

5th August 2022 (4 Topics)
Context
New Delhi is working through diplomatic channels to fetch an entry into a new US-led partnership initiative called the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP).
About
Minerals Security Partnership (MSP):
- It will focus on the supply chains of minerals such as Cobalt, Nickel, Lithium and also the 17 ‘rare earth’ minerals.
- The alliance is seen as primarily focused on evolving an alternative to China, which has created processing infrastructure in rare earth minerals and has acquired mines in Africa for elements such as Cobalt.
- Goal: The goal of the MSP is to ensure that critical minerals are produced, processed, and recycled in a manner that supports the ability of countries to realize the full economic development benefit of their geological endowments.
- Partners: The US and 10 partners — Australia, Canada, Finland, France, Germany, Japan, the Republic of Korea (South Korea), Sweden, the United Kingdom, and the European Commission — have come together to form the MSP.
- The new grouping is aimed at catalysing investment from governments and the private sector to develop strategic opportunities.
- Need: Demand for critical minerals, which are essential for clean energy and other technologies, is projected to expand significantly in the coming decades.
- The MSP will help catalyse investment from governments and the private sector for strategic opportunities — across the full value chain — that adhere to the highest environmental, social, and governance standards.
What are rare earth elements?
- Rare earth elements include wind turbine magnets, solar cells, smart phone components, cells used in electric vehicles, among others.
- The 17 Rare Earths are cerium (Ce), dysprosium (Dy), erbium (Er), europium (Eu), gadolinium (Gd), holmium (Ho), lanthanum (La), lutetium (Lu), neodymium (Nd), praseodymium (Pr), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), scandium (Sc), terbium (Tb), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb), and yttrium (Y).
- REEs are classified as light RE elements (LREE) and heavy RE elements (HREE).
- Some REEs are available in India — such as Lanthanum, Cerium, Neodymium, Praseodymium and Samarium, etc.
- Others such as Dysprosium, Terbium, and Europium, which are classified as HREEs, are not available in Indian deposits in extractable quantities.
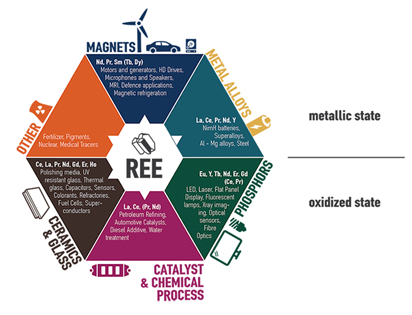
Usage:
- Electronic technologies: These elements are important in technologies of consumer electronics, computers and networks, communications, clean energy, advanced transportation, healthcare, environmental mitigation, and national defence, among others.
- Scandium is used in televisions and fluorescent lamps, and yttrium is used in drugs to treat rheumatoid arthritis and cancer.
- Defence equipments: While Rare Earth elements are used in building consumer electronics, in healthcare and transportation, they are especially important for governments because of their use in manufacturing defence equipment.
- Space: Rare Earth elements are used in space shuttle components, jet engine turbines, and drones.
- Cerium, the most abundant Rare Earth element, is essential to NASA’s Space Shuttle Programme.
What is India’s major concern at this moment?
- If India is not able to explore and produce these minerals, it will have to depend on a handful of countries, including China, to power its energy transition plans to electric vehicles. That will be similar to our dependence on a few countries for oil.


