

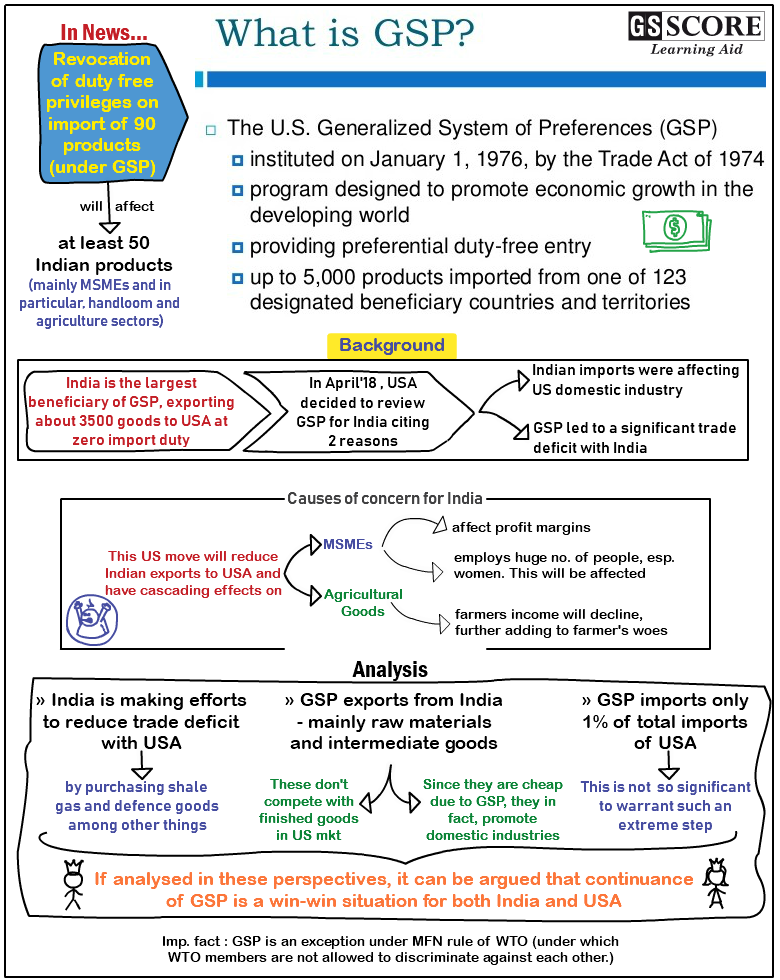
- The Trump administration recently revoked duty-free concessions on import of 90 products of which at least 50 are also Indian products.
- The products which were so far subject to duty-free provisions under the Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) will now be exposed to US tariffs. Such a move is going to cost approximately $241 million to India.
Issue
Context
- The Trump administration recently revoked duty-free concessions on import of 90 products of which at least 50 are also Indian products.
- The products which were so far subject to duty-free provisions under the Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) will now be exposed to US tariffs. Such a move is going to cost approximately $241 million to India.
- USA’s move to cancel concessions for GSP products have come amidst the news of India imposing retaliatory tariffs against 29 American products, although the imposition has been deferred further by more than a month.
About Generalized system of preferences
- The Generalized Scheme of Preferences, or GSP, is a U.S. trade program which provides for a formal system of exemption from the more general rules of the World Trade Organization (WTO).
- It exempts countries from the Most favored nation principle (MFN) that obliges them to treat the imports of all other WTO member countries no worse than they treat the imports of their "most favored" trading partner.
- The GSP, instituted on January 1, 1976, by the Trade Act of 1974, is meant to promote economic development in developing and least developed nations without lowering tariffs for rich countries.
Background
- The recent episode of revoking GSP exemptions has come at a time when international trade is facing protectionism and a threat of an all out trade war among countries.
- Most fierce participants of such a trade war have been US and China with Canada, India and EU too suffering.
- Trade war refers to trade conflicts between countries by imposing higher barriers in form of tariffs or custom duties on importing goods. This is a protectionist practice undermining the principle of free and fair international trade.
- Incidences between trade wars have increased in presidentship of Donald Trump. US has been accusing India of higher import tariffs on Harley Davidson luxury motorcycles. Moreover, India raised tariff for 29 US imported products in response to US duty hike on steel and aluminum.
- US has also imposed sanctions on countries doing trade with Russia lately under the Countering America’s Adversaries through Sanctions Act (CAATSA). Although India might be granted waiver to CAATSA for proceeding procurement of S400 Triumf missile system from Russia.
Analysis
Impact of revoking GSP exemptions
- MSME:
- Given the nature of affected items, small and medium sized businesses are likely to be the worst hit which are already facing competition from cheaper imports and capital financing issues.
- State of Indian exports:
- According to Federation of Indian Exports, the slowdown in global trade due to increasing protectionism will affect the Indian exports negatively.
- Though India runs a trade surplus with US and it exports more to US than what it imports from it, still overall state of Indian exports is expected to worsen.
- Biggest loser:
- India, which gets $5.6 billion duty concessions through the programme, is the largest beneficiary of GSP program.
- Revocation will make it the biggest loser in exports.
- Sector wise impacts:
- Handloom and agricultural sector are most affected by revoking GSP product concessions.
- Such a move can have domino effect on capital formation, employment generation and production by these sectors, negatively affecting overall economy.
- Tightening of visa norms has been another contentious issue between US and India which can also potentially affect Indian IT sector.
- Discriminatory move:
- Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry (FICCI) in a submission to the United States Trade Representative (USTR) has protested against the move.
- According to FICCI, negating tariff concessions violate the objectives of Trade Act of 1974 of furthering the economic development of developing countries.
- Weakening rupee:
- Such an act will deteriorate the already falling rupee vis-à-vis dollar.
- Also, the current account deficit can eventually rise in absence of tariff regulating mechanisms impacting India’s macroeconomic stability.
The recent incident should not be seen as in isolation but a negative fallout of populist tendencies by political leaders and protectionist trade regimes. India and US have been cordial trading partners with India-US bilateral trade growing eightfold from 1991 to the present times standing at $72 billion in 2017. Major trading nations like USA, India, China and EU should bilaterally and multilaterally (via WTO) make amicable decisions to prevent any kind of trade war. Countries should realize that there will be no winner in this war and instead co-operate to make global trade free, fair and sustainable.
Learning Aid
Practice question:
US recently revoked 50 Indian products from tariff concession granted under the Generalized Scheme of Preferences. What is Generalized Scheme of Preferences? In context to the recent incident, discuss the threats posed by trade wars on developing countries like India.


