

Context
Eugene Parker, a physicist who theorized the existence of solar wind and became the first person to witness the launch of a spacecraft bearing his name, has died recently.
About
About Physicist Eugene Parker:
- He is hailed as a visionary in his field of heliophysics, focused on the study of the sun and other stars.
- He is best known for his 1958 theory of the existence of solar wind — a supersonic flow of particles off the sun's surface.
- He was vindicated in 1962 when a NASA spacecraft mission to Venus (NASA's Mariner 2 spacecraft) confirmed his theory and solar wind's effect on the solar system, including occasional disruptions of communications systems on Earth.
- NASA honoured Mr. Parker's scientific contributions in 2018 by naming a spacecraft after him that was destined to travel straight into the sun's crown.
- Thus, he became the first person to witness the launch of a spacecraft bearing his name, NASA's Parker Solar Probe.
About Solar wind:
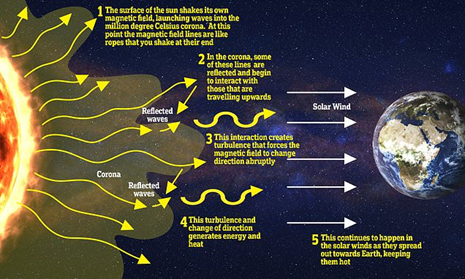
- The surface of the sun is blisteringly hot at 6,000 degrees Fahrenheit—but its atmosphere, called the corona, is more than a thousand times hotter.
- The corona is so hot that the sun’s gravity can’t hold it, so particles are flung off into space and travel throughout the solar system in every direction.
- As the sun spins, burns and burps, it creates complex swirls and eddies of particles.
- These particles, mostly protons and electrons, are traveling about a million miles per hour as they pass Earth.
- This flow of particles, called the “solar wind”.
Effects of solar wind – Aurora
- An aurora is a natural light display in the sky, predominantly seen in the high latitude (Arctic and Antarctic) regions. (This is due to magnetic field lines of earth and solar wind)
- Auroras are caused by charged particles, mainly electrons and protons, entering the atmosphere from above causing ionisation and excitation of atmospheric constituents, and consequent optical emissions.

Impact on Earth:
Solar wind has an enormous impact on our lives.
- The solar wind magnetically blankets the solar system, protecting life on Earth from even higher-energy particles coming from elsewhere in the galaxy.
- But the effects of storms on the sun’s surface can also affect our telecommunications networks.
- The wind would also pose a threat to astronauts traveling through space.
|
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe:
|


