

16th May 2022 (7 Topics)
Context
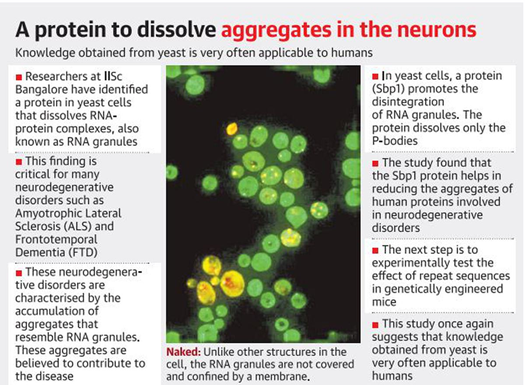
Researchers at IISC Bangalore have identified a protein in yeast cells that dissolves RNA-protein complexes, also known as RNA granules.
Background
Messenger RNA (mRNA):
- mRNA fate decisions play a crucial role in regulating variety of cellular processes including development and differentiation, synaptic plasticity, ageing and diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders and cystic fibrosis.
- The proteins associated with mRNA control its individual fate in the cytosol by promoting certain functional transitions and inhibiting others.
- Unlike other structures in the cell (such as mitochondria), the RNA granules are not covered and confined by a membrane.
- This makes them highly dynamic in nature, thereby allowing them to constantly exchange components with the surrounding.
- RNA granules are present in the cytoplasm at low numbers under normal conditions but increase in number and size under stressful conditions including diseases.
- Important feature of RNA granule protein components is the presence of stretches containing repeats of certain amino acids.
- Such stretches are referred to as low complexity regions. Repeats of arginine (R), glycine (G) and glycine (G) — known as RGG — are an example of low complexity sequence.
Protein synthesis:
- Messenger RNAs are converted to proteins (building blocks of the cell) by the process of
- RNA granules determine messenger RNA (mRNA) fate by deciding when and how much protein would be produced from mRNA.
- Protein synthesis is a multi-step and energy expensive process.
- Therefore, a common strategy used by cells when it encounters unfavorable conditions is to shut down protein production and conserve energy to deal with the stressful situation.
- RNA granules help in the process of shutting down protein production.
- Some RNA granule types (such as Processing bodies or P-bodies) not only regulate protein production but also accomplish degradation and elimination of the mRNAs, which in turn helps in reducing protein production.
Key findings:
- In recent years, a strong link has emerged between RNA granules and neurodegenerative disorders such as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD).
- The proteins implicated in these diseases such as ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1 (EWSR1) and fused in sarcoma (FUS) are RNA binding proteins that can reside in RNA granules.
- These above-mentioned proteins also contain low complexity sequences (repeats of amino acids) that are important for their movement into RNA granules.
- In fact, these proteins are deposited as insoluble granules/aggregates in the neurons of ALS and FTD patients which are believed to contribute to the pathophysiology of these diseases.
Messenger RNA (mRNA):
- mRNA fate decisions play a crucial role in regulating variety of cellular processes including development and differentiation, synaptic plasticity, ageing and diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders and cystic fibrosis.
- The proteins associated with mRNA control its individual fate in the cytosol by promoting certain functional transitions and inhibiting others.
- Unlike other structures in the cell (such as mitochondria), the RNA granules are not covered and confined by a membrane.
- This makes them highly dynamic in nature, thereby allowing them to constantly exchange components with the surrounding.
- RNA granules are present in the cytoplasm at low numbers under normal conditions but increase in number and size under stressful conditions including diseases.
- Important feature of RNA granule protein components is the presence of stretches containing repeats of certain amino acids.
- Such stretches are referred to as low complexity regions. Repeats of arginine (R), glycine (G) and glycine (G) — known as RGG — are an example of low complexity sequence.
Protein synthesis:
- Messenger RNAs are converted to proteins (building blocks of the cell) by the process of
- RNA granules determine messenger RNA (mRNA) fate by deciding when and how much protein would be produced from mRNA.
- Protein synthesis is a multi-step and energy expensive process.
- Therefore, a common strategy used by cells when it encounters unfavorable conditions is to shut down protein production and conserve energy to deal with the stressful situation.
- RNA granules help in the process of shutting down protein production.
- Some RNA granule types (such as Processing bodies or P-bodies) not only regulate protein production but also accomplish degradation and elimination of the mRNAs, which in turn helps in reducing protein production.
Key findings:
- In recent years, a strong link has emerged between RNA granules and neurodegenerative disorders such as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD).
- The proteins implicated in these diseases such as ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1 (EWSR1) and fused in sarcoma (FUS) are RNA binding proteins that can reside in RNA granules.
- These above-mentioned proteins also contain low complexity sequences (repeats of amino acids) that are important for their movement into RNA granules.
- In fact, these proteins are deposited as insoluble granules/aggregates in the neurons of ALS and FTD patients which are believed to contribute to the pathophysiology of these diseases.


