

Context
According to a report by the American Cancer Society, deaths due to cancer have declined by 33% in the United States since 1991 attributing the success to early detection, lower rates of smoking, and improvements in cancer treatment.
- This trend is yet to be reflected in India. Even with improvements in treatment, both the incidence of cancer and mortality continue to rise in the country.
About
About the Disease:
- Cancer is a disease in which abnormal cells divide uncontrollably and destroy body tissue.
- It can start almost anywhere in the human body, which is made up of trillions of cells. Normally, human cells grow and divide to form new cells as the body needs them. When cells grow old or become damaged, they die and new cells take their place.
- When cancer develops, this orderly process breaks down. As cells become more and more abnormal, old or damaged cells survive when they should die and new cells form when they are not needed. These extra cells can divide without stopping and forms tumors, which can spread through the blood or the lymph system and form new tumors far from the original tumor.
- Causes of Cancer:
- Biological or internal factors, such as age, gender, inherited genetic defects and skin type.
- Environmental exposure, for instance to radon and UV radiation, and fine particulate matter.
- Occupational risk factors, like carcinogens such as chemicals, radioactive materials and asbestos.
- Lifestyle-related factors.
Cancer Detection:
- The detection should be based on biopsy and histopathological studies of the tissue and blood and bone marrow tests for increased cell counts in the case of leukemias.
- Techniques like radiography (use of X-rays), CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are very useful to detect cancers of the internal organs.
- Antibodies against cancer-specific antigens are also used for detection of certain cancers.
- Techniques of molecular biology can be applied to detect genes in individuals with inherited susceptibility to certain cancers.
Treatment:
- The common approaches for treatment of cancer are surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy and immunotherapy.
- Several chemotherapeutic drugs are used to kill cancerous cells. Some of these are specific for particular tumors. Majority of drugs have side effects like hair loss, anaemia, etc.
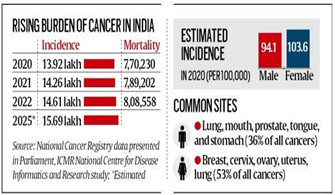
What is the incidence of cancer and mortality in India currently?
- An estimated 14.6 lakh new cancer cases were detected in 2022, up from 14.2 lakh in 2021 and 13.9 lakh in 2020, as per data from the National Cancer Registry of the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) presented in Parliament.
- Deaths due to cancer increased to an estimated 8.08 lakh in 2022 from 7.9 lakh in 2021 and 7.7 lakh in 2020.
- The incidence of all cancers is estimated to increase to 15.7 lakh by 2025, according to the data.
- One in nine Indians will develop cancer during their lifetime, according to an ICMR study using data from population-based cancer registries.
- One in 68 men will develop lung cancer and one in 29 women will develop breast cancer, according to the study.
- The incidence of cancer is higher among women — 103.6 per 100,000 in 2020 compared to 94.1 among men.
- Among men, the most common cancers were of the lung, mouth, prostate, tongue, and stomach; for women, they were breast, cervix, ovary, uterus, lung.
What is the pattern of cancer cases in India?
- The incidence of cervical cancer has dropped in India over the last 50 years from 45 to 10 per 100,000 population
- Rates of cervical cancer have declined because of later marriages, fewer children, better hygiene, and vaccination.
- There is an increase in rates of breast cancer, especially in urban centres.
- And the incidence of breast cancer has gone up because of the same reasons — later age of marriage, having the first child at a later age, not breastfeeding, and a high protein diet.
- The rates of tobacco-related cancers — oral, oesophageal cancers are also coming down.
- This is largely due to tobacco laws that have brought down smoking in public places,
- Lung cancers, however, remain a cause for concern.
- Lung cancer is caused not only by smoking. For example, lung cancer rates are high in Arunachal Pradesh because they light fires indoors in winter.
- Unfortunately, the survival rate for lung cancer is not very high and it is mostly diagnosed in the late stages.
- The cure rate for pancreatic cancer has doubled from 3% 50 years ago to 6%.
Challenges in India:
- In India, most cancer research is carried out in tertiary cancer centres and specialised institutions of biomedical science, against well-developed cancer research networks in high-income countries.
- The rising burden of cancer in India acts as a major drain on research time, particularly for clinical staff. According to estimates, there are only 2,000 cancer specialists in India for 10 million patients. Besides, infrastructure to support cancer research has a long way to go.
- Treatment of cancer is quite expensive and not every patient can afford it. The cost of the drug is around Rs. 50,000-60,000 per month and the duration varies from patient to patient.
Methods to reduce the cancer burden:
- Patients should pay attention to symptoms and get check-ups regularly.
- Advice persons who addicted to tobacco to avoid at any cost. Vaccines also help lower the cancer risk in human.
- Government should cap the prices of cancer medicines as these are very expensive.
- Finally, changes in diets can make big difference in cancer prevention. Eat organic and loading up with good dose antioxidants can help in prevention of cancer.
Government Interventions:
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS)are being implemented under the National Health Mission (NHM). The primary components include awareness generation for cancer prevention, screening, early detection and referral to an appropriate institution for treatment.
- 'Tertiary Care for Cancer’scheme was launched with primary purpose to set up individual units in every state.
- National Tobacco Control Programme is launched to create awareness about the dangerous effects of tobacco consumption, reduce the demand and supply of tobacco products.
- Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi (RAN)was launched to meet the financial demands for cancer treatment
- The recent finding of a drug for breast cancer patients will be able to extend the life duration. The drug has an advantage over chemotherapy and may have less side effects compared to standard treatment.


