

24th May 2023 (6 Topics)
Context
- Recently, the White House and Republicans in Congress are in a standoff over US government borrowings.
Key highlights:
- The US government made the decision following Treasury Secretary Warnings of an "unprecedented economic and financial storm" and yet another meeting with Republican counterparts to reach an agreement on the US debt ceiling.
- Without lifting the debt ceiling, the US government will default on its obligations, a historic first with potentially disastrous implications.
- Furloughs would be issued to federal employees, worldwide stock markets would plummet, and the US economy would very certainly enter a recession.
What is the debt ceiling?
- The debt ceiling is the limit on the amount of money the US government can borrow to pay for services, such as social security, Medicare and the military.
- The deficit left at the end of the year is tacked on to the country’s total debt.
- Congress is in charge of setting the debt limit, which currently stands at $31.4tn.
- The ceiling has been raised 78 times since 1960, under both Democrat and Republican presidents.
- At times, the ceiling was briefly suspended and then reinstated at a higher limit, a retroactive raising of the debt ceiling.

What happens if the US defaults?
- The US has never defaulted on its payments before, so what will happen is unclear.
- Investors would lose faith in the US dollar, job cuts would be imminent, and the US federal government would not have the means to continue all its services.
- Mortgage rates would likely soar, tanking the housing market.
Why is the US debt so high?
- The US debt grows when the government is spending more money or when its revenue is lower.
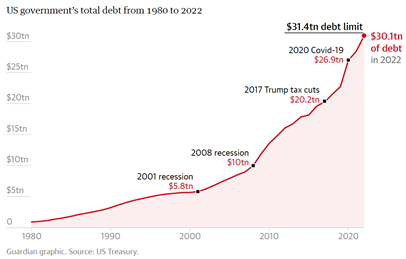
- The US has had a debt problem since the 80s, when Ronald Reagan's tax cuts caused it to grow.
- In the early 2000s, the dotcom bubble burst, George W Bush cut taxes, and in the 2008 Great Recession, the government had to bail out banks and increase social services.
- In 2017, Donald Trump passed a major tax cut, raising the debt by $7.8tn.
- And then the Covid-19 pandemic hit. The US government passed a series of stimulus bills to offset the worst of the pandemic’s impacts that ultimately totaled $5tn.
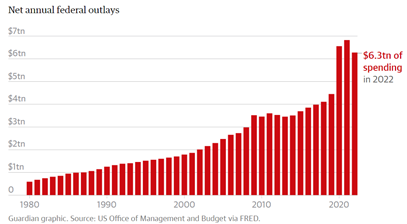
What are the main contributors to federal government spending?
- US government spending is dominated by mandatory programs such as social security, Medicaid and Medicare, with military spending taking up 12% of the budget.
- Other big-ticket items include education, employment training and benefits for veterans.
Why isn’t Congress raising the debt ceiling?
- Republicans passed a bill in April that would raise the debt ceiling by $1.5tn and mandate $4.8tn in spending cuts over a decade.
- Democrats have refused to negotiate spending cuts over the debt ceiling, but Republicans are using the high-stakes timeline towards default to pressure Democrats into agreeing to spending cuts. This stalemate could bring the US economy closer to disaster.


