Union Minister for Home Affairs, Amit Shah chaired the 29th meeting of the Northern Zonal Council held at Chandigarh.
Context
Union Minister for Home Affairs, Amit Shah chaired the 29th meeting of the Northern Zonal Council held at Chandigarh.
About
What are Zonal councils?
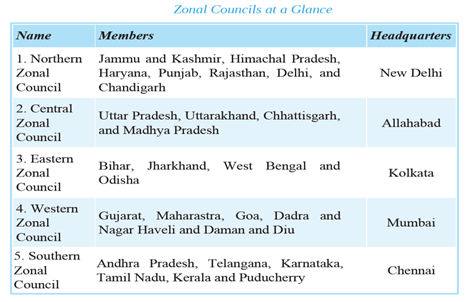
- The Zonal Councils are the statutory (and not the constitutional) bodies. They are established by an Act of the Parliament, that is, States Reorganisation Act of 1956.
- The act divided the country into five zones (Northern, Central, Eastern, Western and Southern) and provided a zonal council for each zone.
- North-Eastern Council:
- In addition to the above Zonal Councils, a North-Eastern Council was created by a separate North-Eastern Council Act of 1971.
- Its members include Assam, Manipur, Mizoram, Arunchal Pradesh, Nagaland, Meghalaya, Tripura and Sikkim.
The factors that have been taken into account during formation of Zonal Councils:
- The natural divisions of the country.
- The river systems and means of communication.
- The cultural and linguistic affinity.
- The requirements of economic development, security and law and order.
Members of the Zonal council:
- Home minister of Central government.
- Chief Ministers of all the States in the zone.
- Two other ministers from each state in the zone.
- Administrator of each union territory in the zone.
- The home minister of Central government is the common chairman of the five zonal councils.
- Each chief minister acts as a vice-chairman of the council by rotation, holding office for a period of one year at a time.
- Advisers - One person nominated by the Planning Commission for each of the Zonal Councils, Chief Secretaries and another officer/Development Commissioner nominated by each of the States included in the Zone.
- Union Ministers are also invited to participate in the meetings of Zonal Councils depending upon necessity.
What makes Zonal Councils different from institutions like the National Development Council, Inter State Council?
- Zonal Councils are regional fora of cooperative endeavour for States linked with each other economically, politically and culturally.
- Being compact high level bodies, specially meant for looking after the interests of respective zones, they are capable of focusing attention on specific issues taking into account regional factors, while keeping the national perspective in view.
- The Zonal Councils provide an excellent forum where irritants between Centre and States and amongst States can be resolved through free and frank discussions and consultations.
Objectives of Zonal Councils:
- Bringing out national integration.
- Arresting the growth of acute State consciousness, regionalism, linguism and particularistic tendencies.
- Enabling the Centre and the States to co-operate and exchange ideas and experiences.
- Establishing a climate of co-operation amongst the States for successful and speedy execution of development projects.
Functions of the Zonal Councils:
Each Zonal Council is an advisory body and may discuss any matter in which some or all of the States represented in that Council, or the Union and one or more of the States represented in that Council, have a common interest and advise the Central Government and the Government of each State concerned as to the action to be taken on any such matter.
In particular, a Zonal Council may discuss, and make recommendations with regard to:
- Any matter of common interest in the field of economic and social planning.
- Any matter concerning border disputes, linguistic minorities or inter-State transport.
- Any matter connected with or arising out of, the re-organization of the States under the States Reorganisation Act.