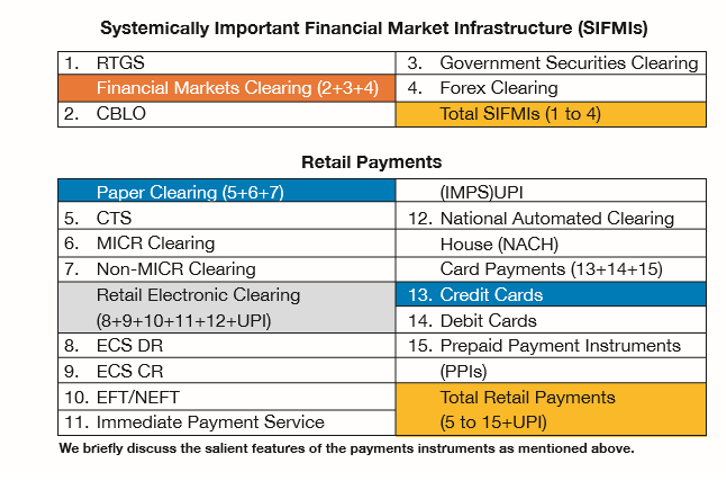
The payment system has two main segments.
- Systemically Important Financial Market Infrastructure (SIFMIs)
- Retail Payments
- Systemically Important Financial Market Infrastructure (SI-FMI)
- Financial Market Infrastructure (FMI):It is defined as a multilateral system among participating institutions, including the operator of the system, used for the purposes of clearing, settling, or recording payments, securities, derivatives, or other financial transactions.
- Under SIFMI, new standards are designed to ensure that the essential financial market infrastructure (FMI) supporting global financial markets is even more robust and thus even better placed to withstand financial shocks than at present.
- Under this segment (SIFMI) there are four instruments of payments:
- Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS): It is defined as the continuous (real-time) settlement of fund transfers individually on an order by order basis (without netting). 'Real Time' means the processing of instructions at the time they are received rather than at some later time; 'Gross Settlement' means the settlement of fund transfer instructions occurs individually (on an instruction by instruction basis). This system is primarily meant for large value transactions. The minimum amount to be remitted through RTGS is Rs 2 lakh. For inter-bank fund transfer there is no floor.
- Collateralized Borrowing and Lending Obligation (CBLO): It is a money market instrument developed by Clearing Corporation of India Ltd. (CCIL), introduced in 2003. This represents an obligation between a borrower and a lender to the terms and conditions of a loan. It also does not entail physical transfer of respective securities from borrower to lender or vice versa.
- Government Securities:A Government Security (G-Sec) is a tradable instrument issued by the Central Government or the State Governments.
- Forex Clearing:The term ‘Forex’ stands for Foreign Exchange. In simple terms it is the trading in currencies from different countries against each other. In India the settlement of Forex transactions is done by CCIL which was started in 2002.
- Retail Payments
Under the Retail Payments segment which has a large user base, there are three broad categories of instruments. They are (1) Paper Clearing, (2) Retail Electronic Clearing, (3) and Card Payments. The instruments under these three categories are discussed below:
- Cheque Truncation System (CTS):CTS or online image-based cheque clearing system is a cheque clearing system undertaken by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) for faster clearing of cheques. It eliminates the associated cost of movement of physical cheques.
- Non-MICR:The Non-MICR clearing refers to the process of manual clearing of cheques where the cheque is physically moved between the bank branches/banks for clearing. MICR (magnetic ink character recognition) is a technology used to verify the legitimacy or originality of paper documents, especially checks.
- ECS DR/CR:ECS (Electronic Clearing System) is an electronic mode of payment/receipt for transactions that are repetitive and periodic in nature. DR/CR is ‘Debit Record or Credit Record’. ECS facilitates bulk transfer of monies from one bank account to many bank accounts or vice versa. ECS includes transactions processed under National Automated Clearing House (NACH) operated by National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- NEFT:National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) is a nation-wide payment system facilitating one-to-one funds transfer. Under this scheme, individuals, firms and corporates can electronically transfer funds from any bank branch to any individual, firm or corporate having an account with any other bank branch in the country participating in the scheme.
- IMPS:Immediate Payment Service (IMPS) offers an instant 24X7 interbank electronic fund transfer service through mobile phones. IMPS is an emphatic tool to transfer money instantly within banks across India through mobile, internet and ATM. It is offered by National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- UPI:Unified Payments Interface (UPI) is a system that powers multiple bank accounts into a single mobile application (of any participating bank), merging several banking features, seamless fund routing & merchant payments into one hood.
- *99#:USSD based mobile banking service of NPCI was initially launched in November 2012. The service had limited reach and only two TSPs (Telecom Service Provider) were offering this service i.e. MTNL & BSNL. Understanding the importance of mobile banking in financial inclusion, *99# was dedicated to the nation by Hon’ble Prime minister on 28th August 2014, as part of ‘Pradhan Manti Jan Dhan Yojna’.
- USSD (Unstructured Supplementary Service Data) is a Global System for Mobile (GSM) communication technology that is used to send text between a mobile phone and an application program in the network.
- NACH:“National Automated Clearing House (NACH)” is a service offered by NPCI to banks which aims at facilitating interbank high volume, low value debit/credit transactions, which are repetitive and electronic in nature. It allows participating banks for centralized posting of inward debit/credit transactions and is run by NPCI.
- Credit Card:A credit card is a card issued by a financial company which enables the cardholder to borrow funds. The issuer pre-sets borrowing limits which have a basis on the individual's credit rating. These cards can be used domestically and internationally and can also be used to withdraw cash from an ATM and for transferring funds to bank accounts, debit cards and prepaid cards within the country.
- Debit Cards:A debit card is a payment card that deducts money directly from a consumer’s bank account to pay for a purchase and eliminate the need to carry cash or physical checks to make purchases. In addition, they offer the convenience of credit cards for small negative balances that might be incurred if the account holder has signed up for overdraft coverage. However, debit cards usually have daily purchase limits.
- Pre-Paid Instruments (PPIs):PPIs are payment instruments that facilitate purchase of goods and services, including financial services, remittance facilities, etc., against the value stored on such instruments. PPIs are classified under three types:
- Closed System PPIs:These PPIs are issued by an entity for facilitating the purchase of goods and services from that entity only and do not permit cash withdrawal.
- Semi-closed System PPIs:These PPIs are used for purchase of goods and services, including financial services, remittance facilities, etc., at a group of clearly identified merchant locations/establishments which have a specific contract with the issuer (or contract through a payment aggregator/payment gateway) to accept the PPIs as payment instruments. These instruments do not permit cash withdrawal.
- Open System PPIs: These PPIs are issued only by banks and are used at any merchant for purchase of goods and services, including financial services, remittance facilities, etc. Banks issuing such PPIs shall also facilitate cash withdrawal at ATMs/Point of Sale (PoS)/Business Correspondents (BCs).
Related Articles