Ministry of Environment and Forests and Climate Change (MoEFCC), in collaboration with the World Bank has released a joint report on forest fire management titled “Strengthening Forest Fire Management in India.”
Context
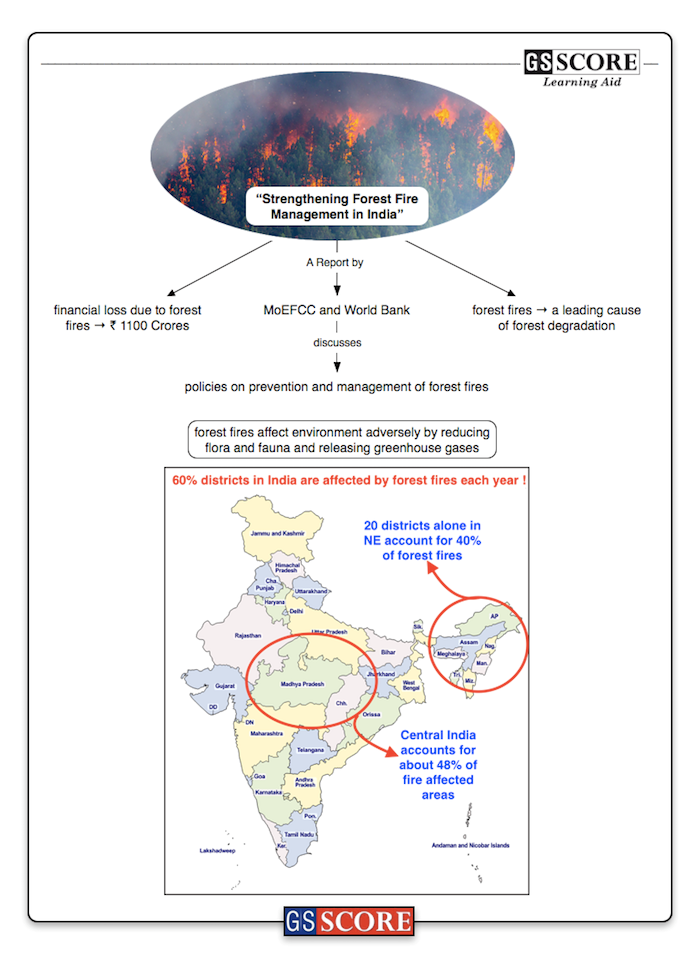
Ministry of Environment and Forests and Climate Change (MoEFCC), in collaboration with the World Bank has released a joint report on forest fire management titled “Strengthening Forest Fire Management in India.”
About
- The report discusses policies on forest fire prevention and management (FFPM) at the national, state and local levels, underscoring the need for a comprehensive national policy and guidelines.
- It provides recommendations on five broad themes – policy, institutions and capacity, community engagement, technology, and data and information and looks at national and international best practices in FFPM.
- According to the report, forest fires are today a leading cause of forest degradation in India.
- 60% districts in India are affected by forest fires each year. Just 20 districts, majority of them located in Northeast India, account for over 40% of all forest fires detected between 2003 and 2016.
- Central India has the largest area affected by forest fire. It accounts for about 48% of total fire-affected area, while having just 12% of the country’s forest cover in the year 2000 and 7% of its land area.
- Report puts financial loss at national level due to forest fires every years at INR 1,100 crore. It is a worrisome finding since at least one in four people in the country are dependent on forests for their livelihood.
Significance
Repeated fires in short succession in the country are reducing diversity of species and harming natural regeneration, while posing a risk to over 92 million who live in areas of forest cover. It also contributes to climate change by releasing carbon stored in trees, undergrowth and soil into the atmosphere. In this context, the findings of the report are significant since preventing forest fires is crucial for India as the country has committed to bringing 33% of its geographical area under forest cover by 2030, as part of NDCs. The report calls for a national plan for the prevention of forest fire.
|
India's Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs)
|
Learning Aid