

21st September 2022 (7 Topics)
Context
A wild Arctic wolf was successfully cloned for the first time in the world by a Beijing-based gene firm.
About
- Cloned Arctic wolf is the first case of its kind in the world. It is named Maya.
- The donor cell of the wolf came from the skin sample of a wild female Arctic wolf and its oocyte was taken from a female dog.
- Maya’s surrogate mother was a beagle, a dog breed.
- The dog was selected as the surrogate as it shares genetic ancestry with ancient wolves and hence, ensures success in cloning.
About Cloning:
- The term cloning describes a number of different processes that can be used to produce genetically identical copies of a biological entity.
- The copied material, which has the same genetic makeup as the original, is referred to as a clone.
- Researchers have cloned a wide range of biological materials, including genes, cells, tissues and even entire organisms, such as a sheep.
- Natural clones, also known as identical twins, occur in humans and other mammals.
- These twins are produced when a fertilized egg splits, creating two or more embryos that carry almost identical DNA.
- Identical twins have nearly the same genetic makeup as each other, but they are genetically different from either parent.
- There are three different types of artificial cloning: gene cloning, reproductive cloning and therapeutic cloning.
-
- Gene cloning produces copies of genes or segments of DNA.
- Reproductive cloning produces copies of whole animals.
- Therapeutic cloning produces embryonic stem cells for experiments aimed at creating tissues to replace injured or diseased tissues.
- Gene cloning, also known as DNA cloning, is a very different process from reproductive and therapeutic cloning. Reproductive and therapeutic cloning shares many of the same techniques, but is done for different purposes.
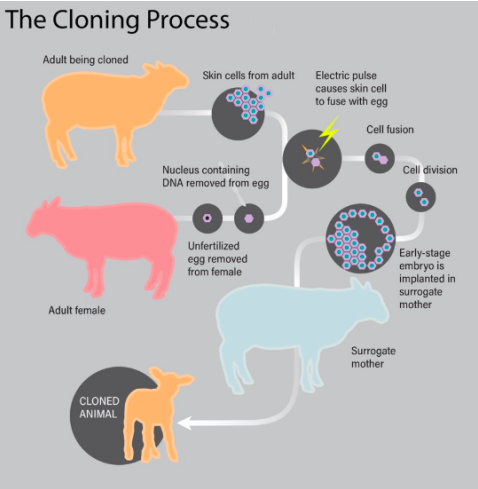
- In 1996, Scottish scientists cloned the first animal, a sheep they named Dolly. She was cloned using an udder cell taken from an adult sheep.
How are animals cloned?
- In reproductive cloning, researchers remove a mature somatic cell, such as a skin cell, from an animal that they wish to copy.
- They then transfer the DNA of the donor animal's somatic cell into an egg cell, or oocyte, that has had its own DNA-containing nucleus removed.
- Researchers can add the DNA from the somatic cell to the empty egg in two different ways.
- In the first method, they remove the DNA-containing nucleus of the somatic cell with a needle and inject it into the empty egg.
- In the second approach, they use an electrical current to fuse the entire somatic cell with the empty egg.
- In both processes, the egg is allowed to develop into an early-stage embryo in the test-tube and then is implanted into the womb of an adult female animal.
- Ultimately, the adult female gives birth to an animal that has the same genetic makeup as the animal that donated the somatic cell.
- This young animal is referred to as a clone. Reproductive cloning may require the use of a surrogate mother to allow development of the cloned embryo, as was the case for the most famous cloned organism, Dolly the sheep.
More Articles


