The Government is taking various initiatives to accelerate growth in rural India thereby catalysing the growth of the Indian economy. About 70 per cent of India resides in its villages. Undoubtedly, the growth of rural sector is central to the overall development of the country.
The Government has been investing in vital areas such as energy, electricity, health, women empowerment, agricultural initiatives and several social security schemes to build a strong foundation for the sustainable growth od India’s rural sector. Hence, Rural development is fundamental to the country’s progress.
Livelihood Development and Diversification-
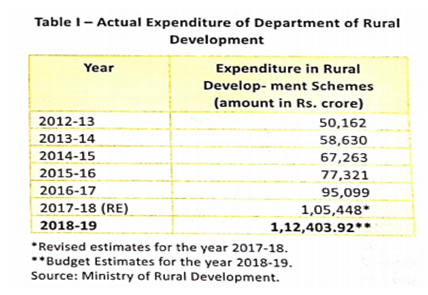
The last 4 years have seen a considerable stepping up of financial resources for improving rural infrastructure,diversifying livelihoods, reducing poverty and thereby improving the well-being of poor households in terms of allocation for Programmes of Department of Rural Development.
- Annual expenditure in 2017-18 is more than double of what it was in 2012-13.
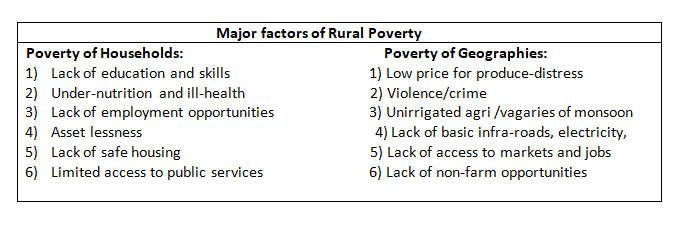
- Major sources of funds for addressing Rural Poverty during this period were:-
- From 2017-18, under the Housing Programme, additional resources were mobilized through Extra Budgetary Resources (EBRs).
- The transfer of funds under the 14th Finance Commission has registered a significant increase compared to the allocations earlier under 13th
- There has been increase in the allocations of Ministry of Agriculture and other Infrastructure and Livelihood Programmes for the poor; thus, the total transfer of financial resources to Rural India has been very significant.
- MGNREGS focused on durable assets and Water Conservation, and also provided for livelihood generating individual benefits like farm ponds, dug wells, goat shed, etc.
Social Security:
- It has been recognised as an instrument for social transformation and progress and must be preserved, supported and developed as such.
- Social security is increasingly seen as an integral part of the development process which helps to create a more positive attitude and not just to a structural and technological change but also the challenge of globalisation and to its potential benefits in terms of greater efficiency and higher productivity.
- Social security may refer to social insurance, where people receive benefits or services in recognition of contribution to an insurance programme.
Related Articles