Context
In a joint statement, permanent members of the UN Security Council (UNSC) pledge to ensure a nuclear war is never fought, amid rising world tensions.
Background
- Nuclear weapons are the most dangerous weapons on earth. One can destroy a whole city, potentially killing millions, and jeopardizing the natural environment and lives of future generations through its long-term catastrophic effects.
- The dangers from such weapons arise from their very existence.
- Although nuclear weapons have only been used twice in warfare—in the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945—about 13,400 reportedly remain in our world today and there have been over 2,000 nuclear tests conducted to date.
- Thus, disarmament is the best protection against such dangers. However, achieving this goal has been a tremendously difficult challenge.
|
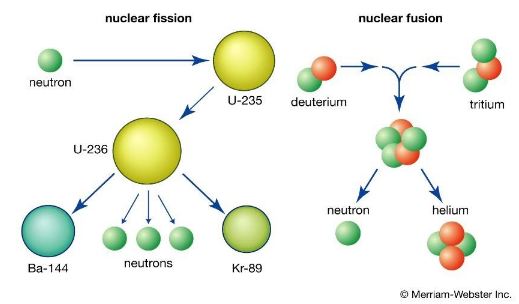
The weapon of destruction Nuclear bombs are weapons of mass destruction. They harness the forces that hold the nucleus of an atom together by using the energy released when the particles of the nucleus (neutrons and protons) are either split or merged. Types of Nuclear Energy
Atomic Bomb
|
Analysis
Important Treaties to prevent nuclear proliferation
- The United Nations has sought to eliminate such weapons ever since its establishment. The first resolution adopted by the UN General Assembly in 1946 established a Commission to deal with problems related to the discovery of atomic energy among others.
- A number of multilateral treaties have been established since then. These include the
- Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT)
- Treaty Banning Nuclear Weapon Tests In The Atmosphere, In Outer Space And Under Water, also known as the Partial Test Ban Treaty (PTBT)
- Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT), which was signed in 1996 but has yet to enter into force
- Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW)
- Other initiatives include:
- the Nuclear Suppliers Group
- the Missile Technology Control Regime
- the Hague Code of Conduct against Ballistic Missile Proliferation
- the Wassenaar Arrangement
Key-highlights of the Statements
- The statement said that the United States, United Kingdom, Russia, China and France – who are the permanent members of the United Nations Security Council – consider it their primary responsibility to avoid war between the nuclear states and to reduce strategic risks, while aiming to work with all countries to create an atmosphere of security.
- They believe strongly that the further spread of such weapons must be prevented.
- A nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.
- The statement also stressed the importance of preventing conflict between nuclear-weapon states from escalating, describing it as a "foremost responsibility."
- The joint pledge was issued ahead of what was to be the latest review of the Treaty of the Non-proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT).
- The five pledged to adhere to the 1970 Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty (NPT) which obligates them "to pursue negotiations in good faith on effective measures relating to cessation of the nuclear arms race at an early date and to nuclear disarmament."
|
Non-proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT)
|
What can be the reason behind the statement?
- The statement comes as tensions between the world powers have risen to heights rarely seen in recent decades.
- In Europe, Russia is massing troops along its border with Ukraine, raising alarms in Washington, London and Paris.
- And in Asia, increased Chinese military activity around the self-governed island of Taiwan has spiked tensions between Beijing and Washington and its Pacific allies.
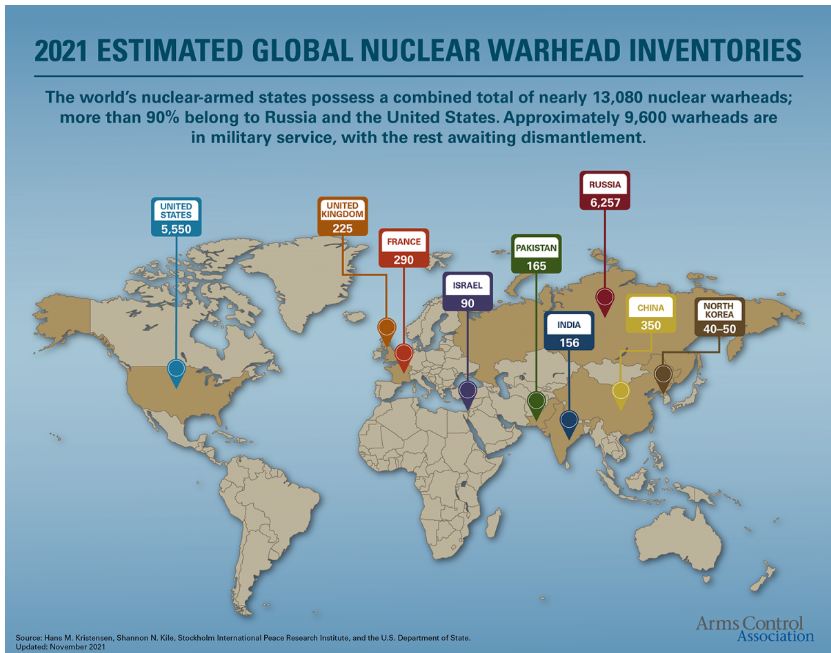
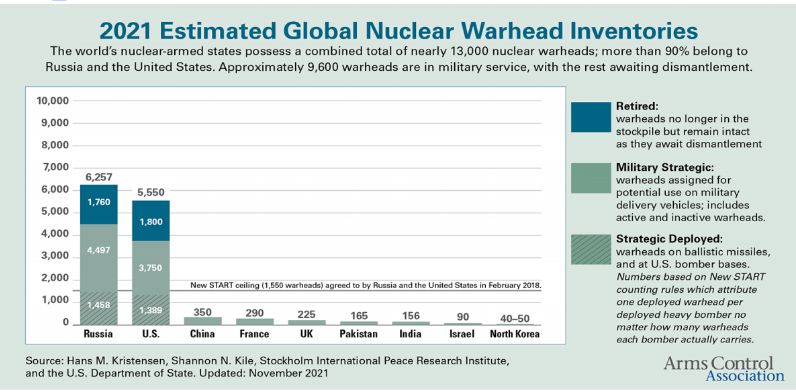
Who has what at a Glance (nuclear weapons)?
- The nuclear-weapon states (NWS) are the five states—China, France, Russia, United Kingdom, and the United States—officially recognized as possessing nuclear weapons by the NPT.
- Russia is believed to have the world's biggest stockpile of nuclear warheads, with 6,255, followed closely by the United States at 5,550, according to the Arms Control Association (ACA).
- China (350), France (290) and the UK (225) round out the top five.
|
The numbers
|
Significance of the pledge
- Confidence enhancement: The agreement will “help build confidence and form the foundations of future control over offensive and defensive arms”.
Building trust and reducing conflicts: The pledge will “increase mutual trust” and reduce the risk of nuclear conflict.