

26th September 2022 (7 Topics)
Context
Big industries and startups around the globe have been working to commercialise algae-based biofuel processes to reduce dependence on conventional fossil fuels like petrol and diesel.
About
Algae biofuel:
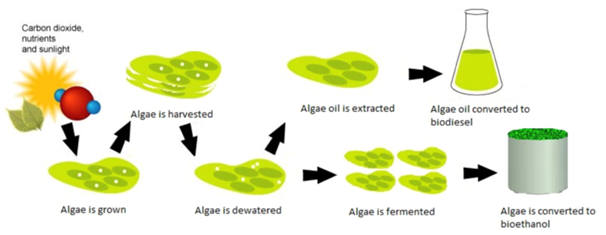
- Algae are sometimes grown to make algae biofuels, which make up the third generation of biofuels.
- Many types of algae can be used and processed to become a biofuel. Biofuel is a fuel made from living things, or the waste of a living thing, also known as biomass.
- The algae oils can be converted to biodiesel and the remaining material can be used to create
- Both biodiesel and bioethanol are developing biofuels. Biodiesel is a renewable fuel made from seed oils.
- Bioethanol is an alcohol made from algae, corn, sugar cane or other sugar containing feedstock. It is usually blended with gasoline and used in internal combustion engines.
- Algae can synthesise large volumes of oil (20 times more than that of mustard per acre), grow fast (10 times quicker than terrestrial plants) and capture carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Microalgae are excellent at converting CO2 and sunlight into oil-rich biomass, especially when compared to land-based crop plants like oil palm and soy.
Algae biofuel industry in India:
- India’s Reliance Industries Ltd has been successfully running large algae raceway ponds the last five years at their facility near Jamnagar, to convert sunshine, CO2 and seawater into bio-oil.
- It also displayed the utilisation of catalytic hydrothermal liquefaction technology to convert algae biomass to oil.
|
Catalytic Hydrothermal Liquefaction Technology:
|
Issues in algae bio-fuel industry:
- The energy cost of extracting oil from algae biomass is 10 times higher than the energy cost of extracting soybean oil.
- The cost has a large variability because of inappropriate assumptions, including those related to the products, cultivation methods, biomass productivities, oil contents, production capacity and conversion technologies.
- The results of the cost estimation were directly impacted by an overestimation of the combined biomass yield and lipid content.
Novel integrated technology:
- Scientists from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, United States have illustrated process which uses medium temperature and low pH to more readily extract available lipids from the algae biomass to further process them into biodiesel.
- This method can reduce per-gallon fuel expenses by up to 33 per cent compared to a standard lipid extraction-only method.
- A research group led by Anushree Malik at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Delhi has designed different models of biofilm reactors to cultivate microalgae, to substantially reduce the algae biomass harvesting cost.
- Algal biofilm reactors offer a robust cultivation system promising high biomass productivity, low harvesting cost and the ability to handle complex industrial effluents.
- These have emerged as important tools for efficient resource recovery from waste streams in terms of algal biofuels.
More Articles


