

Context
The World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) recently published two studies named "Global Annual to Decadal Climate Update 2023-2027" and "State of Global Climate 2022."
Key highlights of the report:
- The WMO has made decadal estimates that between 2023 and 2027, the annual mean global surface temperature will be 1.1–1.8 degrees Celsius higher than the baseline temperature of 1850–1900 or pre-industrial levels.
- The average will surpass 1.5 degrees by 2027, which will mark a turning point beyond which there may be no turning back. In 2022, it was 15 degrees above the baseline.
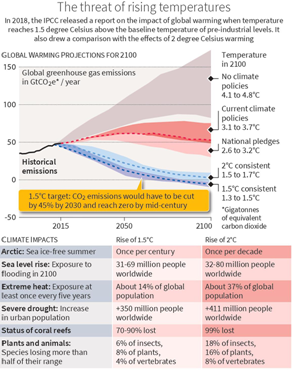
What is the 1.5 degree Celsius target?
- The 1.5 degree Celsius target is a global climate target that aims to limit warming by 2100.
- It was initially seen as unrealistic and unachievable, but was accepted by small island countries.
- In 2010, the Cancun COP16 agreed to limit the global average warming to below 2 degree Celsius.
- In 2015, the Paris Agreement pledged to limit the average temperature rise to below 2 degree, while actively aiming for 1.5 degree above pre-industrial levels.
- This was endorsed as a global target by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in 2018.
Why is the 1.5 degree target critical?
- The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) released a special report in 2018 on the impact of global warming when temperature reaches 1.5 degree Celsius above baseline.
- It estimated that anthropogenic activities would have caused 1 degree of warming, likely to reach 1.5 degree between 2030 and 2052 at the current rate.
- However, regional differences and vulnerability factors make it more urgent for climate action to limit the average planetary warming to 1.5 degree.
Why are we missing the target?
- The Climate Performance Index has shown that developed countries have made little progress in meeting their pledges to reduce GHG emissions.
- Polluters like China, Iran and Saudi Arabia rank low in climate performance.
- The pandemic has pushed the world into a socio-economic crisis, but there is little consideration for building-back in a sustainable manner.
- The Ukraine conflict has further added to the woes and sparked an energy crisis, threatening climate goals.
Are extreme weather events linked to the global rise in temperature?
- Effect of Heat Wave: The most important details in this text are the predictions of precipitation anomalies and an increase in marine heat waves, the El Nino, the shrinking cryosphere, and the melting of the Greenlandic ice sheet.
- Climate Change: Climate risks and hazards impact human population and the ecosystem, such as food insecurity, displacement, and deaths.
- Food Scarcity: Climate change has been affecting crop yield negatively and the risks posed by agricultural pests and diseases have also increased.
- Countries like Ethiopia, Nigeria, South Sudan, Somalia, Yemen, and Afghanistan are facing acute food shortages due to the complex interaction of climate conditions with other factors such as droughts, cyclones, and political and economic instability.
- Extreme Weather Anomalies: It caused the deaths of two million people and incurred $4.3 trillion in economic damages over the past fifty years. In 2020-2021, 22,608 disaster deaths were recorded globally.
How is India impacted?
- India has been facing the brunt of climate change, with February 2023 being the hottest month since record-keeping began in 1901. Last year, Indian monsoons were wetter than usual, leading to wildfires and acute food shortages.
- India is attempting to balance its development needs with ongoing climate action both at the domestic and international levels.
- Reducing Emissions: Domestic measures such as the Green Hydrogen Mission and the introduction of green bonds are performing fairly well despite contributing only a miniscule to cumulative GHG emissions.
- Efforts: At the international level, India can prove to be a responsible climate player through the International Solar Alliance and Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure.
- Target: The 1.5 degree Celsius target is the global climate target that aims to limit warming to said level by 2100, to prevent the planet from slipping into further climate crises.
- Climate risks and hazards impact human population and the ecosystem depending on exposure, vulnerability, and adaptive capacity, and have exacerbated food insecurity, displacement, and deaths.
|
According to the Climate Change Performance Index 2023, India ranked eighth with a high-performance after Denmark, Sweden, Chile, and Morocco. |


