Context
TIGER
The tiger is an iconic species. The tiger is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List. As of 2015, the global wild tiger population was estimated to number between 3,062 and 3,948 mature individuals, with most of the populations living in small isolated pockets. India currently hosts the largest tiger population.
TIGER CONSERVATION
Tiger conservation is most crucial for the whole planet for numerous reasons. As a large predator, tiger plays significant role in maintaining the equilibrium of the ecosystem. Tiger along with other predators keeps a check on the herbivore animals, thus help in maintaining the right balance of animals. This in turn checks deforestation. This way with just one tiger several acres of forests can be protected. Apart from the benefits to human beings, tigers and other animals will also get their natural habitat.
Global Tiger Day, often called International Tiger Day, is an annual celebration to raise awareness for tiger conservation, held annually on 29 July. It was created in 2010 at the Saint Petersburg Tiger Summit in Russia
NEED FOR TIGER CONSERVATION
- Barometers of Ecological health: Tigers are indicators of the ecological wellness of planet earth. Being the dominant predators of the ecosystem, they ensure that the numbers of herbivore like deer are kept balanced
- Tiger is an umbrella species whose conservation eventually leads to the conservation of many other species such as the ungulates, pollinators and other small animals.
- Carbon storage value: Poaching or killing of large bodied vertebrates such as tigers results in increase of herbivore population, which in turn results in forests getting decimated
- There is a tremendous decline in the tiger population as compared to the past 100 years and to prevent the deteriorating condition of tigers, it’s important to conserve them.
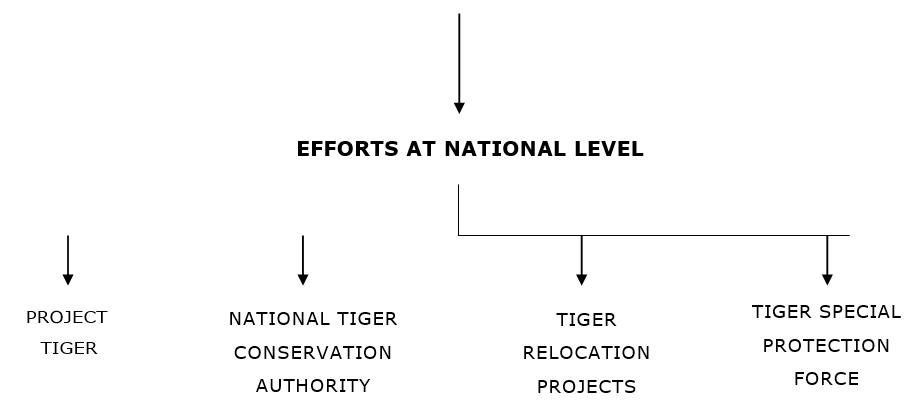
PROJECT TIGER
- Project Tiger was launched in 1973 for conserving our national animal.
- It is a Centrally sponsored scheme of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and climate change.
- The project is administered by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
NATIONAL TIGER CONSERVATION AUTHORITY
- It is a statutory body
- Established in 2005 following the recommendations of the Tiger Task Force.
- It was Established in 2005, following the recommendations of the Tiger Task Force.
- It was given statutory status by the 2006 amendment of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 for strengthening tiger conservation, as per powers and functions assigned to it.
- Funtions under the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change.
TIGER RELOCATION PROJECTS
- The tiger relocation project was initiated in 2018 wherein two big cats, a male (Mahavir) from Kanha Tiger Reserve and a female (Sundari) from Bandhavgarh from Madhya Pradesh were relocated to Satkosia Tiger Reserve in Odisha, to shore up the tiger population in the state.
- The relocation was meant to serve two purposes:
- Reducing tiger population in areas with excess tigers to reduce territorial disputes.
- To reintroduce tigers in areas where the population has considerably reduced due to various reasons.
TIGER SPECIAL PROTECTION FORCE
- It will be effective in checking illegal human intrusion into the reserve through villages located on its fringes and serve as a second layer of protection for tigers
- The decision is in line with Central Government’s guidelines for providing three-tier protection to tigers at reserves
- Three-tier protection to tigers at reserves
1st layer of protection: It is provided in the inner range by beat level forest guards through regular patrols.
2nd layer of protection: It is provided by STPF.
3rd layer of protection: it comes from intelligence-gathering mechanisms in which forest, police and central intelligence agency personnel work together to prevent crimes like the poaching of tigers.
GLOBAL TIGER FORUM
- It is an Inter-Governmental international body working exclusively for the conservation of Tigers.
- Established in 1994, the Global Tiger Forum (GTF) has its headquarters in New Delhi
- The General Assembly of GTF meets after every three years.
- It is a global commitment to double the worlds wild tigers by 2022
- The base year is 2006
- The goal has been set by the world wildlife Fund (WWF) through the Global Tiger Initiative, Global Tiger Forum, and other critical platforms
- All 13 tiger range governments came together for the first time at the Petersburg Summit(Russia- 2010) where they committed to double the number of wild tigers by 2022
GLOBAL TIGER INITIATIVE
- Global Tiger Initiative (GTI) was launched in 2008 as a global alliance of governments, international organizations, civil society, conservation, and scientific communities, and the private sector, with the aim of working together to save wild tigers from extinction.
- In 2013, the scope was broadened to include Snow Leopards.
- The GTI’s founding partners included the World Bank, the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the Smithsonian Institution, the Save the Tiger Fund, and International Tiger Coalition (representing more than 40 non-government organizations).
- The initiative is led by the 13 tiger range countries (TRCs).
INTEGRATED TIGER HABITAT CONSERVATION PROGRAM (ITHCP)
- ITHCP was launched in 2014. It is a strategic funding mechanism that aims to save tigers in the wild, their habitats and to support human populations in key locations throughout Asia.
- It has already facilitated 12 projects in six countries (Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Indonesia, Nepal and Myanmar) to better manage Tiger Conservation Landscapes.
- It is contributing to the Global Tiger Recovery Programme (GTRP), a global effort to double tiger numbers in the wild by 2022.
ST. PETERSBURG DECLARATION
- It aimed at promoting a global system to protect the natural habitat of tigers and raise awareness among people on white tiger conservation
- This resolution was adopted In November 2010, by the leaders of 13 tiger range countries (TRCs) assembled at an International Tiger Forum in Petersburg, Russia
- The resolution’s implementation mechanism is called the Global Tiger Recovery Program whose overarching goal was to double the number of wild tigers from about 3,200 to more than 7,000 by
- 13 Tiger range countries are: Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Russia, Thailand and Vietnam.
TIGER CENSUS IN INDIA
- Every 4 years the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) conducts a tiger census across India.
- The first was conducted in 2006, followed by 2010 and in 2014
- The Census (2014) had reported 2,226 tigers in the country, up from 1,706 in 2010.
- The fourth tiger census (All India Tiger Estimation 2018-19) estimated to be released in May 2019.
Various Methods Used for Counting Tigers
- Pug Mark Method: In this method, the foot print of the tiger is important. It is considered that each pug mark is unique in itself & by analyzing various foot prints in the areas of tigers, the number of tigers in that area can be counted.
- Camera Trap: In this various method, cameras are installed in the tiger areas having night vision facility as By recording various tigers in the camera, the number of tigers can be estimated.
- Poop/scat Method: In this method the number of tigers is counted by poop/scat. The poop is analyzed by DNA sampling and then we can arrive at a more accurate count.
- Radio Collar Method: Tigers are captured in this method & are fitted with a radio In this way the tigers can be counted.
FOURTH TIGER CENSUS 2018
- This 2018 tiger census uses more technology including a mobile app named “MSTrIPES” for the very first time to store information of the counting.
- Another primary focus of the tiger census 2018 is to cover the northeast India that was not included in the previous census.
- For the very first time three neighbouring countries Bhutan, Nepal and Bangladesh are helping in counting the number of tigers all across India, especially in the region with mutual borders.
- Madhya Pradesh saw the highest number of tigers, closely followed by Karnataka and Uttarakhand.
- Chhattisgarh and Mizoram saw a decline in tiger population and all other States saw a “positive” increase.
- Pench Tiger Reserve in Madhya Pradesh recorded the highest number of tigers; Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve in Tamil Nadu registered the “maximum improvement
M-STrIPES
- MSTrIPES program uses Global Positioning System (GPS), General Packet Radio Services (GPRS), and remote sensing, to collect information from the field, create a database using modern Information Technology (IT) based tools, analyses the information using GIS and statistical tools to provide inferences that allow tiger reserve managers to better manage their wildlife resources.
- Forest guards in tiger reserves are equipped with personal digital assistants and GPS devices to capture data relating to tiger sightings, deaths, wild life crime and ecological observations while patrolling.
Challenges in Conservation
Although, we are moving progressively towards conserving more and more tigers, but few threats are still there standing as a resistance in the conservation practices:
- Three tiger reserves of India: Mizoram's Dampa reserve, West Bengal's Buxa reserve and Jharkhand's Palamau reserve have no tigers left.
- The tiger reserves are having a poor interconnectivity with each other due to which the gene exchange among the tiger population can barely take place.
- There has occurred a human-tiger conflict as the tiger conservation practice has grown but their natural habitats are already shrinking and hence, they are seeking their habitat in the human habitation.
- Poaching of tigers is taken as a pride and every part of tiger has a market value therefore they are being hunted indiscriminately for personal as well as commercial purpose.
- The constrained mentality of the local communities regarding tiger poaching as their only job is a major challenge to tiger conservation.
- The linear developments such as that of railways and roadways is a critical issue in creating the conservation ethos.
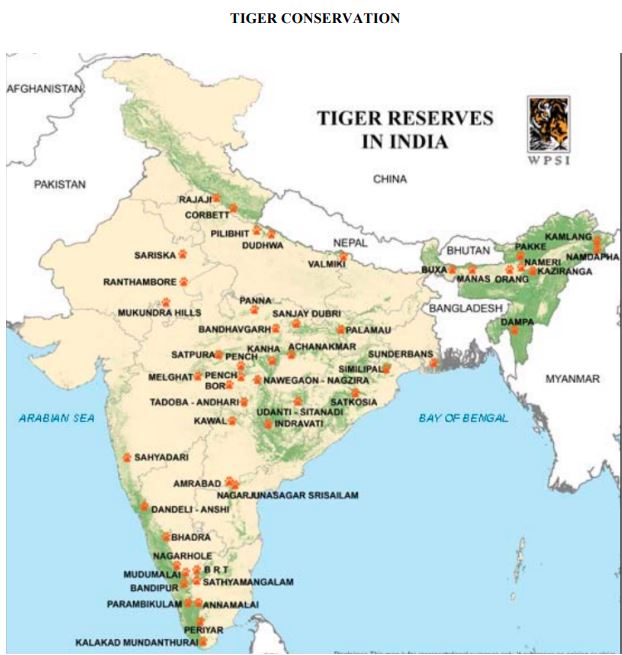
Tiger Reserve Conservation In India
Recently Srivilliputhur Meghamalai Tiger Reserve located in the Nilgiris District of Tamil Nadu state at the tri-junction on of three states, viz, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu was declared the 51st tiger reserve of India.
|
Sl. No. |
Name of Tiger Reserve |
State |
|
1 |
Nagarjunsagar Srisailam |
Andhra Pradesh |
|
2 |
Namdapha |
Arunachal Pradesh |
|
3 |
Kamlang Tiger Reserve |
Arunachal Pradesh |
|
4 |
Pakke |
Arunachal Pradesh |
|
5 |
Manas |
Assam |
|
6 |
Nameri |
Assam |
|
7 |
Orang Tiger Reserve |
Assam |
|
8 |
Kaziranga |
Assam |
|
9 |
Valmiki |
Bihar |
|
10 |
Udanti-Sitanadi |
Chattisgarh |
|
11 |
Achanakmar |
Chattisgarh |
|
12 |
Indravati |
Chhattisgarh |
|
13 |
Palamau |
Jharkhand |
|
14 |
Bandipur |
Karnataka |
|
15 |
Bhadra |
Karnataka |
|
16 |
Dandeli-Anshi |
Karnataka |
|
17 |
Nagarahole |
Karnataka |
|
18 |
Biligiri Ranganatha Temple |
Karnataka |
|
19 |
Periyar |
Kerala |
|
20 |
Parambikulam |
Kerala |
|
21 |
Kanha |
Madhya Pradesh |
|
22 |
Pench |
Madhya Pradesh |
|
23 |
Bandhavgarh |
Madhya Pradesh |
|
24 |
Panna |
Madhya Pradesh |
|
25 |
Satpura |
Madhya Pradesh |
|
26 |
Sanjay-Dubri |
Madhya Pradesh |
|
27 |
Melghat |
Maharashtra |
|
28 |
Tadoba-Andhari |
Maharashtra |
|
29 |
Pench |
Maharashtra |
|
30 |
Sahyadri |
Maharashtra |
|
31 |
Nawegaon-Nagzira |
Maharashtra |
|
32 |
Bor |
Maharashtra |
|
33 |
Dampa |
Mizoram |
|
34 |
Similipal |
Odisha |
|
35 |
Satkosia |
Odisha |
|
36 |
Ranthambore |
Rajasthan |
|
37 |
Sariska |
Rajasthan |
|
38 |
Mukandra Hills |
Rajasthan |
|
39 |
Kalakad-Mundanthurai |
Tamil Nadu |
|
40 |
Anamalai |
Tamil Nadu |
|
41 |
Mudumalai |
Tamil Nadu |
|
42 |
Sathyamangalam |
Tamil Nadu |
|
43 |
Kawal |
Telangana |
|
44 |
Amrabad |
Telangana |
|
45 |
Dudhwa |
Uttar Pradesh |
|
46 |
Pilibhit |
Uttar Pradesh |
|
47 |
Amangarh (buffer of Corbett TR) |
Uttar Pradesh |
|
Corbett |
Uttarakhand |
|
|
48 |
Rajaji TR |
Uttarakhand |
|
49 |
Sunderbans |
West Bengal |
|
50 |
Buxa |
West Bengal |
|
51 |
Srivilliputhur Megamalai |
Tamil Nadu |