

28th June 2023 (8 Topics)
Context
Recently, it was found that evolution of eukaryotes from prokaryotes can answer the question of how complex cells with nuclei and organelles emerged.
- The existing ‘theory of endosymbiosis’suggests that eukaryotes evolved from a symbiotic relationship between an ancient archaeon (a primitive group of microorganisms that thrive in extreme habitats) and a bacterium.
What are Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes?
- Prokaryotes: They are organisms that lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
- Their genetic material, typically a circular DNA molecule, is present in the cytoplasm without being enclosed within a nuclear membrane.
- Prokaryotes include bacteria and archaeon.
- Key features include small, simple cells without a nucleus or organelles.
- Eukaryotes: are organisms that have cells containing a well-defined nucleus enclosed within a membrane.
- Eukaryotic cells have a variety of membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and a complex network of internal membranes.
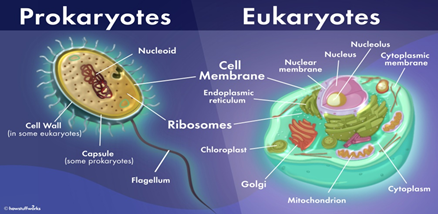
- Eukaryotic cells have a variety of membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and a complex network of internal membranes.
About the Evolution:
- Endosymbiosis is a process where “one organism lives inside another and both benefit from the relationship.”
- The endosymbiotic theory suggests that eukaryotes evolved from a small archaeon engulfing a bacterium.
- The archaeon protected the bacterium and provided a stable environment, while the bacterium supplied energy to the archaeon.
- Over time, they became dependent on each other and formed a new type of cell called a eukaryote.
- The engulfed bacterium became the mitochondrion, which produces energy for the cell.
- In plants, another endosymbiotic event occurred with a cyanobacterium becoming the chloroplast, responsible for photosynthesis.
- This symbiotic relationship allowed eukaryotes to grow larger, become more complex, and adapt to different environments.
Significance of the evolution:
- Mitochondria in eukaryotic cells and chloroplasts in plant cells have evolved from free-living bacteria.
- These organisms are found in a geological formation where geothermally heated water is forced out of a ridge in the Atlantic Ocean floor at a depth of 2400 meters below sea level.


