

US President Donald Trump has questioned ‘Developing Tag’ for India and China.
Context
US President Donald Trump has questioned ‘Developing Tag’ for India and China.
About
World Trade Organization (WTO)
- It is a successor to the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) established in the wake of the Second World War.
- Several rounds of negotiations were held under GATT.
- WTO came into existence in Uruguay Rounds of 1986-1994 through Marrakesh Agreement in 1995.
- Members – 164 and together, they constitute 98% of the global trade
- In 2000, 4th WTO Ministerial led to a new round of negotiation, Doha Development Agenda, which is still in progress.
- Mandate – to open trade for the benefit for all
- All decisions are made by consensus.
- WTO Headquarters is in Geneva, Switzerland. It has no other branch office.
- Ministerial Conference is WTO’s top level decision making body. It meets once in two years.
- WTO Agreements
- For Goods – Marrakesh Agreement (1995) and Trade Facilitation Agreement ( 2017)
- For Services – General Agreement on Trade in Services
- For Intellectual Property - The Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS)
- Functions
- Administering WTO Trade Agreement
- Act as forum for trade negotiation
- Handling trade disputes
- Monitoring trade policies
- Cooperation with other international organization
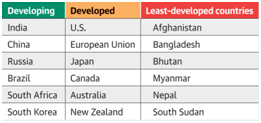
Criteria for Developing, Developed and Least Developed Countries
- There are no WTO definitions of “developed” and “developing” countries.
- Members announce for themselves whether they are “developed” or “developing” countries.
- However, other members can challenge the decision of a member to make use of provisions available to developing countries.
Advantages for Developing Members:
The special provisions include:
- longer time periods for implementing Agreements and commitments,
- measures to increase trading opportunities for developing countries,
- provisions requiring all WTO members to safeguard the trade interests of developing countries,
- support to help developing countries build the capacity to carry out WTO work, handle disputes, and implement technical standards, and
- Provisions related to least-developed country (LDC) Members.

