According to scientists weakening of AMOC could have drastic consequences on global climate.
Context
According to scientists weakening of AMOC could have drastic consequences on global climate.
About
What is Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)?
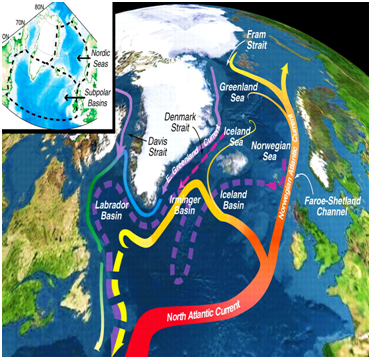
- The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is a large system of ocean currents that carry warm water from the tropics northwards into the North Atlantic.
- AMOC ensures the oceans are continually mixed, and heat and energy are distributed around Earth.
How does the AMOC work?
- The AMOC is a large system of ocean currents, like a conveyor belt, driven by differences in temperature, salt content and the water’s density.
- As warm water flows northwards it cools and some evaporation occurs, which increases the amount of salt. Low temperature and a high salt content make the water denser, and this dense water sinks deep into the ocean.
- The cold, dense water slowly spreads southwards, several kilometres below the surface. Eventually, it gets pulled back to the surface and warms in a process called “upwelling” and the circulation is complete.
Has the AMOC been changing?
- For thousands of years, AMOC has remained stable, but since the past 15 years, it has been weakening which could have dramatic consequences for Europe and other parts of the Atlantic rim.
- Indirect evidence (for example from sediments on the sea floor) shows that there have been some large, rapid changes in the AMOC in the past (for example around the end of the last ice age).
What will be the effect of climate change on the AMOC?
- Climate models suggest that the AMOC will weaken over the 21stCentury as greenhouse gases increase. This is because as the atmosphere warms, the surface ocean beneath it retains more of its heat.
- All these changes make the ocean water lighter and so reduce the sinking in the ‘conveyor belt’, leading to a weaker AMOC. So the AMOC is very likely to weaken, but it’s considered very unlikely that large, rapid changes in the AMOC, as seen in past times, will happen in the 21st
- A weaker AMOC will bring less warm water northwards, and this will partly offset the warming effect of the greenhouse gases over Western Europe.
What is the role of Indian Ocean?
- As the Indian Ocean warms faster and faster, it generates additional precipitation. This draws more air from other parts of the world to the Indian Ocean, including the Atlantic.
- With so much precipitation in the Indian Ocean, there will be less precipitation in the Atlantic Ocean. Less precipitation will lead to higher salinity in the waters of the tropical portion of the Atlantic because there won’t be as much rainwater to dilute it.
- This saltier water in the Atlantic, as it comes north via AMOC, will get cold much quicker than usual and sink faster.