Environment & Ecology: Environment and Health
Draft National Education Policy 2019

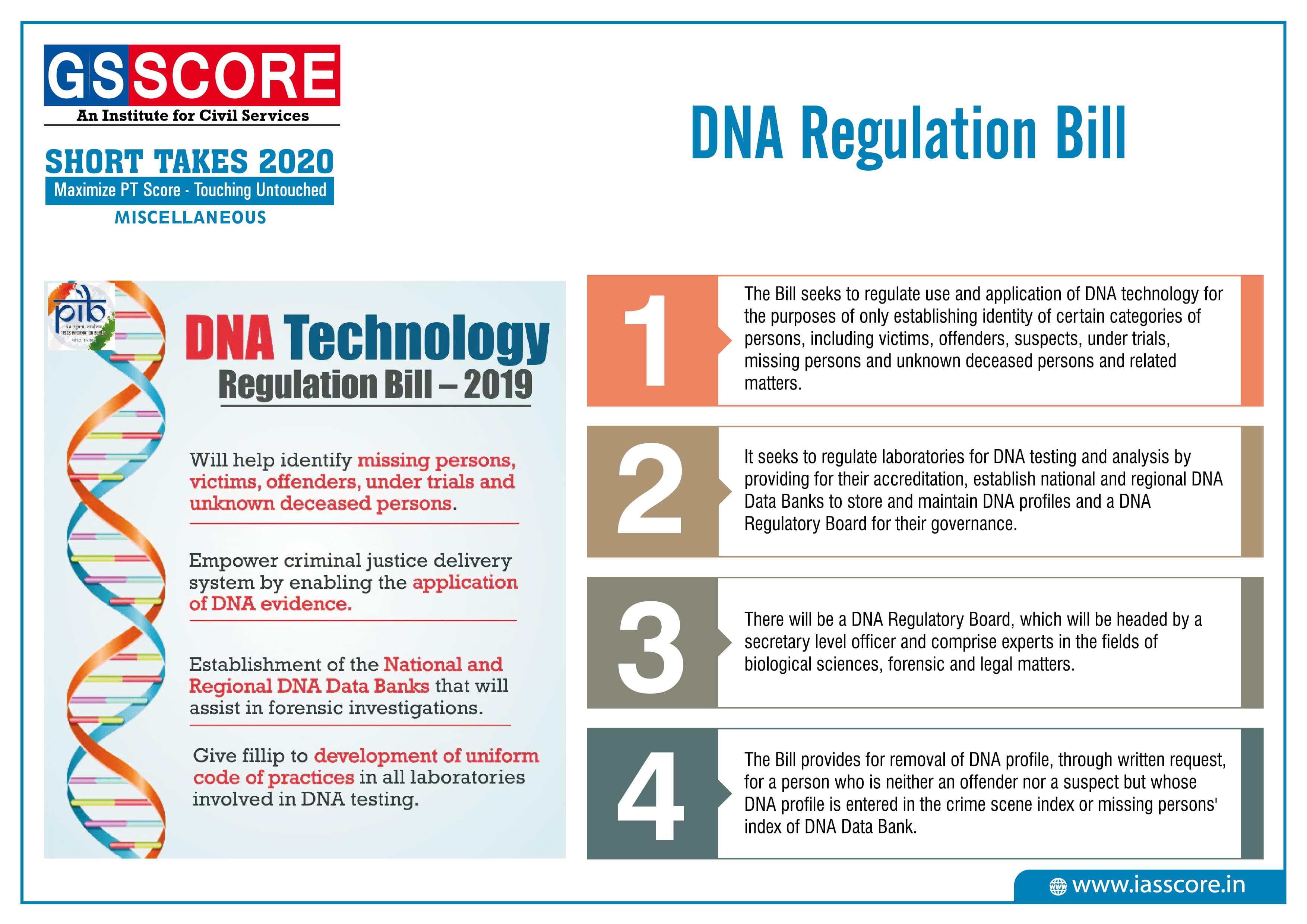
DNA Regulation Bill
Van Dhan Yojana

Jal Shakti Abhiyan

Code on Wages Bill, 2019

Environment and Health
An environmental illness can occur when you are exposed to toxins or substances in the environment that make you sick. These health hazards may be found where you live, work, or play.
What causes environmental illnesses?
Exposure to some types of chemicals can cause an environmental illness. The more of the chemical you are exposed to, the more likely you are to get ill. Examples include:
- Chemicals in cigarettes are known to cause lung cancer.
- Exposure to asbestos, an insulating material found in some older buildings, can cause tumors, lung cancer, and other diseases.
- Wood-burning stoves and poorly vented gas ranges can produce smoke or gases that can cause breathing problems.
- Unsafe drinking water from a rural well polluted with pesticides or other poisons from a nearby industrial plant could cause allergies, cancer, or other problems.
- Certain chemicals in the workplace may cause sterility in men or fertility problems in women.
- Lead poisoning can cause health problems, most commonly in children. It can also cause high blood pressure, brain damage, and stomach and kidney problems in adults.
Some of the environmental diseases are mentioned below:
Allergies and Asthma
- Slightly more than half of the 300 million people living in the U.S. are sensitive to one or more allergens.
- They sneeze, their noses run and their eyes itch from pollen, dust and other substances.
- Some suffer sudden attacks that leave them breathless and gasping for air.
- This is allergic asthma. Asthma attacks often occur after periods of heavy exercise or during sudden changes in the weather.
- Some can be triggered by pollutants and other chemicals in the air and in the home.
- Doctors can test to find out which substances are causing reactions.
- They can also prescribe drugs to relieve the symptoms.
Birth Defects
- Sometimes, when pregnant women are exposed to chemicals or drink a lot of alcohol, harmful substances reach the fetus.
- Some of these babies are born with an organ, tissue or body part that has not developed in a normal way.
- Aspirin and cigarette smoking can also cause birth problems. Birth defects are the leading cause of death for infants during the first year of life. Many of these could be prevented.
Blue Baby Syndrome
- Blue baby syndrome refers to the bluish appearance of body. Blue baby syndrome can occur due to multiple reasons.
- It is also believed to be caused by the consumption of high nitrate content in water which leads decrease in the oxygen-carrying capacity of haemoglobin, particularly among children.
Cancer
- Cancer occurs when a cell or group of cells begins to multiply more rapidly than normal.
- As the cancer cells spread, they affect nearby organs and tissues in the body.
- Eventually, the organs are not able to perform their normal functions.
- Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the U.S., causing more than 500,000 deaths each year.
- Some cancers are caused by substances in the environment: cigarette smoke, asbestos, radiation, natural and man-made chemicals, alcohol, and sunlight.
- People can reduce their risk of getting cancer by limiting their exposure to these harmful agents.
Dermatitis
- Dermatitis is a fancy name for inflamed, irritated skin.
- Many of us have experienced the oozing bumps and itching caused by poison ivy, oak and sumac.
- Some chemicals found in paints, dyes, cosmetics and detergents can also cause rashes and blisters.
- Too much wind and sun make the skin dry and chapped.
- Fabrics, foods, and certain medications can cause unusual reactions in some individuals.
Emphysema
- Air pollution and cigarette smoke can break down sensitive tissue in the lungs. Once this happens, the lungs cannot expand and contract properly. This condition is emphysema. For these people, each breath is hard work.
- Even moderate exercise is difficult.
- Some emphysema patients must breathe from tanks of oxygen.
Heart Disease
- Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States and is a major cause of disability.
- While these may be due in part to poor eating habits and/or lack of excercise, environmental chemicals also play a role.
- While most chemicals that enter the body are broken down into harmless substances by the liver, some are converted into particles called free radicals that can react with proteins in the blood to form fatty deposits called plaques, which can clog blood vessels. A blockage can cut off the flow of blood to the heart, causing a heart attack.
Itai-Itai Disease
- It was first documented in Japan in 1912. It is also called ‘ouch-ouch’ disease.
- The term ‘itai-itai’ disease was coined by the locals due to the severe pain felt in the spine and joints.
- The disease occurs from cadmium poisoning and leads to the softening of bones and kidney failure.
Lead Poisoning
- Sometimes, infants and children will pick up and eat paint chips and other objects that contain lead.
- Lead dust, fumes and lead-contaminated water can also introduce lead into the body.
- Lead can damage the brain, kidneys, liver, and other organs.
- Severe lead poisoning can produce headaches, cramps, convulsions, and even death. Even small amounts can cause learning problems and changes in behavior.
- Doctors can test for lead in the blood and recommend ways to reduce further exposure.
Mercury Poisoning
- Mercury is a silvery metal that is extremely poisonous.
- Very small amounts can damage the kidneys, liver and brain.
- Years ago, workers in hat factories were poisoned by breathing the fumes from mercury used to shape the hats.
- Today, mercury exposure usually results from eating contaminated fish and other foods that contain small amounts of mercury compounds. Since the body cannot get rid of mercury, it gradually builds up inside the tissues.
- If it is not treated, mercury poisoning can eventually cause pain, numbness, weak muscles, loss of vision, paralysis and even death
Nervous System Disorders
- The nervous system, which includes the brain, spinal cord and nerves, commands and controls our thoughts, feelings, movements, and behavior.
- The nervous system consists of billions of nerve cells. They carry messages and instructions from the brain and spinal cord to other parts of the body.
- When these cells are damaged by toxic chemicals, injury or disease, this information system breaks down.
- This can result in disorders ranging from mood changes and memory loss to blindness, paralysis and death.
Pneumoconiosis
- Pneumoconiosis is also called ‘black lung disease’.
- It is caused by the deposition of coal dust in the lungs of coal miners. Thus, it affects the respiratory system of the victims.
Queensland Fever
- People do not usually get diseases from farm animals. However, those who work with hides and animal products can get sick from breathing the infected dust around them.
- This illness is called Queensland fever because it was first discovered among cattle ranchers and dairy farmers in Queensland, Australia.
- It is caused by a tiny organism that infects livestock and then spreads to the milk and feces.
- Symptoms include fever, chills, and muscle aches and pains.
- Researchers have developed vaccines to protect livestock workers from this illness.
Sunburn and Skin Cancer
- Almost everyone has stayed in the sun too long and been burned.
- Too much sunlight can also produce the most common type of cancer—skin cancer.
- Some skin cancers are easy to treat because they do not spread beyond the surrounding tissue.
- Others, like melanoma, are much more dangerous because they spread to other parts of the body. Deaths due to melanoma are increasing by 4 percent each year.
Tooth Decay
In the 1930’s, health experts noticed that people who lived in areas where the water contained natural chemicals called fluorides had fewer cavities. Today, all U.S. residents are exposed to fluoride to some degree, and its use has resulted in a significant decline in tooth decay. National surveys report that the incidence of tooth decay among children 12 to 17 years of age has declined from 90 percent in 1971 to 67 percent in 1988. Dentists can also protect young
Uranium Poisoning
- Uranium is a dangerous element because it is radioactive.
- This means it gives off high-energy particles that can go through the body and damage living tissue.
- A single high dose of radiation can kill. Small doses over a long period can also be harmful.
- For example, miners who are exposed to uranium dust are more likely to get lung cancer. Uranium poisoning can also damage the kidneys and interfere with the body’s ability to fight infection.
- While most people will never come in contact with uranium, those who work with medical x-rays or radioactive compounds are also at risk.
Xeroderma Pigmentosa
- Xeroderma is a rare condition that people inherit from their parents.
- When these people are exposed to direct sunlight, their skin breaks out into tiny dark spots that look like freckles.
- If this condition is not treated, the spots can become cancerous. These areas must then be removed by a surgeon.
Yusho Poisoning
- In 1968, more than one thousand people in western Japan became seriously ill.
- They suffered from fatigue, headache, cough, numbness in the arms and legs, and unusual skin sores.
- Pregnant women later delivered babies with birth defects.
- These people had eaten food that was cooked in contaminated rice oil.
- Toxic chemicals called PCB’s (polychlorinated biphenyls) had accidentally leaked into the oil during the manufacturing process. Health experts now refer to this illness as”Yusho,” which means”oil disease.”
- For years, PCB’s were widely used in the manufacturing of paints, plastics and electrical equipment.
- When scientists discovered that low levels of PCB’s could kill fish and other wildlife, their use was dramatically reduced.
- By this time, PCB’s were already leaking into the environment from waste disposal sites and other sources.
- Today, small amounts of these compounds can still be found in our air, water, soil, and some of the foods we eat.
Zinc Deficiency/ Poisoning
- Zinc is a mineral that the body needs to function properly.
- In rare cases, people can be poisoned if there is too much zinc in their food or water.
- However, most people can take in large quantities without any harmful effects.
- In areas where nutrition is a problem, people may not get enough zinc from their diet.
- This can lead to retarded growth, hair loss, delayed sexual maturation, eye and skin lesions, and loss of appetite.
Climate Emergency CoP 25
Context
As announced by the UNFCCC Secretariat on 1 November 2019, the COP Bureau agreed that COP 25 will take place from 2-13 December, in Madrid, Spain.
About
- The 2019 United Nations Climate Change Conference, also known as COP25, is the 25th United Nations Climate Change conference.
- It was held in Madrid, Spain, under the presidency of the Chilean government.
- The conference incorporates the 25th Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), the 15th meeting of the parties for the Kyoto Protocol (CMP15), and the second meeting of the parties for the Paris Agreement.
Why climate emergency?
- In the climate lexicon, tipping points are thresholds beyond which certain impacts can no longer be avoided even if temperatures are brought down later. Examples include the loss of the Amazon rainforest or of the West Antarctic ice sheet.
- Recent IPCC reports, including last year’s Global Warming of 1.5°C and this year’s Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate, suggest that tipping points could be exceeded even between 1 and 2 °C of warming.
- This is worrying as we are on track to a 3.2 degree warmer world, suggests the UNEP’s Emissions Gap Report.
- The report addresses biosphere tipping points such as Amazonian deforestation, which can trigger abrupt carbon releases into the atmosphere, amplify climate change and reduce remaining emission budgets.
It calls on governments to:
- Increase implementation across all thematic areas to realize multiple benefits;
- Create the conditions needed for non-Party action;
- Continue and strengthen the Global Climate Action agenda within the UNFCCC process post- 2020;
- Align finance flows with finance needs, and;
- Strengthen the completeness and robustness of the reporting of results from climate action.
Several issues been discussed in the meeting
- The Warsaw International Mechanism for Loss and Damage associated with Climate Change Impacts (WIM);
- International climate finance;
- Capacity building;
- Matters relating to least developed countries (LDCs);
- The forum on the impact of the implementation of response measures;
- Gender and climate change;
- Common time frames for Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) to the Paris Agreement
- The Koronivia joint work on agriculture;
- National adaptation plans (NAPs)
- The Local Communities and Indigenous Peoples Platform (LCIPP)
The World Soil Day
Context
The World Soil Day (WSD) was observed across the world on December 5, 2019.
About
The day is observed annually to highlight the importance of healthy soil and advocate for the sustainable management of soil resources. The theme for WSD 2019 was ‘Stop Soil Erosion, Save Our Future’.
Historical background:
- In 2002 the International Union of Soil Science (IUSS) voted for a resolution to dedicate 5th December every year as World Soil Day to promote the importance of Nature and human wellbeing.
- Food and Agriculture organization (FAO) supported this initiative together with the Kingdom of Thailand leadership as a part of “Global soil partnership”.
- FAO took the initiative to establish Soil Day. Consequently, unanimously approved it in its FAO conference 2013.
- Later in 2013, December with FAO’s request, UN adopted World Soil Day in its 68th UN General Assembly. Further, announced that the day would be observed on 5th December every year.
- Especially, this is a tribute to late King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand for his contribution in improving quality and sustainable management of soil.
- Thereby, FAO has been celebrating world soil day since 2012.
Highlights about the World Soil Day:
- Annually, to celebrate the day, World Soil Day award is distributed to honour the contributions made by people. That is, FAO gives two awards in line with this day-
- The King Bhumibol World Soil Day Award- an annual award that honours individuals, communities, organizations and countries that organized remarkable and engaging World Soil Day activities or campaigns in the previous year.
- The Glinka World Soil Prize- An annual award for dynamic change-makers dedicated to solving one of our world’s most pressing environmental issue: soil degradation. It honours individuals and organizations whose leadership and activities have contributed, or are still contributing to the promotion of sustainable soil management and the protection of soil resources.
Air Quality Index and Safar
About Air Quality Index
- The AQI is an index for reporting daily air quality.
- It tells you how clean or polluted your air is, and what associated health effects might be a concern for you.
- The AQI focuses on health affects you may experience within a few hours or days after breathing polluted air.
- AQI is calculated for eight major air pollutants: Ground-level ozone, PM10, PM2.5, Carbon monoxide, Sulphur dioxide, Nitrogen dioxide, Ammonia, Lead.
- There are six AQI categories, namely Good + Satisfactory, Moderately polluted, Poor, Very Poor, and Severe.
About SAFAR
- The System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting And Research (SAFAR) is an initiative introduced by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)
- The system is indigenously developed by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune and is operationalized by the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- The giant true colour LED display gives out real-time air quality index on 24x7 basis with colour coding along with 72-hour advance forecast.
- The system will be an integral part of India’s first Air Quality Early Warning System operational in Delhi.
- SAFAR will accelerate public awareness and preparedness of air pollution and weather extremes.
- It will also lead to better understanding of linkages among emissions, weather, pollution and climate. It will monitor all weather parameters like temperature, rainfall, humidity, and wind speed and wind direction.
- In addition to regular air quality parameters like PM2.5, PM10, Sulphur Dioxide, Ozone, Nitrogen Oxides, Carbon Monoxide, the system will also monitor the existence of Benzene, Toluene and Xylene.
- SAFAR system would benefit cost savings to several other sectors like agriculture, aviation, infrastructure, disaster management skill, tourism and many others, which directly or indirectly get affected by air quality and weather.


