24th September 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
In Odhisha’s Navagarh district, the administration has launched the ‘Aliva programme’ to keep a record of all adolescent girls in the district to come across the information regarding their child marriage and its prevention.
About
About the Programme
- Under Aliva Programme, the following features were included;
- Anganwadi workers had been asked to identify every adolescent girl in their jurisdiction.
- The 100-page register maintains a record of the girl along with the name of her father.
- Data of the adolescent girl including, address, education status, birth registration date, Aadhaar Card Number, contact details and family details is to be noted.
- The age of the girl should be approved by the local school head master, father, supervisor and child marriage prohibition officer (CMPO).
- Also, information about child marriage, educational progress, skill training status and health issues of the adolescent girls is registered.
- The programme is targeted to be implemented for 10 years from 2020 to 2030 under Odisha government’s child marriage prevention strategy.
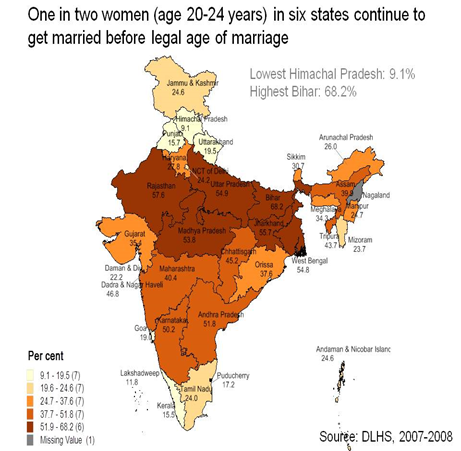
Child Marriages in India
- Child marriage, according to the Indian law, is a marriage where either the woman or man is below the age of 21.
- Most child marriages involve girls, many of whom are in poor socio-economic conditions.
- Child marriages are prevalent in India.
- Estimates vary widely between sources as to the extent and scale of child marriages. A 2015–2016 UNICEF report estimated that India's child marriage rate is 27%.
- The Census of India has counted and reported married women by age, with proportion of females in child marriage falling in each 10 year census period since 1981.
What are the reasons for early age marriages?
- Socio-cultural factor and patriarchal societies
- Religious affair: Practice of child marriage, or Kanya Dan(gift of a daughter, in Sanskrit)
- Social importance and familial pride and prestige attributed to it
- Other factors include:
- Lack of education
- Less awareness about rights
- Lack of empowerment
- Lack of say in decision-making
Impact
- Impact on women’s health: Mortality, childhood stunting and underweight, impact on overall childhood, reproductive health issues
- Social issue: domestic violence, mental health issues, widespread gender inequality and discrimination
- Public health issue: Childbirth complications, high risk of infections, affected child health
- Economic impact: Lower empowerment, intergenerational cycle of poverty.
Laws related to Child Marriage Prohibition
- The Child Marriage Restraint Act of 1929: The Child Marriage Restraint Act, also called the Sarda Act, was a law to restrict the practice of child marriage.
- This Act defined the age of marriage to be 18 for males and 14 for females.
- In 1949, after India's independence, the minimum age was increased to 15 for females, and in 1978, it was increased again for both females and males, to 18 and 21 years, respectively.
- The Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006:
- Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA): It provides for prohibition of solemnisation of child marriages and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.