Operation (BIMSTEC)
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC)
- International Narcotics Control Board (INCB)
What corrective measures can be adopted?
- Detection and prevention: Safety and security against violent extremism tool that will help detect and prevent radicalization of youth.
- National strategy: Develop a national strategy to counter violent extremism.
- Improved media: Improve media sensitization on terrorism and drug-trafficking reporting.
- Enhanced coverage: Enhanced security coverage of critical infrastructures is required. Private security agencies, especially those run by ex-servicemen, have a great role to perform in this domain.
- Robust law for money laundering: Formulate a more robust anti-money laundering law and combating the financing of terrorism framework. Engaging the local political, religious and opinion leaders within vulnerable communities, as a proactive strategy to deny terrorism entry points into the radicalization of our youth,
- Focusing on bilateral relations: Enhancing bilateral and multilateral collaboration in counter terrorism efforts.