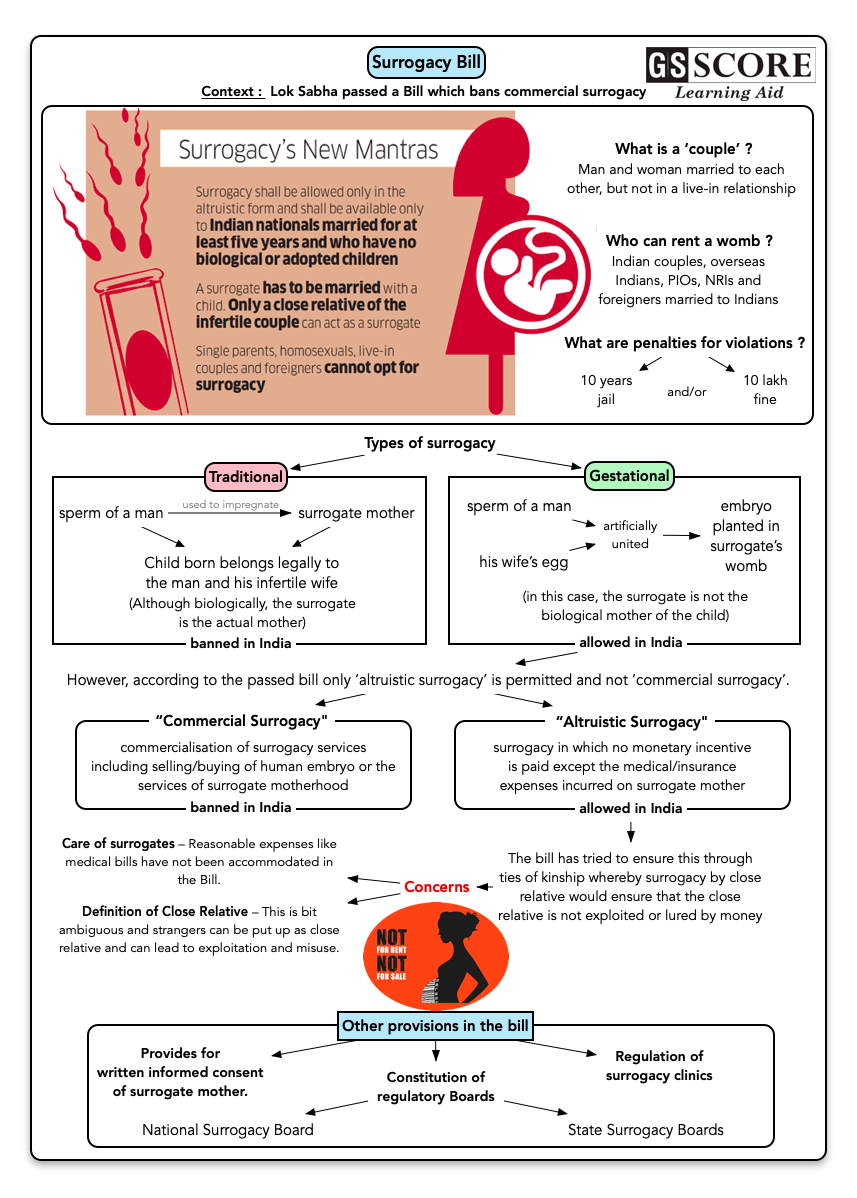
- The Lok Sabha recently passed Bill banning commercial surrogacy with penal provisions of jail term of up to 10 years and fine of up to ?10 lakh.
- The bill is significant since India had become a hub of commercial surrogacy.
Issue
Context
- The Lok Sabha recently passed Bill banning commercial surrogacy with penal provisions of jail term of up to 10 years and fine of up to ?10 lakh.
- The bill is significant since India had become a hub of commercial surrogacy.
Background
- India has been a preferred destination for those wanting a surrogate child.
- The cheap availability of the service enables an overuse of the practice with commissioning parents arriving from various other countries as well.
- In 2002, the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) laid out guidelines for surrogacy, which made the practice legal, but did not give it legislative backing. This led to a booming surrogacy industry which had lax laws and no enforcements.
- A study conducted in July 2012, backed by the UN, put the surrogacy business at more than $400 million with more than 3000 fertility clinics all over the country.
About
- Surrogacy is a method or agreement whereby a woman agrees to carry a pregnancy for another person or persons, who will become the new-born child's parent(s) after birth.
- Intended parents may seek a surrogacy arrangement when either pregnancy is medically impossible, pregnancy risks present an unacceptable danger to the mother's health or is a same sex couple's preferred method of having children.
- The legality and costs of surrogacy vary widely between jurisdictions, sometimes resulting in interstate or international surrogacy arrangements. There are laws in some countries which restrict and regulate surrogacy and the consequences of surrogacy.
Types of Surrogacy
On the basis of selection of Surrogate Mother:
- Altruistic surrogacy: The surrogate mother receives no financial rewards for her pregnancy or the relinquishment of the child to the genetic parents except necessary medical expenses. This usually happens when the surrogate mother is a relative.
- Commercial surrogacy: The surrogate mother is paid over and above the necessary medical expenses. This usually happens when the surrogate mother is not related to the mother.
On the basis of Embryos:
- Traditional surrogacy: In this method, the surrogate mother carries the child for the full term and delivers it for the couple through artificial insemination. The surrogate mother is the biological mother of the child.
- Gestational surrogacy: In this, the eggs of the mother are fertilized with father’s/donor’s sperm and then the embryo is placed into the uterus of the surrogate. In this case, the biological mother will be the one whose eggs are used and surrogate mother is called the birth mother.
Analysis
Advantages
- Surrogacy allows infertile couples, single people and members of the LGBT community to become parents when they may not be able to have children otherwise.
- In most cases, gestational surrogacy allows one or both parents to be biologically related to their child.
- Surrogacy gives hopeful parents the opportunity to raise a child from birth.
- Intended parents may face fewer restrictions with surrogacy than with adoption; those who cannot adopt due to agency restrictions on factors like age can still pursue surrogacy.
- Surrogates have already carried other pregnancies and have a proven uterus, increasing their chances of successfully carrying a surrogate pregnancy. This may make surrogacy more likely to be successful than fertility treatments for intended parents.
- Surrogacy gives intended parents more control and peace of mind throughout the pregnancy than they usually have with fertility treatments or adoption.
Issues related to Surrogacy in India
- There had been many cases of death related to surrogacy which neither commissioning parents nor the doctors were ready to take responsibility of.
- Sometimes, Indian adoption laws or citizenship laws of some other countries also create problems. For example, Germany gives citizenship by mother; this creates issues in determining the nationality of child.
- There were no strong laws for following issues such as rights of surrogate mother for fair compensation, maternal health care, right to abort etc.
- Question of parentage: In case of three parents for a surrogated child- Each of the donors, surrogate mother, commissioning parents, question of who are the parents, what rights do the children have against each of them, and more largely remained unaddressed.
- The number of times surrogacy is permissible is not clear, consent of married husband is not required.
- Homosexuals and single parents are not allowed to go for surrogate mothers.
- There had been few cases in which commissioning parents left surrogate mother because they did not like the surrogated child.
- There have been instances where girls and women were forced to become surrogate
- There were no rules for medical insurance for issues that could arise in the pregnancy or later, and also the insurance to cover the child’s upbringing if the surrogate mother is abandoned by the legal parents.
- The research states that clinics do not provide the mother with a copy of the contract that is signed by the adoptive parents. In order to escape social stigma, pregnant women often stayed in shelter homes that provided them with lesser security and assistance than required.
- ICMR guidelines (2005) did not set accountability within the agencies indulged in providing surrogate mothers; they did not properly address the issues of sex selection.
Provisions of the recently passed Bill
- It completely abolishes commercial surrogacy. Defining commercial surrogacy as “surrogacy or its related procedures undertaken for a monetary benefit or reward (in cash or kind) exceeding the basic medical expenses and insurance coverage”, this provision is aimed at cracking down on the inside businesses of surrogacy that encourage exploitation.
- It allows only close Indian relatives to be surrogate mothers and purely for “altruistic” reasons. It states an Indian infertile couple, married for five years or more, can go in for ‘altruistic surrogacy’ where the surrogate mother will not be paid any compensation except medical expenses and insurance.
- All surrogacy clinics will have to be registered, the surrogate mother cannot be paid directly and there will be national and state surrogacy boards which will be the regulating authorities for the practice.
- As per the Government, the definition of a close relative will be clearly given in the rules of the Bill.
- Only a defined mother and family can avail of surrogacy and it won’t be permitted for live-in partners or single parents.
Concerns with the bill
- It sets no rules as to how much compensation a surrogate mother can get and should get. According to the CSR report, surrogate mothers are paid $4000-$5000 for bearing the child. Clinics, however, charge the adoptive parents double the money. The reason driving the mothers to surrogacy is usually poverty and lack of education, which further ensures their inability to challenge the exploitation.
- Supreme Court has recently decriminalised Section 377 and the LGBT community has been accepted to be a part of the mainstream. But, in this Bill, there is no mention of same sex couples.
- There is a need to stop “fashion surrogacy” since some celebrities were opting for it as they did not want their figures destroyed.
- The bill does not define who is a close relative.
Way Forward
- In India, people are practicing surrogacy when nearly 12 million several children are orphans. Adoption of a child in India is a complicated and a lengthy procedure for those childless couples who want to give a home to these children. Hence, they are forced to opt for IVF or surrogacy.
- There is a strong need to modify and make the adoption procedure simple as an alternative to surrogacy.
- Surrogacy industry in India is fully grown today. Banning it at this stage may create implementation challenges and push the business underground. A proper law with strict regulations and enforcement which would address the concerns of all stakeholders in the industry is required.
Learning Aid
Practice Question:
India had become a hub of commercial surrogacy wherein surrogate mothers are being exploited. In this light, discuss the issues of surrogacy in India. Also, examine the significance of the recently passed bill in the Parliament banning commercial surrogacy.