

Context
A group of scientists and the activists have warned to Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) by writing regarding the adverse impacts on health and livelihoods and oppose the central government’s plan against mandatory fortification of food items.
What are Fortified foods?
- These are those that have nutrients added to them that don’t naturally occur in the food.
- These foods are meant to improve nutrition and add health benefits.
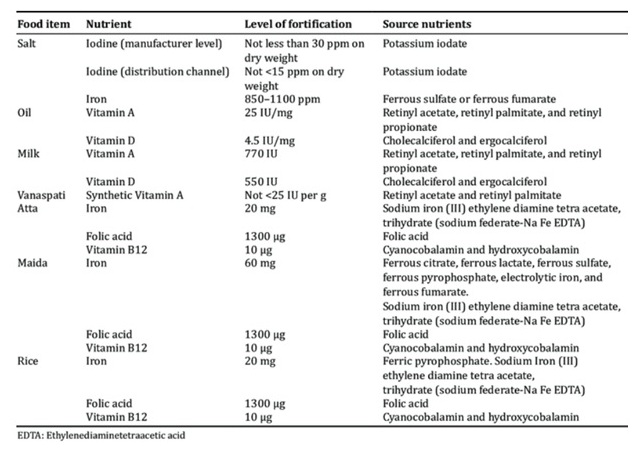
- Fortification adds the key vitamins and minerals such as Iron, Iodine, Zinc, Vitamins A & D to the staple foods such as rice, wheat, oil, milk, and salt to improve their nutritional content.
Why the fortification is required for India?
- India has a very high burden of micronutrient deficiencies of Vitamin A, Iodine, Iron, and Folic Acid that leads to Night Blindness, Goitre, Anaemia and various birth defects. According to the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-4)
- 4 % of children (6-59 months) are anemic
- 1 %of women in the reproductive age group are anemic
- 7 % of children under 5 are underweight
Concerns about the food fortification
- Mandatory fortification can lead to hypervitaminosis
- Nutrients don’t work in isolation but need each other for optimal absorption
- This will lead to monotonous cereal-based diets with low consumption of vegetables and animal protein
- To promote fortification FSSAI relies on food companies who would benefit from it, leading to conflicts of interest.
- Mandatory fortification would harm a vast informal economy of Indian farmers and instead benefit a small group of multinational corporations
|
Regulation of food fortification in India
|

