

1st July 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
Recently, researchers published a new paper describing the results of the latest global planetary defense exercise which used an imaginary sweep of asteroid ‘Apophis’ near Earth.
About
What is an Asteroid?
- Asteroids are small, airless rocky worlds revolving around the sun that are too small to be called planets.
- They are also known as planetoids or minor planets.
- In total, the mass of all the asteroids is less than that of Earth’s moon. But despite their size, asteroids can be dangerous.
- Many have hit Earth in the past, and more will crash into our planet in the future.
Where asteroids are located?
- Most asteroids lie in a vast ring between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
- Not everything in the main belt is an asteroid, for instance, comets have recently been discovered there, and Ceres, once thought of only as an asteroid, is now also considered a dwarf planet.
- Many asteroids lie outside the main belt. For instance, a number of asteroids called Trojans lie along Jupiter’s orbital path.
- Three groups — Atens, Amors, and Apollos — known as near-Earth asteroids orbit in the inner solar system and sometimes cross the path of Mars and Earth.
What is a planetary defense exercise?
- Planetary defense is the term used to encompass all the capabilities needed to detect the possibility and warn of potential asteroid or comet impacts with Earth, and then either prevent them or mitigate their possible effects.
- Asteroid impact avoidancecomprises the methods by which near-Earth objects (NEO) on a potential collision course with Earth could be diverted away, preventing destructive impact events.
- An impact by a sufficiently large asteroid or other NEOs would cause, depending on its impact location, massive tsunamis or multiple firestorms, and an impact winter caused by the sunlight-blocking effect of large quantities of pulverized rock dust and other debris placed into the stratosphere.
|
Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (PHAs):
|
Various Defense mechanisms against Asteroids
- Deflecting Asteroids: Blowing up the asteroid before it reaches Earth, or deflecting it off its Earth-bound course by hitting it with a spacecraft may ward off the threat.
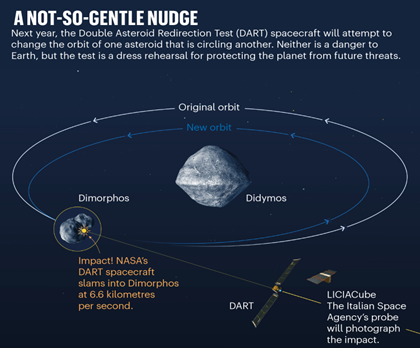
- AIDA: The measure undertaken so far is the Asteroid Impact and Deflection Assessment (AIDA), which includes NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission and the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Hera.
- DART: In 2018, NASA announced that it had started the construction of DART, which is scheduled to launch in 2021 with an aim to slam into the smaller asteroid of the Didymos system at around 6 km per second in 2022. Didymos, is a binary near-Earth asteroid, that could pose the most likely significant threat to Earth.
- Hera: It is scheduled to launch in 2024, and will arrive at the Didymos system in 2027 to measure the impact crater produced by the DART collision and study the change in the asteroid’s orbital trajectory.
- Monitoring of PHAs: It is not necessary that asteroids classified as PHAs will impact the Earth. It only means there is a possibility of a threat.
- By monitoring these PHAs and updating their orbits as new observations, it is possible to predict the close-approach statistics and thus their Earth-impact threat.
More Articles


