Context
Recently, the NTPC Vindhyachal in Madhya Pradesh limited has taken an initiative to capture the carbon as electricity production by coal accounts for 40% of the CO2 emissions.
About
- India stands third among the GHG-emitting countries in the world, emitting 2,310 megatons of CO2 in 2019.
- These scenarios necessitate the mitigation of GHG reduction in the country to combat the effects of climate change.
- The pioneer project of a carbon capture plant installed in NTPC Vindhyachal is in line with this, which is designed to capture 20 tonnes of CO2 per day.
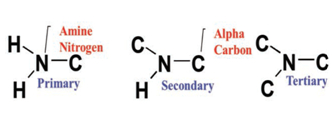
- It uses modified ‘tertiary amine’ to capture CO2 from flue gas from fossil-fired power plants, with a purity of more than 99 per cent.
- Tertiary amine (3oamine): An amine in which the nitrogen atom is directly bonded to three carbons of any hybridization which cannot be carbonyl group carbons.
- CO2 will eventually be integrated with hydrogen to produce 10 tonnes of methanol per day through a catalytic hydrogenation process.
|
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum.
|
- Currently, there are no Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS) projects in the pipeline in power plants for carbon capture in India.
The Carbon capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS) Technique:
- Carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS), also referred to as carbon capture, utilization and sequestration, is a process that captures carbon dioxide emissions from sources like coal-fired power plants and either reuses or stores it so it will not enter the atmosphere.
- Carbon dioxide storage in geologic formations includes oiland gas reservoirs, un-mineable coal seams and deep saline reservoirs -- structures that have stored crude oil, natural gas, brine and carbon dioxide over millions of years.
- The Energy Department supports research and development of tools to assess the environmental fitness and predictability of future capacity within -- proposed geologic storage sites.