

Context
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has discovered the farthest star ever seen to date.
About
About the star:
- The star is more than 9 billion light-years away.
- It is likely existed within the first billion years after the beginning of the universe.
- The star system is officially called WHL0137-LS.
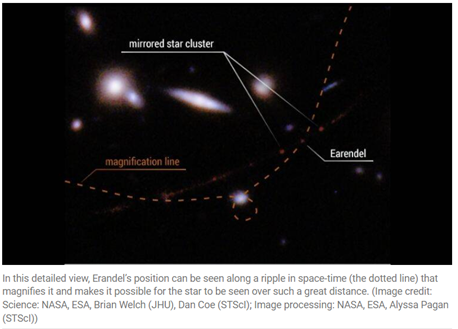
- It has been nicknamed “Earendel”, which means “morning star” in Old English.
Other record-holding star:
- Icarus:
- This discovery is a massive leap from the previous record-holding star: “Icarus” or officially, MACS J1149+2223 Lensed Star 1.
- Icarus existed at a time when the universe was about 4 billion years old or about one-third of its current age, at a time that astronomers refer to as “redshift 1.5.”
- Scientists use the word “redshift” because as the universe expands, light from distant objects is stretched or “shifted” to longer, redder wavelengths as it travels toward us.
- The oldest known star, nicknamed “Methuselah,” discovered by Hubble in 2013.
- Hubble also holds the cosmic distance record for a galaxy. Its light took 13.4 billion years to reach Earth.
What made such farthest star visible?
- It happened because of phenomenon of gravitational lensing.
- Gravitational lensing occurs when a cluster of stars warps the fabric of space.
- This creates a sort of massive magnifying glass that distorts and amplifies the light from distant objects behind it.
- In the case of Earendel, this is caused by a huge galaxy cluster called WHL0137-08.
- Scientists expect Earendel to remain highly magnified in the years to come when it can be observed by NASA’s new James Webb Space Telescope.
- Webb has a high sensitivity to infrared light which will be useful when trying to learn more about the newly-discovered star because its light is redshifted to longer infrared wavelengths.
|
Hubble Space Telescope
|


