

14th December 2022 (5 Topics)
Context
- Researchers at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in the U.S. have announced a major advance in the long-running quest to harness energy from nuclear fusion.
Details:
- The researchers have for the first time produced more energy in a fusion reaction than was used to ignite it.
- They are referring to it as something called net energy gain.
- The researchers have used lasers to produce temperatures multiple times hotter than the centre of the sun to create an extremely brief fusion reaction.
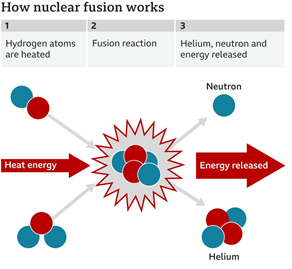
What is Nuclear Fusion?
- Nuclear fusion is the process whereby nuclei join together into one nucleus. The fusion of two atomic nuclei into one nucleus is not possible under standard temperature and pressure.
- It results in a subsequent release of huge amounts of energy.
- It is the opposite reaction of fission, where heavy isotopes are split apart.
- Harnessing fusion, the process that powers the Sun, could provide a limitless, clean energy source.
- In the sun, the extreme pressure produced by its immense gravity creates the conditions for fusion to happen.
- Fusion reactions take place in a state of matter called plasma. Plasma is a hot, charged gas made of positive ions and free-moving electrons that has unique properties distinct from solids, liquids, and gases.
- At high temperatures, electrons are ripped from an atom’s nuclei and become a plasma or an ionized state of matter. Plasma is also known as the fourth state of matter.
- The Plasma is then controlled by humongous magnets.
Advantages of Nuclear Fusion
- Abundant energy: Fusing atoms together in a controlled way releases nearly four million times more energy than a chemical reaction such as the burning of coal, oil, or gas.
- Sustainability: Fusion fuels are widely available and nearly inexhaustible. Deuterium can be distilled from all forms of water, while tritium will be produced during the fusion reaction as fusion neutrons interact with lithium.
- No emission of CO?: Fusion doesn't emit harmful toxins like carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Its major by-product is helium: an inert, non-toxic gas.
- No long-lived radioactive waste: nuclear fusion reactors produce no high-activity, long-lived nuclear waste.
- Limited risk of proliferation: Fusion doesn't employ fissile materials like uranium and plutonium (Radioactive tritium is neither a fissile nor a fissionable material).
- No risk of meltdown: It is difficult enough to reach and maintain the precise conditions necessary for fusion—if any disturbance occurs, the plasma cools within seconds and the reaction stops.
Significance:
- In the future it may produce nearly limitless, carbon-free energy, displacing fossil fuels and other traditional energy sources.
- Fusion energy systems may help to tackle climate change and energy security.
- The net energy gain is of immense importance because fusion happens at such high temperatures and pressures that it is incredibly difficult to control.
- The fuel does not want to stay hot -- it wants to leak out and get cold.
- Containing it is an incredible challenge.
Related Initiatives:
- International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) Assembly: It aims to build the world's largest tokamak to prove the feasibility of fusion as a large-scale and carbon-free source of energy. It is based in France.
- China’s Artificial Sun: The Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) device designed by China replicates the nuclear fusion process carried out by the sun.
- ITER-India is a special project under Institute for Plasma Research. It is governed by the Empowered Board, which is chaired by the Secretary of, the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE).



