

Context
Recently, a Task Force and an Expert Committee have been constituted by the Ministry of Coal to prepare the roadmap for coal-based hydrogen production.
About
About Task Force on coal-based hydrogen production
- It is constituted under the Chairmanship of Additional Secretary Coal Shri Vinod Kumar Tiwari.
- The broad terms of reference of the Task Force are as follows:
- Identification of role to be played by each stakeholder Ministry
- Coordination with Stakeholder Ministries
- Monitoring of activities towards achieving coal based Hydrogen production and usage
- Setting up sub committees to achieve the objective
- To coordinate with Coal Gasification Mission and NITI Aayog
About Expert Committee on coal-based hydrogen production
- The Expert Committee is set up under the chairmanship of Shri R.K. Malhotra.
- The broad terms of reference of Expert Committee are as follows:
- Identifying experts in India and co-opting as members
- Desk based review of progress in hydrogen technology and also review ongoing research projects in Hydrogen technology
- Coordinate with various national/international technology institutions in hydrogen
- Prepare a road map for coal based Hydrogen production and usage including economic viability, environmental sustainability and policy enablers required
- Identifying activities for implementation of coal based hydrogen production and usage
- Assisting Task force in implementation of Coal based Hydrogen production and usage
Need for Coal-based Hydrogen Production
- Coal is an important source of hydrogen making (brown hydrogen) along with the production of natural gas (grey hydrogen) and renewable energy (green hydrogen) through electrolysis.
- The surplus solar power is used to electrolyze water into hydrogen and oxygen in case of renewable energy (green hydrogen).
- Globally, 73 MT Hydrogen is used for refining, ammonia making and other pure use and about 42 MT is used for Methanol, steel making and other mixed uses.
- The experts believe that the cost of hydrogen produced from coal can be cheaper and less sensitive to imports when compared with hydrogen production through electrolysis and Natural Gas respectively.
- The Indian Coal Reserve could become a great source of hydrogen when the carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide formed during coal to hydrogen process are trapped and stored in an environmentally sustainable manner (CCS and CCUS).
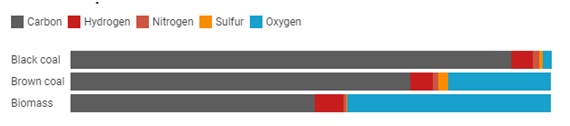
Composition of Coal
- It is a mixture of two components i.e.
- Carbon-based matter (the decayed remains of prehistoric vegetation); and
- Mineral matter (which comes from the ground from which the coal is dug).
- The carbon-based matter is composed of five main elements i.e. carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur.
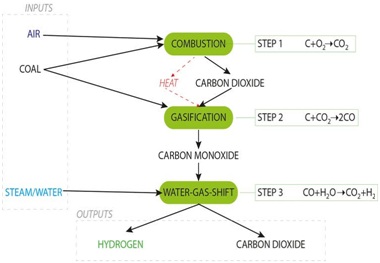
Process involved in production in coal-based hydrogen
- The process of coal-based production of hydrogen starts with partial oxidation which implies that some air is added to the coal, which generates carbon dioxide gas through traditional combustion.
- The air is added to coal to make some heat for the gasification reaction and the partial oxidation also makes its own gasification agent i.e. carbon dioxide.
- Carbon dioxide reacts with the rest of the carbon in the coal to form carbon monoxide which is an endothermic gasification reaction but no hydrogen is produced yet.
- Carbon monoxide in the gas stream is now further reacted with steam and results in generation of hydrogen and carbon dioxide.
- The hydrogen can then be run through an on-site fuel cell to generate high-efficiency electricity.
- The hydrogen can then be run through an on-site fuel cell to generate high-efficiency electricity.
|
Why Brown Coal is preferred for gasification?
What is Carbon Capture and Storage?
What is Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS)?
|


