

25th February 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) aims to increase India’s share in global additive manufacturing to 5 percent within the next three years.
About
About 3D Printing:
- 3D printing or additive manufacturing uses computer-aided designing to make prototypes or working models of objects by laying down successive layers of materials such as plastic, resin, thermoplastic, metal, fiber or ceramic.
- With the help of software, the model to be printed is first developed by the computer, which then gives instructions to the 3D printer.
- This technology makes use of CAD (Computer-Aided Design) or 3D object scanners to take precise measurements of the product to be custom designed.
- Additive Manufacturing has its applications in several industries like defence, automotive industry, surgical equipment’s’ design segment, etc.
Types of 3D Printing:
- Binder Jetting:
- Binder jetting, also known as material jetting or inkjet powder printing is among the most common additive manufacturing types.
- This method works similarly to your run-of-the-mill office printer except it prints three-dimensional objects.
- Directed Energy Deposition (DED):
- Directed energy deposition (DED) utilizes welding principles to create three-dimensional objects.
- The material typically metal wire or powder is melted by a focused energy source like a laser or electron beam.
- The liquid material is then precisely poured onto the build platform, where it quickly hardens, forming a layer. This process repeats until the object is finished printing.
- Material Extrusion:
- Material extrusion works similarly to a hot glue gun.
- The material feeds into the printer from a coil.
- The tip of the nozzle heats and melts the material.
- The liquid material is then placed layer by layer on the build platform, where it can cool and solidify, forming the object.
- Powder Bed Fusion (PBF):
- Powder bed fusion, otherwise known as electron beam melting (EBM), starts with a large bed of powdered material, typically plastic, metal, sand, or ceramic powders mixed with sand.
- The powder is selectively fused together using a laser or electron beam.
- Once a layer of material is fused, the working area moves down, and the new layer is built on top using the same process.
- Sheet Lamination:
- Sheet lamination, otherwise known as ultrasonic additive manufacturing (UAM) or laminated object manufacturing (LOM) is an additive manufacturing process that stacks thin sheets of material and bonds them together through ultrasonic welding, bonding, or brazing.
- Vat Polymerization:
- Vat polymerization is similar to powder bed fusion, except instead of a bed of powder, it uses a vat of photopolymer resin, which is hardened in layers by an ultraviolet laser.
- Material Jetting:
- Similar to binder jetting, material jetting layers material to construct an object.
- However, instead of layering adhesive on a bed of powder, material jetting melts wax-like materials and precisely deposits droplets onto the build platform.
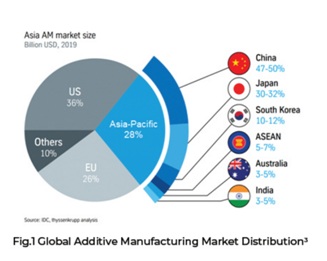
Global Market Scenario:
- The global market revenue generated by this sector accounts for USD 12 Billion in the year 2020 and it is anticipated to reach around USD 78 Billion by the year 2028.
- The market growth dynamics accounts for around CAGR of 26%- 32% during the forecast period, 2020-2028.
- North America dominates the global market with a market value of USD 24 Billion owing to the increasing R&D investment in this sector coupled with an infrastructure that supports the same.
- Europe is the second-largest segment; this is due to the growing industrialization of this market coupled with the low production cost of additive manufacturing.
Historical Timeline of Additive Manufacturing (AM) Technology: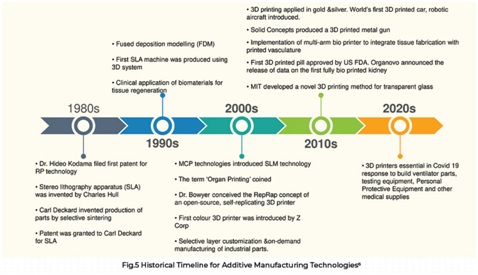
Potential in India:
- Additive Manufacturing (AM) has immense potential to revolutionize India’s manufacturing and industrial production landscape through digital processes, communication, imaging, architecture and engineering.
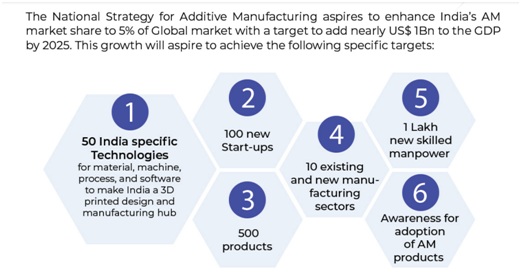
- It could likely add $ 1 billion to the GDP by 2025.
- The Strategy aspires to achieve 5% of Global AM market share.
Goals of National Strategy for Addictive Manufacturing:
- The key goals include positioning India as a global hub for Additive Manufacturing development and deployment, create and protect the integrity of India's AM intellectual properties.
- Our goal is to have 50 India specific technologies, 100 new startups, 500 products, 10 new manufacturing sectors, 1 lakh skilled manpower."
Aim and Objective of the National Strategy on Additive manufacturing (AM):
- The National Strategy on Additive manufacturing (AM) aims
- to create a conducive ecosystem for design, development, and deployment, and
- to overcome technical and economic barriers for Global AM leaders to set up their operations with supporting ancillaries in India,
- facilitating development of the domestic market and enhancement of global market share
- The mission is to ensure creation of a sustainable ecosystem for the AM industry
- to compete globally,
- encourage AM transformation and driving capabilities in the country for developing core competencies,
- position India as a global Innovation and Research hub for Additive Manufacturing,
- ensure AM manufactured end-user functional components for domestic and export markets,
- promote creation of Indian IPR and
- Ensure adequate measures for the protection of AM technology.
- The use of smart manufacturing processes to develop products and the predominant role of 3D printing in Industry 4.0 is one of the upcoming applications of this technology.
- Industry 4.0 is a rising trend that is anticipated to shift the global market dynamics and bring a radical change to manufacturing processes.


