2nd September 2023 (8 Topics)
Context
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has announced its first-ever solar mission on 2nd September, 2023, named as Aditya-L1 Missionthat could revolutionise the understanding of the Sun's dynamics and space weather.
About
About the Mission:
- According to ISRO, the Aditya-L1 mission is the first space-based observatory-class Indian solar mission to study the Sun.
- Objective:TheAditya L1 mission aims to understand the Sun's coronal heating and solar windacceleration, coupling the dynamics of the solar atmosphere, solar wind distribution and temperature anisotropy and initiation of coronal mass ejection (CME), flares and near-earth space weather.
- Launch details:
- ISRO is going to use 'XL', the more powerful variant of the polar satellite launch vehicle (PSLV)that would carry the spacecraft.
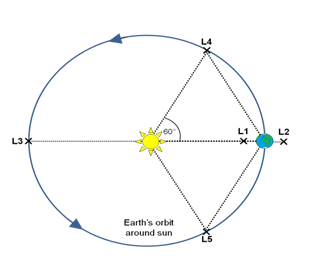
- Aditya-L1 will be placed in a halo orbit around the Lagrangian Point 1 (L1), which is 1.5 million km from the Earth in the direction of the Sun.
- The journey to the designated mission site is a staggering 5 million km from the Earth and will take about four months to cover.
- It will revolve around the Sun with the same relative position and hence can see the Sun continuously.
- Payloads:The seven payloads are-
- Visible Emission Line Coronagraph(VELC)
- Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT)
- Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS)
- High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer(HEL1OS)
- Aditya Solar wind Particle Experiment(ASPEX)
- Plasma Analyser Package For Aditya (PAPA)
- Advanced Tri-axial High Resolution Digital Magnetometers
- Among those seven payloads, four of which will observe the light from the Sun and the remaining three will measure insitu parameters of the plasma and magnetic fields.
- Details of payload aims:
- The Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), the primary payload of Aditya L1 will be sending 1,440 images per day to the ground station for analysis on reaching the intended orbit.
- SoLEXS payload: It is a soft X-ray spectrometer onboard Aditya-L1. The payload is designed to measure the solar soft X-ray flux to study solar fares.
- SUIT payload: The Solar Ultra-violet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) payload images the Solar Photosphere and Chromosphere in near Ultra-violet (UV) and also measures the solar irradiance variations in near UV.
What is L1 point?
- L1 is among the five Lagrange points in the Earth-Sun system.
- At this point, the gravitational forces of the two bodies balance the centrifugal force felt by a smaller object.
- Due to the balance of force, the object is not attracted by the Sun, hence would be able to effectively “hover" in a stable position relative to the two larger bodies.
- Significance:This point is located on the line connecting the two bodies. It is situated in the Earth's orbital path around the Sun.
Why study of Sun is significant?
- The Sun emits radiation/light in nearly all wavelengths along with various energetic particles and magnetic field.
- The atmosphere of the Earth as well as its magnetic field acts as a protective shield and blocks a number of harmful wavelength radiations including particles and fields.
- Without the solar energy the life on earth, cannot exist. The gravity of the sun holds all the objects of the solar system together.
|
Key facts about Sun:
|
More Articles