Social Schemes: Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
Assistance to Disabled Persons for Purchase / Fitting of Aids / Appliances
Objective
- The main objective of the Scheme is to assist the needy disabled persons in procuring durable, sophisticated and scientifically manufactured, modern, standard aids and appliances that can promote their physical, social and psychological rehabilitation, by reducing the effects of disabilities and enhance their economic potential.
- The aids and appliances supplied under the Scheme must be ISI.
Eligibility of Implementing Agency
The following agencies would be eligible to implement the Scheme on behalf of Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, subject to fulfillment of laid down terms and conditions:
- Societies, registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860 and their branches, if any,
- Registered charitable trusts
- District Rural Development Agencies, Indian Red Cross Societies and other Autonomous Bodies headed by District Collector/Chief Executive Officer/District Development Officer of Zilla Parishad.
- National/Apex Institutes including ALIMCO functioning under administrative control of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment/Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- State Handicapped Development Corporations.
- Local Bodies- Zilla Parishad, Municipalities, District Autonomous Development Councils and Panchayats.
- Nehru Yuvak Kendras.
- Grant-in-aid under the Scheme will not be given for commercial supply of aids/appliances.
- The NGOs should preferably possess professional/technical expertise in the form of professionally qualified staff (from recognized courses) for the identification, prescription of the required artificial aids/appliance, and fitment and post-fitment care of the beneficiaries as well as the aid/appliance.
- The NGO should also preferably possess infrastructure in the form of machinery/equipment for the fabrication, fitment and maintenance of artificial aid/appliance to be given to a disabled person under ADIP Scheme.
- Implementing Organisations should network and establish linkages with medical colleges/district hospitals/rural hospitals/PHCs/fitment centers of ALIMCO/DRCs/ any other professionally competent agency to acquire/avail the requisite infrastructure for fitment and maintenance of aids/appliances distributed under ADIP Scheme available with these bodies.
- The Implementing Agencies shall also avail of the professional/technical expertise of above-mentioned agencies for fitment and post-fitment care of the beneficiaries as well as aids/appliances.
- National Institutes, fitment centers of ALIMCO and DDRCs functioning under the administrative control of Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment shall also assist DRDAs and other autonomous organizations to develop requisite manpower and infrastructure over a period of time to provide satisfactory service to the beneficiaries under the Scheme.
- Such organizations while applying for the grant under the Scheme shall produce sufficient proof of linkages with the professional agencies preferably in the form of a Memorandum of Understanding.
2. Assistance for Skill Development of OBCs/DNTs/EBCs
Objective
- The aim of this scheme is to involve the Voluntary Organization and National Backward Classes Finance and Development Corporation (NBCFDC) to improved educational and socio-economic conditions of the target group i.e. OBCs/DNTs/EBCs, with a view to upgrade their skill to enable them to start income generation activities on their own or get gainfully employed in some sector or the other.
Target Group and Eligibility Criteria
- The beneficiaries who parents/guardians income from all sources including the income of beneficiary does not exceed Rs.1.00 lakh per annum are eligible under the Scheme.
Scope
- Assistance under the scheme will be given to eligible voluntary organisations working for welfare of OBCs/DNTs/EBCs can also be taken up in the villages covered under the Saansad Adarsh Gram Yojana (SAGY).
3. Free Coaching for SC and OBC Students
Objective
- The objective of the Scheme is to provide coaching of good quality for economically disadvantaged Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Other Backward Classes (OBCs) candidates to enable them to appear in Competitive examination and succeed in obtaining an appropriate job in Public/Private sector.
The courses for which the Coaching will be imparted shall be as follows:
- Group A and B examinations conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC), the Staff Selection Commission (SSC) and the various Railway Recruitment Boards (RRBs);
- Group A and B examinations conducted by the State Public Service Commissions;
- Officers’ Grade examinations conducted by Banks, Insurance Companies and Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs)
- Premier Entrance Examinations for admission in (i) Engineering (eg. IIT-JEE & AIEEE),(ii) Medical (eg. AIPMT), (iii) professional courses like Management (eg. CAT) and Law (eg. CLAT) and (iv) such other disciplines, Ministry may decide from time to time.
- Finishing courses/Job oriented courses for employment in the private sector like IT, Bio-technology etc. in need of soft skill and other professional courses specified by the Government from time to time.
Implementing Agencies
The Scheme will be implemented through the reputed institutions/centres run by the
- Central Government/State Governments/UT Administrations/PSUs/autonomous bodies under Central/State Governments;
- Universities (both Central and State including the Deemed Universities in the private sector) and,
- Registered private institutions/NGOs
4. Deendayal Disabled Rehabilitation Scheme
The umbrella Central Sector Scheme of this Ministry called the "Scheme to Promote Voluntary Action for Persons with Disabilities" was revised w.e.f. 01.04.2003 and was renamed as the "Deendayal Disabled Rehabilitation Scheme (DDRS)".
Objectives
- To create an enabling environment to ensure equal opportunities, equity, social justice and empowerment of persons with disabilities.
- To encourage voluntary action for ensuring effective implementation of the People with Disabilities (Equal Opportunities and Protection of Rights) Act of 1995.
Approach and Strategy
The approach of this Scheme is to provide financial assistance to voluntary organizations to make available the whole range of services necessary for rehabilitation of persons with disabilities including early intervention, development of daily living skills, education, skill-development oriented towards employability, training and awareness generation. With a view to inclusion of persons with disabilities in the mainstream of society and actualizing their potential, the thrust would be on education and training programmes. In order to achieve the objectives of the scheme the key strategies will be as follows:
- To enhance educational opportunities at all levels and in all forms and enlarge the scope of vocational and professional opportunities, income generation and gainful occupations.
- To support all such measures as may be necessary for promoting formal as well as nonformal employment and placement opportunities.
- To implement outreach and comprehensive Community Based Rehabilitation programmes in urban and rural environments.
- To support manpower development activities to train required personnel at different levels for all programmes/ projects/activities for persons with disabilities.
- To support the development, publication and dissemination of information, documentation and training materials.
- To set up well equipped resource centres at different levels. To promote and support the development of self-help groups, parent organizations and independent living.
- To encourage coordination, cooperation and networking and multi-sectoral linkages.
- To support people with disabilities in projects which are environment friendly and ecopromotive.
- To support construction and maintenance of buildings, provision of furniture and fixtures and installation and maintenance of machinery and equipment.
- To establish and support facilities for sport, recreation, leisure-time activities, excursions, creative and performing arts, cultural and socially inclusive activities.
- To support and facilitate the availability of appropriate housing, homes and hostel facilities.
- To support the conduct of surveys and other forms of epidemiological studies.
- To promote research in various development areas, innovative strategies, assistive devices and enabling technologies and support production of such devices ensuring quality control.
- To support effort to ensure protection of human, civil and consumer rights of persons with disabilities.
- To support legal literacy, including legal counseling, legal aid and analysis and evaluation of existing laws.
- To support such other measures, which may meet the needs of the persons with disability and fulfill the obligations as prescribed in the People with Disabilities (Equal Opportunities and Protection of Rights) Act of 1995.
Grants-in-aid to NGOs
To facilitate delivery of various services to persons with disabilities by voluntary organizations, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment is administering DDRS scheme and providing grants-in-aid to NGOs for the following projects:-
- Vocational Training Centres
- Sheltered Workshops
- Special Schools for the Persons with Disabilities
- Project for Cerebral Palsied Children
- Project for Pre-School and Early Intervention and Training
- Home based Rehabilitation Program / Home Management Programme
- Project for Rehabilitation of Leprosy Cured Persons (LCPs)
- Project relating to Survey, Identification, Awareness and Sensitization
- Project for Community Based Rehabilitation
- Project for Human Resource Development
- Seminars / Workshops / Rural Camps
- Project for Legal Literacy, Including Legal Counselling, Legal Aid and Analysis and Evaluation of Existing Laws
- Environment Friendly and Eco-Promotive Projects for the Handicapped
- Grant for Purchase of Vehicle
- Construction of Building
- Grant for Computer
- Project for Low Vision Centres
- Half Way Home for Psycho-Social Rehabilitation of Treated and Controlled Mentally Ill Persons
- District Disability Rehabilitation Centres (DDRCs)
The maximum level of support could be up to 90% of the eligible amount of grant for the project.
5. Integrated Programme for Older Persons
- The main objective of the Scheme is to improve the quality of life of the Senior Citizens by providing basic amenities like shelter, food, medical care and entertainment opportunities and by encouraging productive and active ageing through providing support for capacity building of State/ UT Governments/Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs)/Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) / local bodies and the community at large.
Scope
Assistance under the scheme will be given to the Panchayati Raj Institutions / local bodies and eligible Non-Governmental Voluntary Organizations for the following purposes:
- Programmes catering to the basic needs of Older Persons particularly food, shelter and health care to the destitute elderly;
- Programmes to build and strengthen intergenerational relationships particularly between children / youth and Older Persons;
- Programmes for encouraging Active and Productive Ageing;
- Programmes for proving Institutional as well as Non Institutional Care / Services to Older Persons;
- Research, Advocacy and Awareness building programmes in the field of Ageing; and
- Any other programmes in the best interests of Older Persons.
Financial Assistance
Up to 90% of the cost of the project indicated in the scheme will be provided by the Government of India and the remaining shall be borne by the Organization/ Institution concerned
WHO award for Rajasthan Health Department
Context
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has selected the Rajasthan government’s Medical & Health Department, only government body in the country which will be awarded for its tobacco-free initiatives.
About
- The department’s Additional Chief Secretary, Rohit Kumar Singh, received the award on World No Tobacco Dayin New Delhi.
- The Medical & Health Department launched several campaigns against tobacco consumption at places such as schools, colleges, police stations and government offices during 2018-19.
- As part of the tobacco-free initiatives, 1.13 crore people took a pledge against tobacco consumption at the events held in 1.56 lakh government institutions on January 30 this year, marking Martyrs’ Day.
World No Tobacco Day
- Every year, on 31 May, WHO and global partners celebrate World No Tobacco Day (WNTD). The annual campaign is an opportunity to raise awareness on the harmful and deadly effects of tobacco use and second-hand smoke exposure, and to discourage the use of tobacco in any form.
- The focus of World No Tobacco Day 2019 is on "tobacco and lung health".The campaign will increase awareness on:
- The negative impact that tobacco has on people’s lung health, from cancer to chronic respiratory disease,
- The fundamental role lungs play for the health and well-being of all people.
WHO
- WHO is a specialized agency of the United Nations that is concerned with international public health. It was established on 7 April 1948, and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. The WHO is a member of the United Nations Development Group.
- WHO has selected five organisations from the South-East Asian region for this prestigious award. Three other organisations in the South-East Asian region have been selected from Thailand and Indonesia, while the Vallabhbhai Patel Chest Institute, New Delhi, is also among the recipients of the award.
Way Ahead
- As State government got international recognition so it would keep striving to accomplish the goal of a “healthy Rajasthan”.
E-cigarettes pose public health risk
Context
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has warned of a potential public health disaster if action was not taken to completely prohibit and dissuade the use of Electronic Nicotine. Delivery Systems (ENDS) or e-cigarettes given that the nicotine delivered by these devices adversely affect almost all systems in a human body.
- Youth are using e-cigarettes (also known as vaping devices) at a rapidly increasing rate.
About
E-cigarette
- An electronic cigarette (or e-cig) is a battery-powered vaporizer that mimics tobacco smoking. It works by heating up a nicotine liquid, called “juice.”
- E-cigarettes contain potentially harmful substances – such as heavy metals like lead, volatile organic compounds and cancer-causing agents.
- Availability of flavour variants and attractive designs are adding to allure of devices and globally there was an increasing trend of e-cigarettes consumption among youth and adolescents.
- As e-cigarettes contain nicotine and not tobacco, they do not fall within the ambit of the Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products (Prohibition of Advertisement and Regulation of Trade and Commerce, Production, Supply and Distribution) Act, 2003 (COTPA), which mandates stringent health warnings on the packaging and advertisements of tobacco products.
Impact of E-cigarette
- It effects on humans include DNA damage; carcinogenesis; cellular, molecular and immunological toxicity; respiratory, cardiovascular and neurological disorders and adverse impact on foetal development and pregnancy.
- According to WHO report, nicotine itself is not a carcinogen, it may function as a “tumour promoter” and seems to be involved in the biology of malignant disease, as well as of neuro-degeneration.
- E-cigarettes also open a gateway for new tobacco addiction, which is a potential threat to the country’s tobacco control laws and ongoing tobacco control programmes and efforts.
Main Concerns
- In India smoking devices are easily available through online shopping portals. Smart marketing and inadequate information on the nicotine content in e-cigarettes has created a false impression that these devices are not as harmful as regular cigarettes. In the absence of a regulation the use of e-cigarettes has grown; they are easily accessible to even the non-smokers.
- Along with the traditional cigarette manufacturing, there is a parallel industry of e-cigarette like devices growing in India, which is under-regulated.
Steps to be taken
- There are more than 460 different e-cigarette brands with varying configurations of nicotine delivery available in the market.
- The ICMR has recommended complete prohibition on ENDS or e-cigarettes in India in the greater interest of protecting public health.
- By bringing together all stakeholders under one umbrella to prevent this impending epidemic of e-cigarettes use.
- Advertising has been shown to promote a positive brand image for vaping devices and to spur youth to try them, while social media marketing has been linked to explosive growth in sales. Therefore, governments globally should promptly ban all e-cigarette advertising.
- Governments should also mandate plain packaging for vaping devices, ban their use wherever tobacco use is banned and strictly limit the accessibility of sales to youth – placing e-cigarettes behind the pharmacy counter.
Climate change is already damaging health of children, says Lancet report
Context
- Climate change poses an unprecedented health risk to children and is already having “persistent and pervasive” effects that will last throughout their lives, a major new study has warned.
About/Outcomes of the report
- The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change’ is a comprehensive yearly analysis tracking progress across 41 key indicators.
- Without drastic reductions in emissions, escalating temperature increases will burden the next generation with high levels of malnutrition, weaker immune systems and higher risk of premature death.
- As temperatures rise, study predicts a reduction in yields of staple crops such as maize, rice and soybean, which will cause prices to rise and leave infants vulnerable to malnutrition, resulting in stunted growth and long-term developmental problems.
- Small children are particularly vulnerable to rises in infectious diseases caused by increasing temperatures and changing rainfall patterns.
- Warmer temperatures caused an increase in the spread of a bacteria that causes diarrhoeal diseases and wound infections.
- Over the past 30 years the number of climatically suitable days for Vibrio bacteria (which causes diarrhoea) to thrive have doubled.
- Dengue is also on the spread.
- The damage done in early childhood is persistent and pervasive, with health consequences lasting for a lifetime.
Global climate risk Index 2020

Jaga Mission
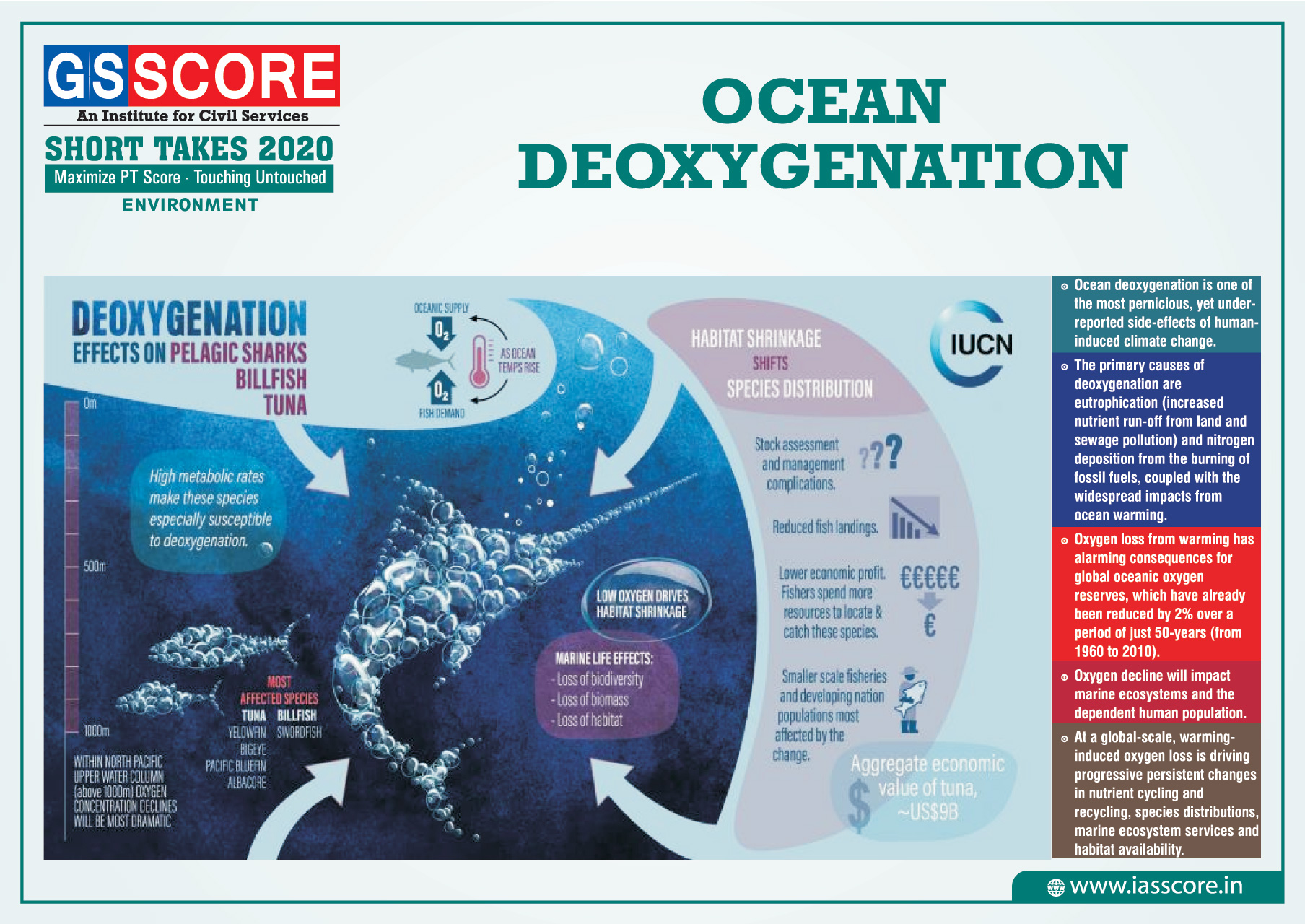
Ocean deoxygenation
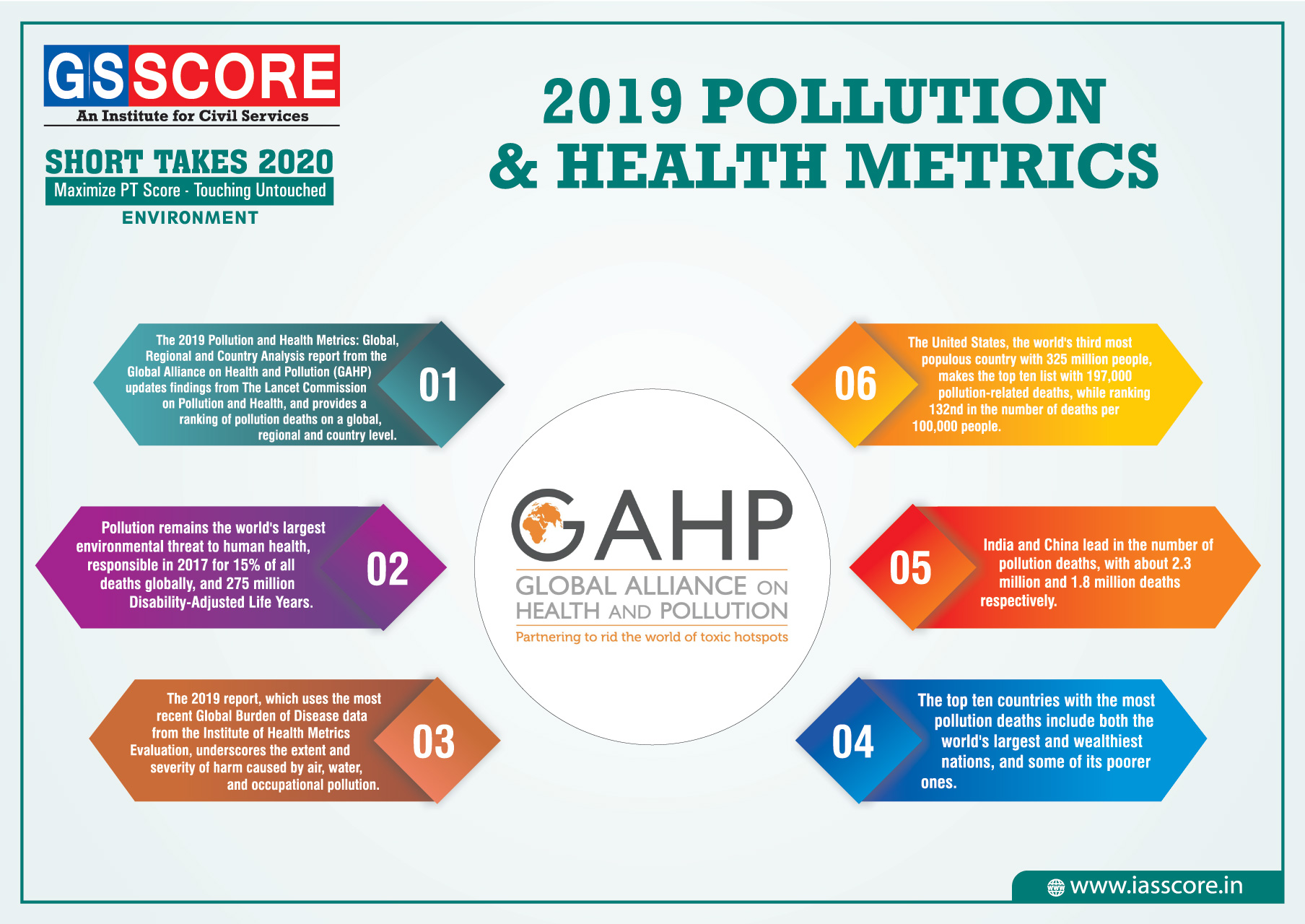
2019 Pollution and Health Metrics
Climate change performance index 2020