26th October 2022 (8 Topics)
Context
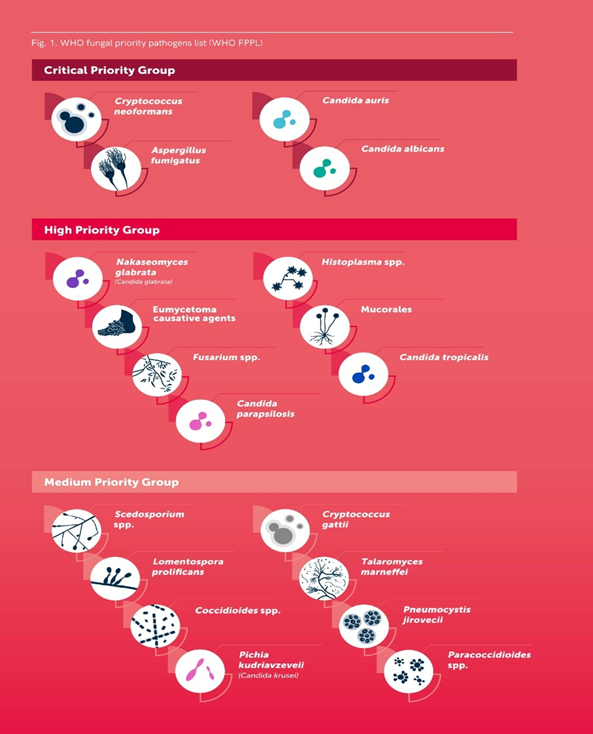
Recently, WHO published a report highlighting the first-ever list of fungal "Priority pathogens" – a catalogue of the 19 fungi that represent the greatest threat to public health.
About
Highlights of the Report:
- The WHO fungal priority pathogens list (FPPL) is the first global effort to systematically prioritize fungal pathogens, considering the unmet research and development (R&D) needs and the perceived public health importance.
- The 19 Fungi identified as categorically as fungi of concern are mentioned in the table below.
- Objective: The WHO FPPL aims to focus and drive further research and policy interventions to strengthen the global response to fungal infections and antifungal resistance.
- Fungal pathogens are a major threat to public health as they are becoming increasingly common and resistant to treatment with only four classes of antifungal medicines currently available.
|
Anti-Fungal Medicines: Antifungal drugs are medications that are used to treat fungal infections. While most fungal infections affect areas such as the skin and nails, some can lead to more serious and potentially life-threatening conditions like meningitis or pneumonia. |
- According to the Report, most fungal pathogens lack rapid and sensitive diagnostics and those that exist are not widely available or affordable globally.
- The invasive forms of these fungal infections often affect severely ill patients and those with significant underlying immune system-related conditions.
- Populations at the greatest risk of invasive fungal infections include those with cancer, HIV/AIDS, organ transplants, chronic respiratory disease, and post-primary tuberculosis infection.
- The WHO FPPL list is divided into three categories:
- Critical,
- High and
- Medium priority.
- The fungal pathogens in each priority category are so ranked primarily due to their public health impact and/or emerging antifungal resistance risk.
Significance of the Initiative:
- Help to prioritize the Level of Infection: The FPPL report underscores strategies for policymakers, public health professionals, and other stakeholders.
- Development of effective drugs: The strategies proposed in the report are collectively aimed at generating evidence and improving response to these fungal priority pathogens including preventing the development of antifungal drug resistance.
- The primary recommended actions are focused on:
- strengthening laboratory capacity and surveillance;
- sustaining investments in research, development, and innovation; and
- Enhancing public health interventions for prevention and control.
Fungal Infections:
There are many types of fungal infections. Some of the most common fungal infections are those of the skin, nails, and mucous membranes. Examples include:
- Ringworm (also known as tinea): a fungal infection of the skin that can occur on your scalp, on your feet (athlete’s foot), in your groin area (jock itch), and on other areas of your body
- Nail fungus: an infection that typically affects your toenails but can also affect your fingernails
- Vaginal yeast infection: an infection that occurs due to the overgrowth of Candida yeast in and around the vagina
- Oral thrush: a condition in which Candida yeast overgrows in your mouth.
|
There are also some less common but more serious fungal infections that can cause fungal pneumonia, fungal meningitis, or even systemic infections. Examples of fungal species that can cause more serious infections to include:
|