

26th August 2022 (7 Topics)
Context
Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change published the Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022 recently to ensure environmentally sound management of waste batteries.
Background
Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022:
- New rules will replace Batteries (Management and Handling) Rules, 2001.
- The rules cover all types of batteries, viz. Electric Vehicle batteries, portable batteries, automotive batteries and industrial batteries.
|
EV Market in India
|
Salient Features of the new Rules:
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): The rules function based on the concept of EPR where the producers (including importers) of batteries are responsible for collection and recycling/refurbishment of waste batteries and use of recovered materials from wastes into new batteries.
- EPR mandates that all waste batteries to be collected and sent for recycling/refurbishment, and it prohibits disposal in landfills and incineration.
- Penalty: The rules also have a provision for penal action on violation and imposition of environmental compensation.
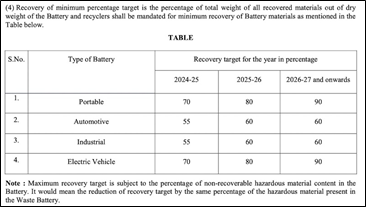
- The ministry has also set a minimum recovery percentage target for recovered materials out of dry weight batteries.
- These recovered materials will be then used for producing new batteries.
- The recovery target set for FY25 is set at 70%, which increases to 80% in FY26 and to 90% in FY27 and onwards.
- Online registration & reporting, auditing, and committee for monitoring the implementation of rules and to take measures required for removal of difficulties are salient features of rules for ensuring effective implementation and compliance.
- On the principle of Polluter Pays Principle, environmental compensation will be imposed for non-fulfilment of Extended Producer Responsibility targets, responsibilities and obligations set out in the rules.
- The funds collected under environmental compensation shall be utilised in collection and refurbishing or recycling of uncollected and non-recycled waste batteries.
Environmental threats posed by EV
- Lack of infrastructure: India currently lacks a commercial-scale recycling system. Retired batteries are piled up and discarded in landfills without being adequately treated.
- Hazardous elements: Lithium (which spontaneously reacts with moisture, causing explosions), nickel, and cobalt are all hazardous elements included in Lithium-ion Batteries.
- Leading to pollution: Lithium mining requires a massive amount of water. Further, lithium mining causes water, soil, and air pollution.
- Release of high amount of lithium-ion waste.
- Toxic chemicals like hydrochloric acid used in the mining process can leak from evaporation pools and contaminate the surrounding area.
Benefits of recycling
- A majority of India’s lithium-ion batteries are imported from China. Recycling will
- lower the cost of EV batteries
- accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles
- EV waste could be a significant source of minerals if recycling can be ramped up. By 2040, recycling could meet up to 12% of the EV industry’s mineral needs in a sustainable development scenario.
|
Lithium, nickel, cobalt and copper used in those batteries were all extracted from the Earth at one time. India have limited stock of them. |


